N-Cadherin: Proteins and Enzymes
Neuronal Cadherin, also known as Cadherin-2, is a 130 kDa type I membrane protein belonging to the Cadherin superfamily of calcium-dependent adhesion molecules. In the nervous system, N-Cadherin mediates adhesion between the opposing faces of developing neuronal synapses and between Schwann cells and neuronal axons. It interacts in cis or in trans homophilically and with the GluR2 subunit of neuronal AMPA receptors. During synaptic maturation, its expression is lost from inhibitory terminals but maintained at excitatory terminals.
ADAM10-mediated shedding of the N-Cadherin ECD alters cell-cell adhesion, synaptic development, and AMPA receptor activity. N-Cadherin can also be cleaved at multiple additional sites within the intracellular or extracellular domains by Calpain, gamma-Secretase, and several MMPs. Cleavage of N-Cadherin in atherosclerotic plaques contributes alternatively to vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation (MMP-9 and -12) or apoptosis (MMP-7). Aberrant cell surface expression of the pro and mature forms of N-Cadherin in cancer results in increased tumor progression and invasiveness. N-Cadherin also mediates the adhesion between hematopoeitic progenitor cells and mesenchymal stromal cells of the bone marrow.
Products:
2 results for "N-Cadherin Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
2 results for "N-Cadherin Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
N-Cadherin: Proteins and Enzymes
Neuronal Cadherin, also known as Cadherin-2, is a 130 kDa type I membrane protein belonging to the Cadherin superfamily of calcium-dependent adhesion molecules. In the nervous system, N-Cadherin mediates adhesion between the opposing faces of developing neuronal synapses and between Schwann cells and neuronal axons. It interacts in cis or in trans homophilically and with the GluR2 subunit of neuronal AMPA receptors. During synaptic maturation, its expression is lost from inhibitory terminals but maintained at excitatory terminals.
ADAM10-mediated shedding of the N-Cadherin ECD alters cell-cell adhesion, synaptic development, and AMPA receptor activity. N-Cadherin can also be cleaved at multiple additional sites within the intracellular or extracellular domains by Calpain, gamma-Secretase, and several MMPs. Cleavage of N-Cadherin in atherosclerotic plaques contributes alternatively to vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation (MMP-9 and -12) or apoptosis (MMP-7). Aberrant cell surface expression of the pro and mature forms of N-Cadherin in cancer results in increased tumor progression and invasiveness. N-Cadherin also mediates the adhesion between hematopoeitic progenitor cells and mesenchymal stromal cells of the bone marrow.
Products:
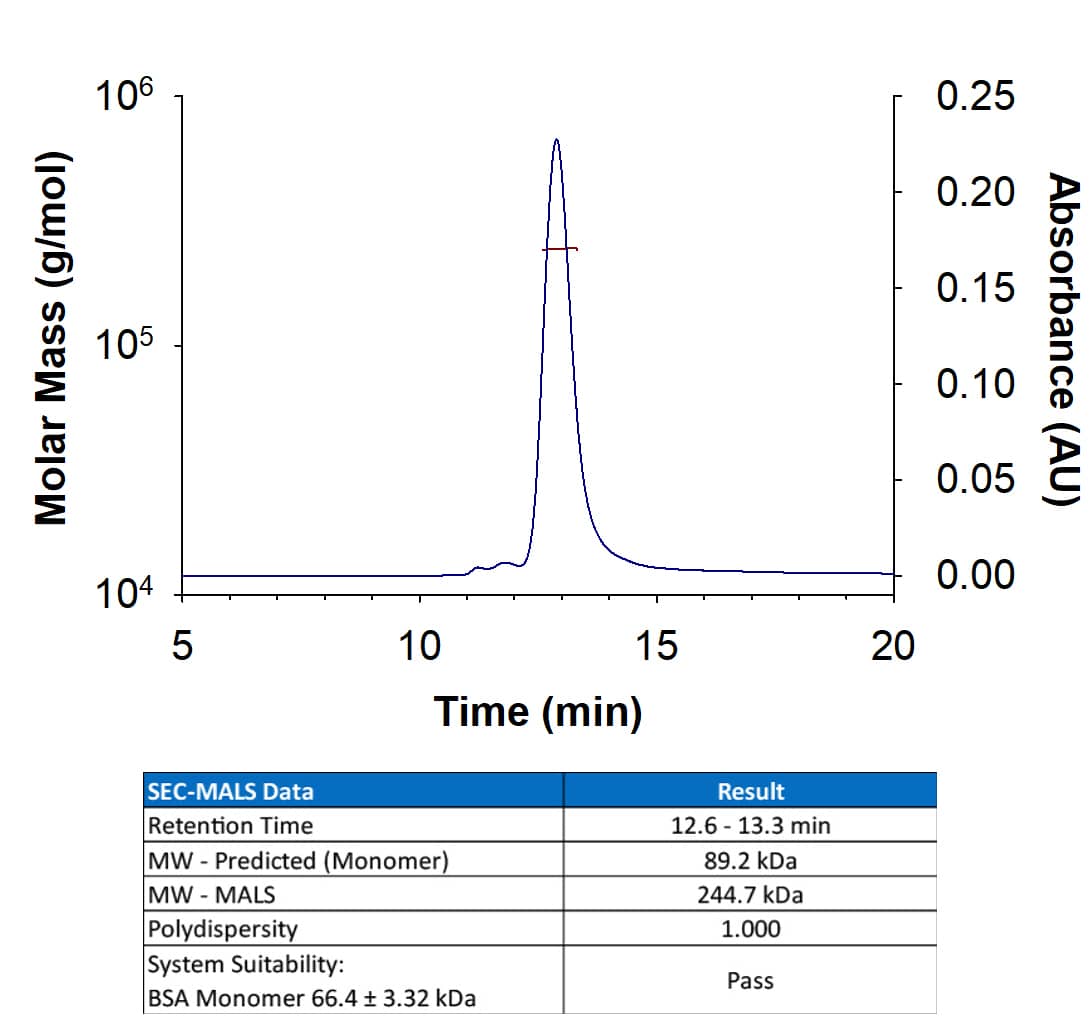
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | P19022.4 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | NP_031690 |
| Applications: | BA |