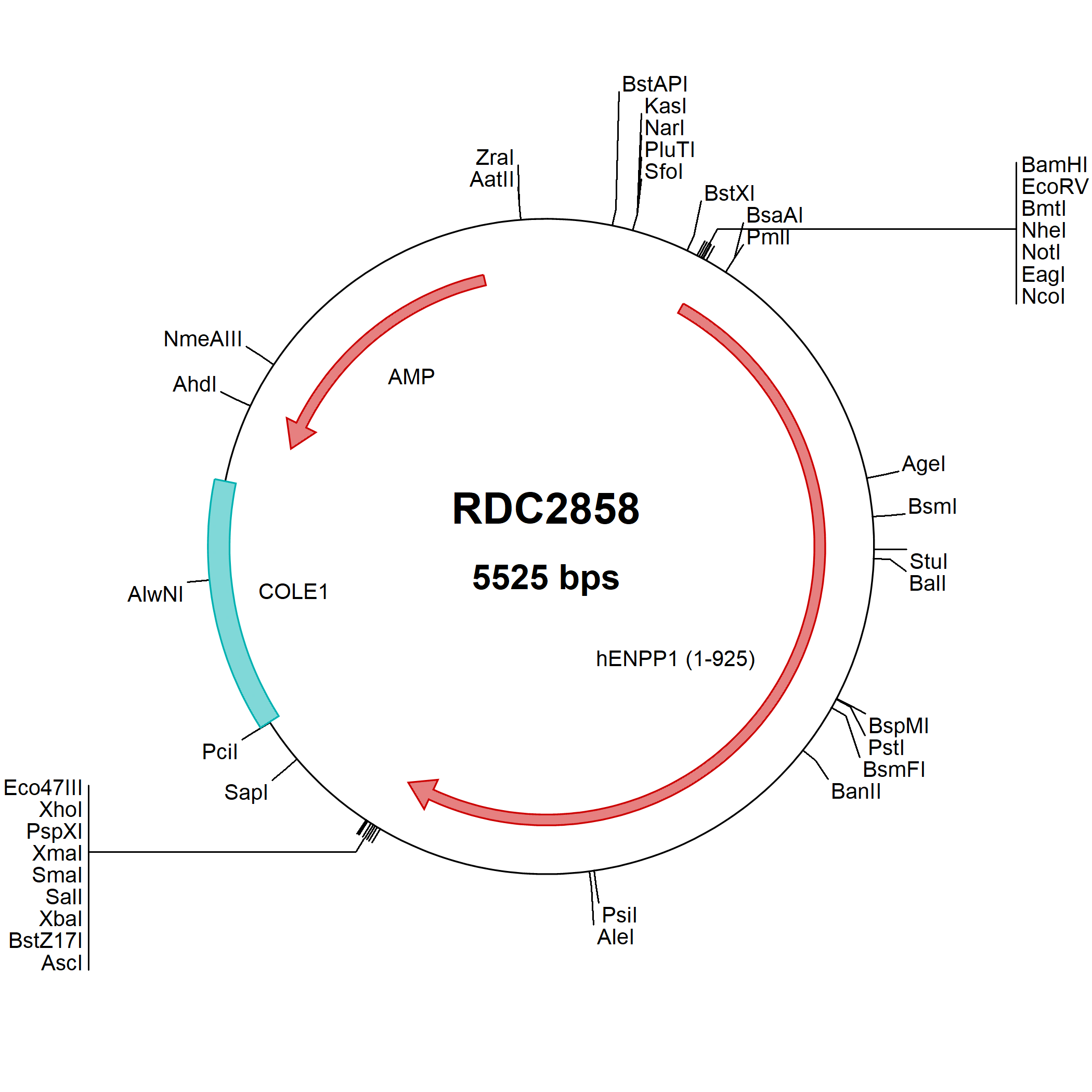
ENPP-1: cDNA Clones
Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that hydrolyzes nucleotides and nucleotide derivatives with the formation of nucleotide-5'-monophosphates. It is inserted into the plasma membrane by an N-terminal transmembrane domain. Human ENPP-1 has a small N-terminal cytoplasmic domain and a large C-terminal region containing two somatomedin B-like domains, a catalytic domain and a nuclease-like domain in the extracellular space. Defects in the ENPP-1 gene cause arterial calcification and bone mineralization abnormalities. ENPP-1 polymorphism or overexpression is also associated with obesity, type II diabetes and insulin resistance, which makes modulation of ENPP-1 activity one of the targets to treat insulin resistance and related diseases. The recombinant hybrid enzyme rhENPP-1 consists of N-terminal somatomedin B-like domains of ENPP-2, the central catalytic phosphodiesterase domain of ENPP-1 and the C-terminal nuclease-like domain of ENPP-2. It has been reported that this hybrid construct generates an enzyme that has higher levels of ENPP-1 activity than the wild type ENPP-1 and is specific for the ENPP-1 substrate.
