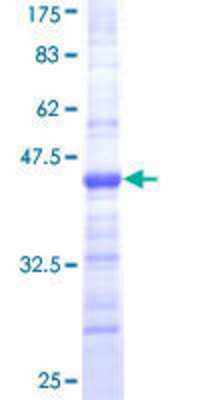
Coronin-1a: Proteins and Enzymes
Coronin was originally discovered in Dictyostelium, where it was found to be involved in the chemotactic response of these ameboid cells. The name derives from the fact that the protein is localized at the leading edge or crown of these highly motile cells. The name derives from Corona, which is latin for crown. Coronin homologues have been found in yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila and many other species, and a family them are known in mammals. All coronins belong to the WD40 or WD family of proteins, the prototype or which is the beta subunit of trimeric G-proteins. Coronins appear to be particularly involved in binding to actin, actin associated proteins, tubulin and phospholipase C and have been implicated in the mechanisms of chemotaxis and phagocytosis. In mammals there are at least five major coronin proteins, named coronins 1 to 5 in one nomenclature. Another nomenclature divides these five proteins in coronins 1a and 1b, 2a, 2b and 2c. The mammalian coronin family members are abundant components of eukaryotic cells, and each type has a restricted cell type specific expression pattern. Coronin 1A is the mammalian coronin most similar in protein sequence to the Dictyostelium protein and is found exclusively in hematopoetic lineage cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages and neutrophils. NB 110-58867 is therefore an excellent marker of cells of this lineage and can also be used to study the leading edges particularly of neutrophils. Since the only hematopoetic cells found within the central nervous system are microglia, this antibody is also an excellent marker of this important cell type. Microglia are numerically fairly minor components of the nervous system, but microglial activation is seen in response to a wide variety of damage and disease states, including ALS, Alzheimer's disease and responses to brain tumors. Since coronin 1a is a constitutive component of microglia, the coronin 1a antibody can be used to study both quiescent and activated microglia.
Show More
1 result for "Coronin-1a Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
1 result for "Coronin-1a Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
Coronin-1a: Proteins and Enzymes
Coronin was originally discovered in Dictyostelium, where it was found to be involved in the chemotactic response of these ameboid cells. The name derives from the fact that the protein is localized at the leading edge or crown of these highly motile cells. The name derives from Corona, which is latin for crown. Coronin homologues have been found in yeast, C. elegans, Drosophila and many other species, and a family them are known in mammals. All coronins belong to the WD40 or WD family of proteins, the prototype or which is the beta subunit of trimeric G-proteins. Coronins appear to be particularly involved in binding to actin, actin associated proteins, tubulin and phospholipase C and have been implicated in the mechanisms of chemotaxis and phagocytosis. In mammals there are at least five major coronin proteins, named coronins 1 to 5 in one nomenclature. Another nomenclature divides these five proteins in coronins 1a and 1b, 2a, 2b and 2c. The mammalian coronin family members are abundant components of eukaryotic cells, and each type has a restricted cell type specific expression pattern. Coronin 1A is the mammalian coronin most similar in protein sequence to the Dictyostelium protein and is found exclusively in hematopoetic lineage cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages and neutrophils. NB 110-58867 is therefore an excellent marker of cells of this lineage and can also be used to study the leading edges particularly of neutrophils. Since the only hematopoetic cells found within the central nervous system are microglia, this antibody is also an excellent marker of this important cell type. Microglia are numerically fairly minor components of the nervous system, but microglial activation is seen in response to a wide variety of damage and disease states, including ALS, Alzheimer's disease and responses to brain tumors. Since coronin 1a is a constitutive component of microglia, the coronin 1a antibody can be used to study both quiescent and activated microglia.
Show More
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |