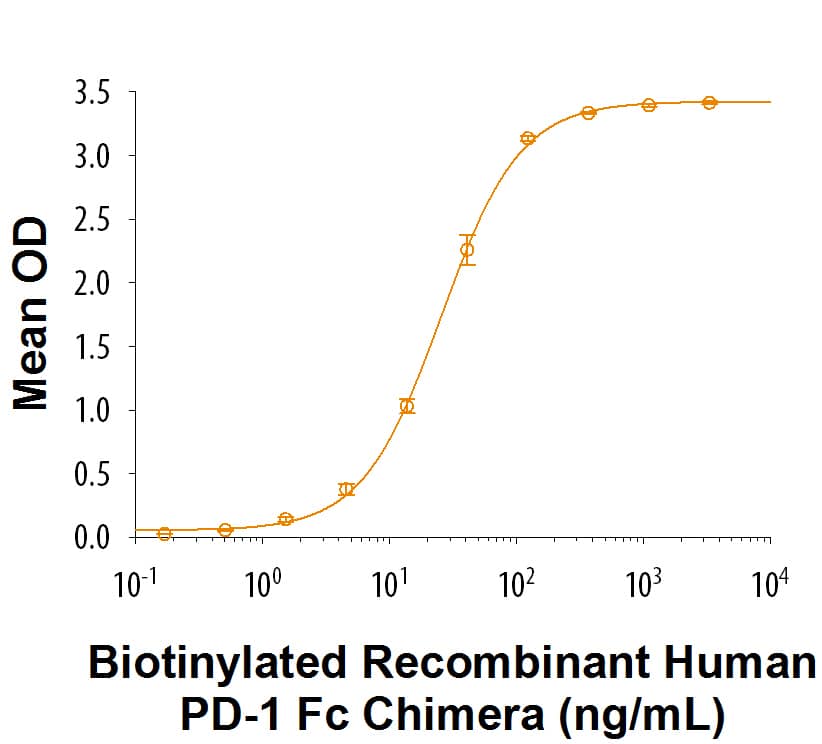
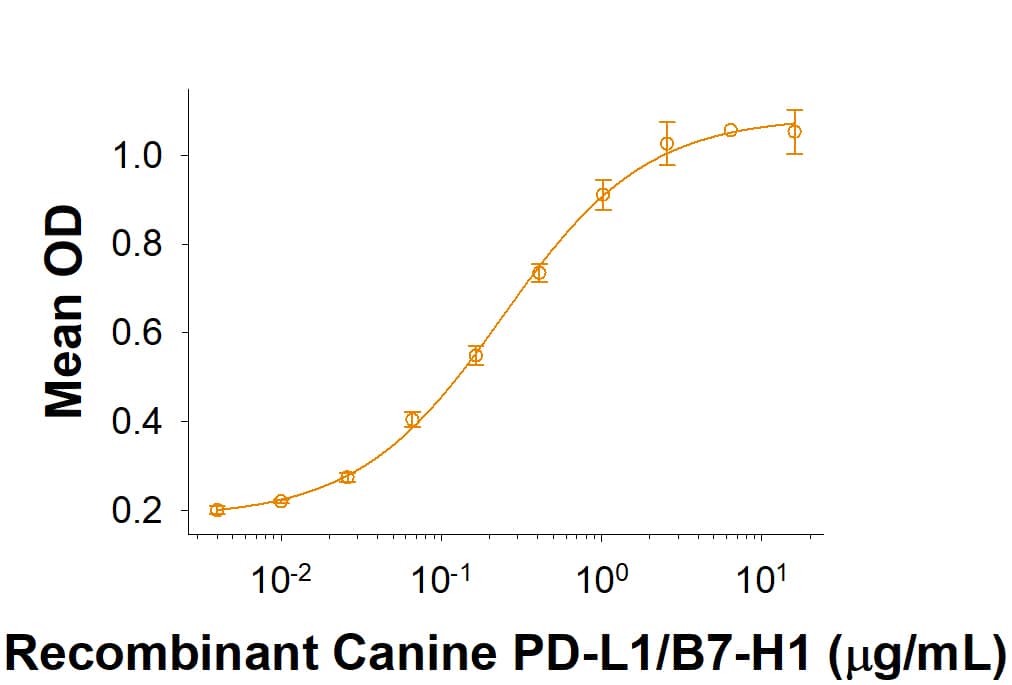
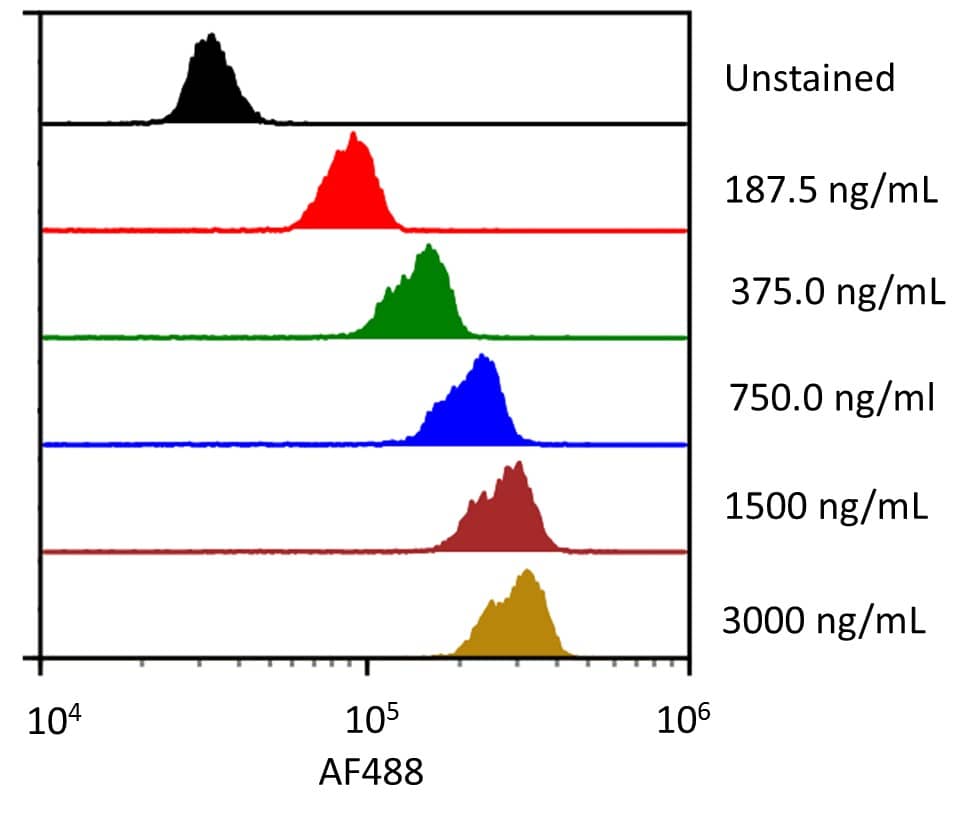
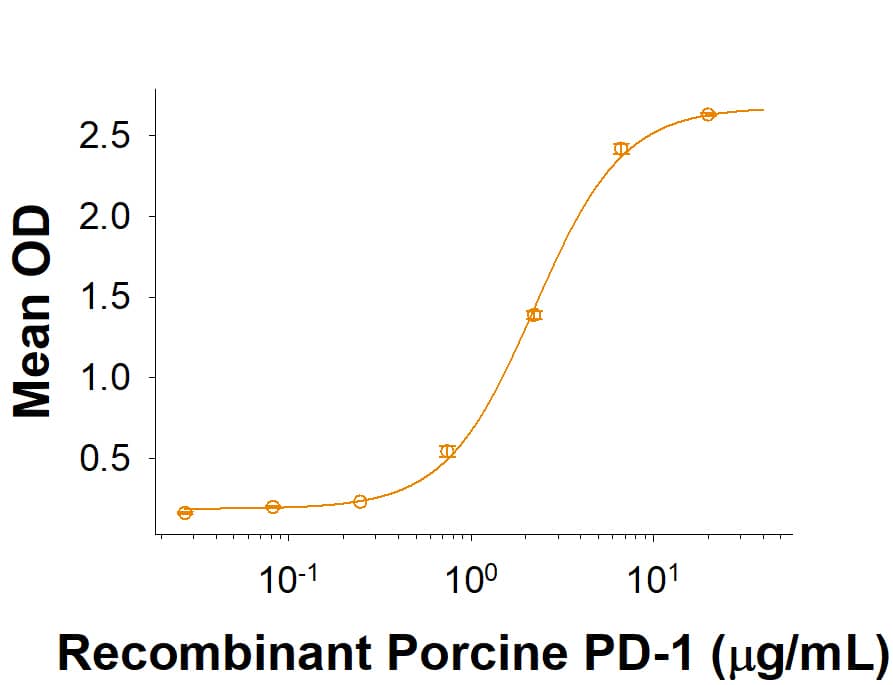
PD-1: Proteins and Enzymes
PD-1 (Programmed Death-1 receptor) is a key regulator of the threshold of immune response and peripheral immune tolerance. It is expressed on activated T cells, B cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells and binds to PD-L1 or PD-L2. PD-1 ligation induces co-inhibitory signals in T cells promoting their apoptosis, anergy, and functional exhaustion. Many tumors overexpress PD-L1 to induce this inhibitory signaling pathway in immune cells.
When PD-1-expressing immune cells come into contact with a tumor cell expressing PD-L1, this interaction blocks activation and prevents an immune response. A new class of anti-cancer therapies disrupt these co-inhibitory signals taking the breaks off the host immune system thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity. The recent success of several antibody therapeutics has spurred great interest in PD-1 and PD-L1 in addition to other co-inhibitory immune checkpoint proteins.
Products:
16 results for "PD-1 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
16 results for "PD-1 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
PD-1: Proteins and Enzymes
PD-1 (Programmed Death-1 receptor) is a key regulator of the threshold of immune response and peripheral immune tolerance. It is expressed on activated T cells, B cells, monocytes, and dendritic cells and binds to PD-L1 or PD-L2. PD-1 ligation induces co-inhibitory signals in T cells promoting their apoptosis, anergy, and functional exhaustion. Many tumors overexpress PD-L1 to induce this inhibitory signaling pathway in immune cells.
When PD-1-expressing immune cells come into contact with a tumor cell expressing PD-L1, this interaction blocks activation and prevents an immune response. A new class of anti-cancer therapies disrupt these co-inhibitory signals taking the breaks off the host immune system thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity. The recent success of several antibody therapeutics has spurred great interest in PD-1 and PD-L1 in addition to other co-inhibitory immune checkpoint proteins.