2 results for "ENPP-1 cDNA Clones" in Products
2 results for "ENPP-1 cDNA Clones" in Products
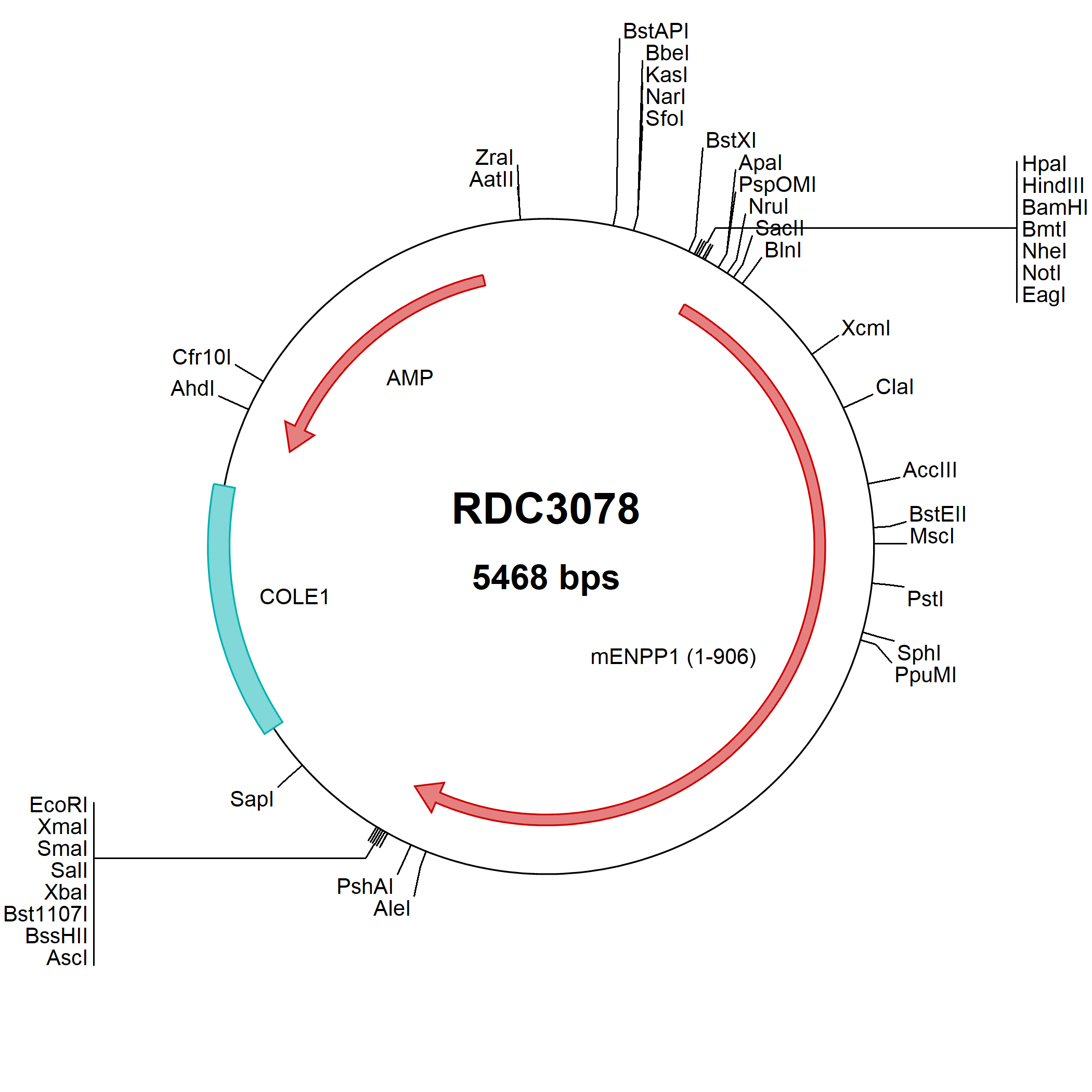
ENPP-1: cDNA Clones
Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that hydrolyzes nucleotides and nucleotide derivatives with the formation of nucleotide-5'-monophosphates. It is inserted into the plasma membrane by an N-terminal transmembrane domain. Human ENPP-1 has a small N-terminal cytoplasmic domain and a large C-terminal region containing two somatomedin B-like domains, a catalytic domain and a nuclease-like domain in the extracellular space. Defects in the ENPP-1 gene cause arterial calcification and bone mineralization abnormalities. ENPP-1 polymorphism or overexpression is also associated with obesity, type II diabetes and insulin resistance, which makes modulation of ENPP-1 activity one of the targets to treat insulin resistance and related diseases. The recombinant hybrid enzyme rhENPP-1 consists of N-terminal somatomedin B-like domains of ENPP-2, the central catalytic phosphodiesterase domain of ENPP-1 and the C-terminal nuclease-like domain of ENPP-2. It has been reported that this hybrid construct generates an enzyme that has higher levels of ENPP-1 activity than the wild type ENPP-1 and is specific for the ENPP-1 substrate.