Products:
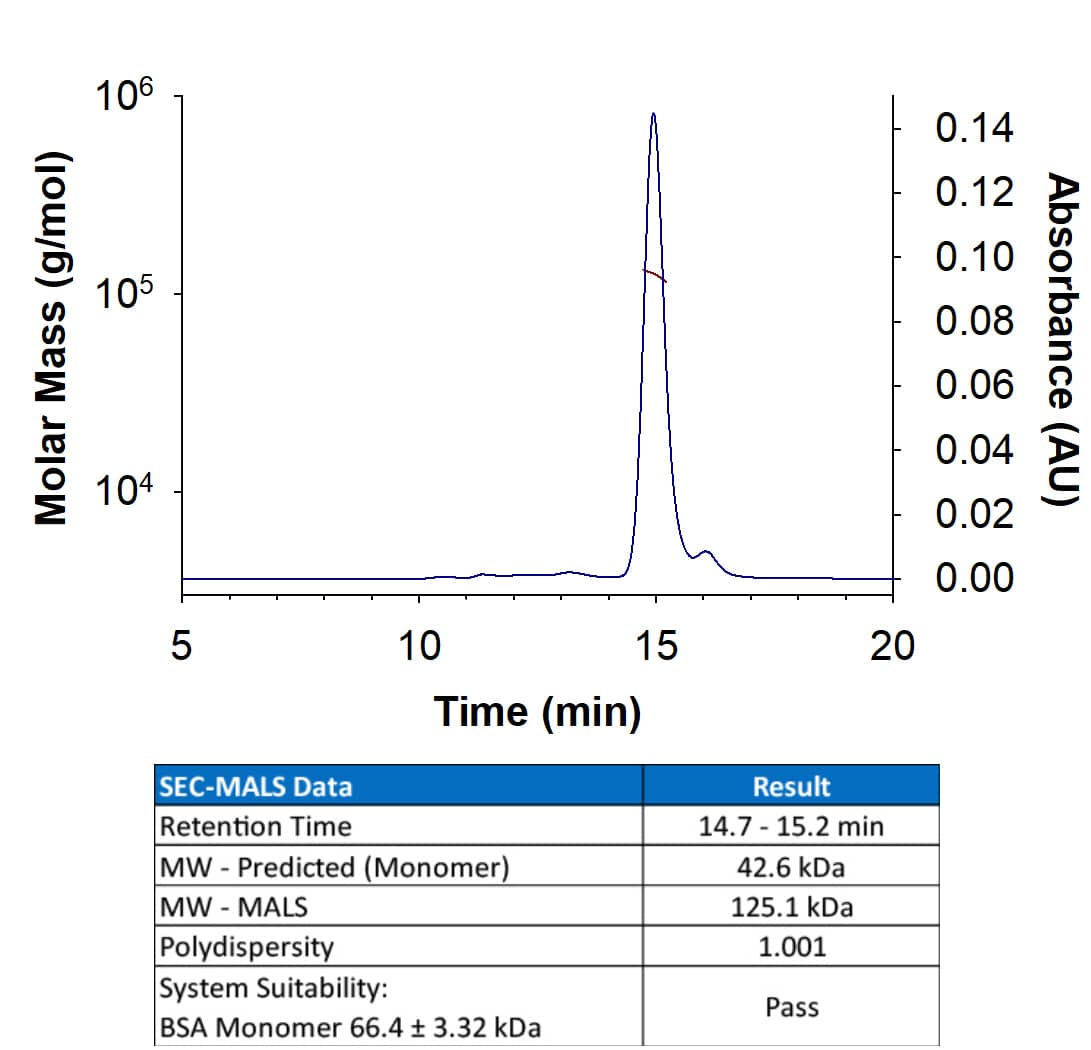
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
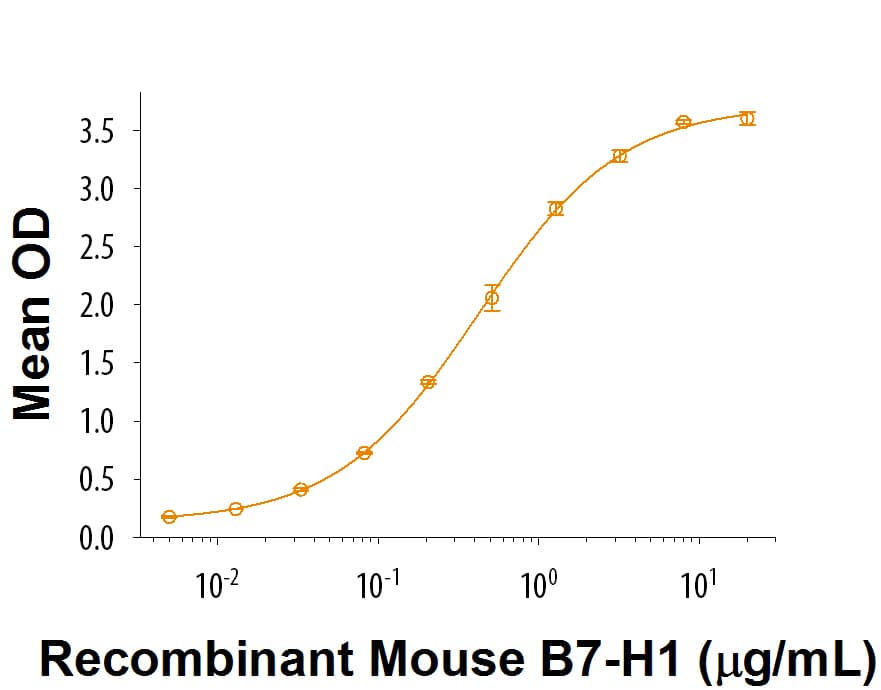
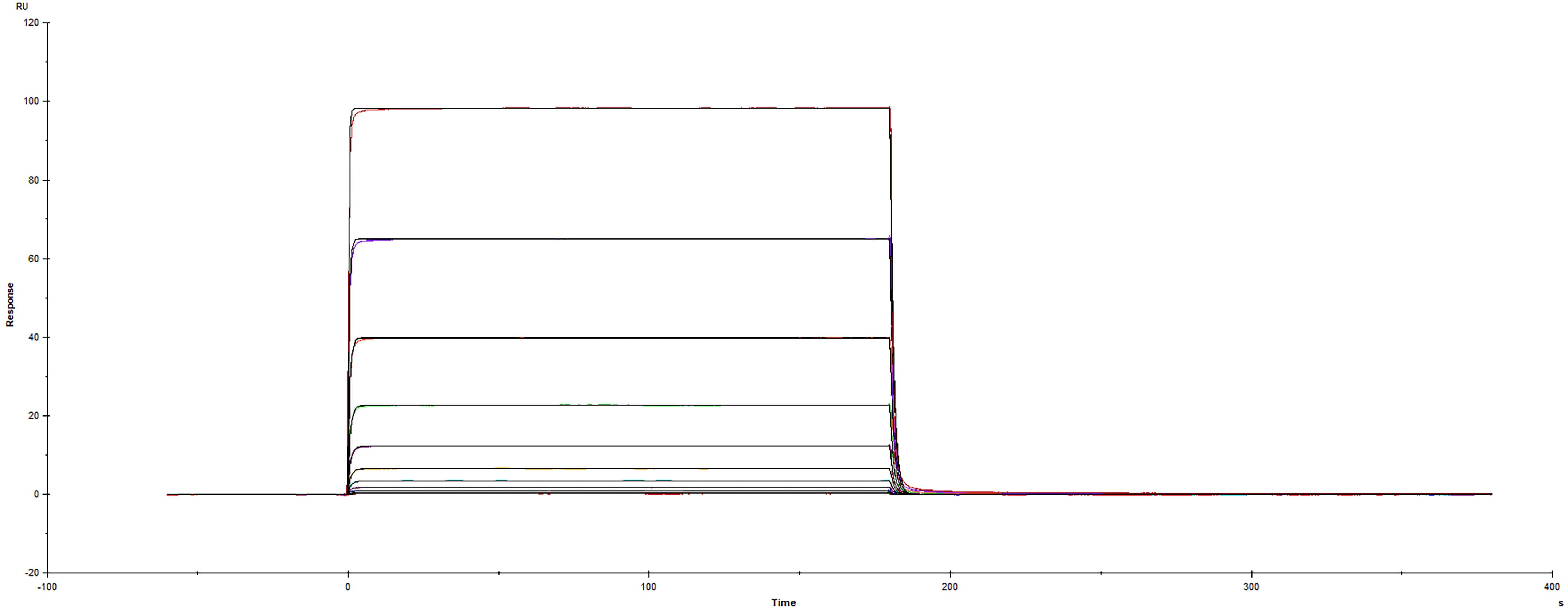
| Applications: | Bind |
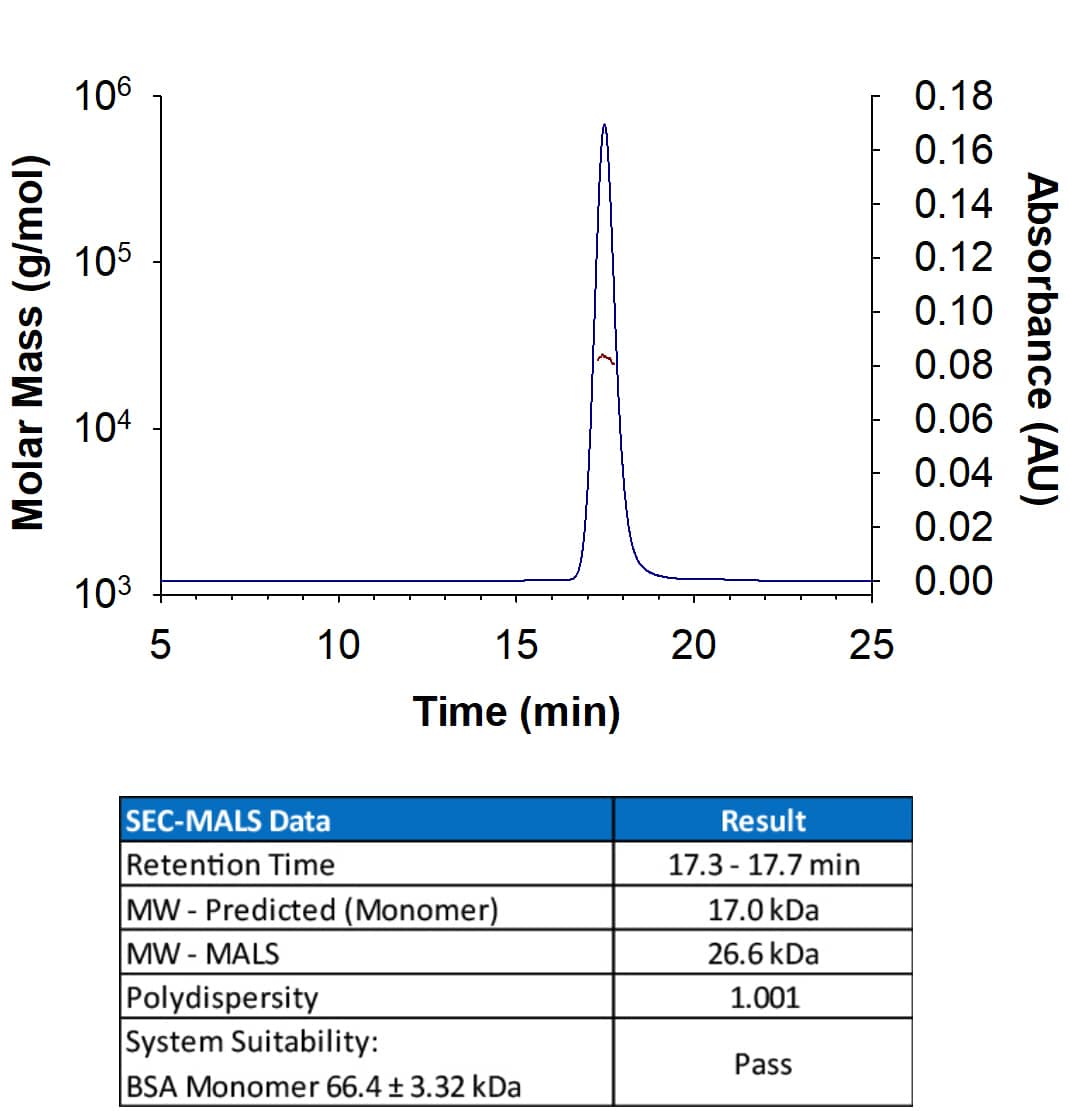
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q02242 |
| Applications: | Bind |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q02242 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | NP_001301026.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | NP_001100397 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | NP_001271065.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | NP_001271065 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q15116.3 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | NP_001191308.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | NP_001191308.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Applications: | AC |