PD-L1/B7-H1: Proteins and Enzymes
PD-L1, also known as B7-H1 and CD274, is an approximately 65 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein in the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. PD-L1 is expressed on inflammatory-activated immune cells including macrophages, T cells, and B cells, keratinocytes, endothelial and intestinal epithelial cells, as well as a variety of carcinomas and melanoma. PD-L1 protein binds to T cell B7-1/CD80 and PD-1.
It suppresses T cell activation and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of activated T cells. It plays a role in the development of immune tolerance by promoting T cell anergy and enhancing regulatory T cell development. PD-L1 favors the development of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and IL-22 producing dendritic cells and inhibits the development of Th17 cells. In cancer, PD-L1 provides resistance to T cell mediated lysis, enhances EMT, and enhances the tumorigenic function of Th22 cells. Many tumors overexpress PD-L1 protein making the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction central to several successful cancer immunotherapy approaches.
Products:
22 results for "PD-L1/B7-H1 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
22 results for "PD-L1/B7-H1 Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
PD-L1/B7-H1: Proteins and Enzymes
PD-L1, also known as B7-H1 and CD274, is an approximately 65 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein in the B7 family of immune regulatory molecules. PD-L1 is expressed on inflammatory-activated immune cells including macrophages, T cells, and B cells, keratinocytes, endothelial and intestinal epithelial cells, as well as a variety of carcinomas and melanoma. PD-L1 protein binds to T cell B7-1/CD80 and PD-1.
It suppresses T cell activation and proliferation and induces the apoptosis of activated T cells. It plays a role in the development of immune tolerance by promoting T cell anergy and enhancing regulatory T cell development. PD-L1 favors the development of anti-inflammatory IL-10 and IL-22 producing dendritic cells and inhibits the development of Th17 cells. In cancer, PD-L1 provides resistance to T cell mediated lysis, enhances EMT, and enhances the tumorigenic function of Th22 cells. Many tumors overexpress PD-L1 protein making the PD-1:PD-L1 interaction central to several successful cancer immunotherapy approaches.
Products:
Analyzed by SEC-MALS
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9EP73 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7 |
| Applications: | Bind |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9EP73 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated.
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7-1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | NP_001020392 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | NP_001020392.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | XP_005581836 |
| Applications: | BA |
Fc Chimera
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Fc Chimera
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | Q9NZQ7.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | Q9EP73.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | Q9EP73.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | NP_001278901.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | NS0 |
| Accession #: | NP_001178883 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | XP_005581836 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | PAGE |
| Applications: | PAGE |




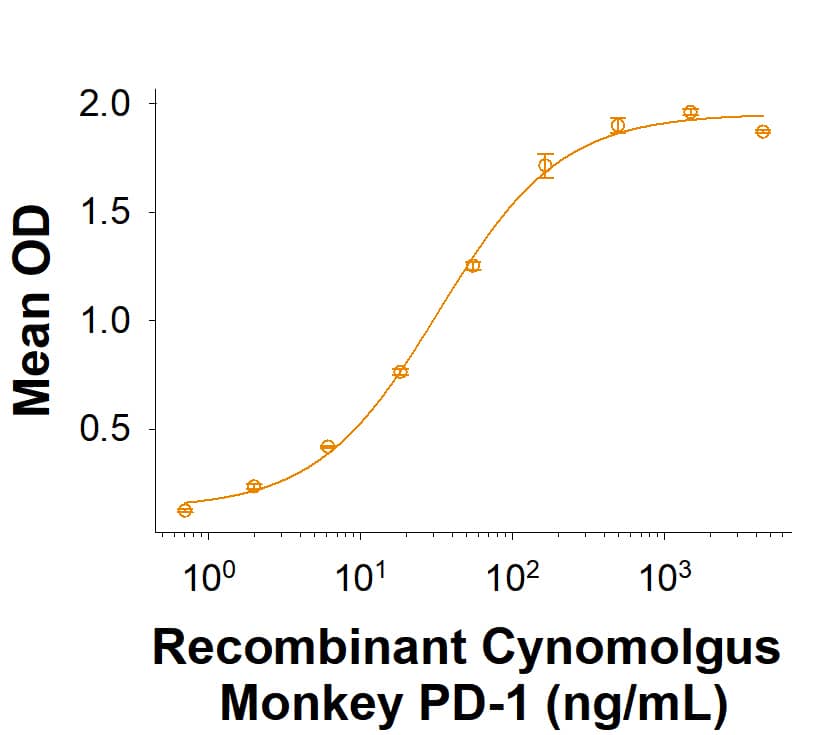

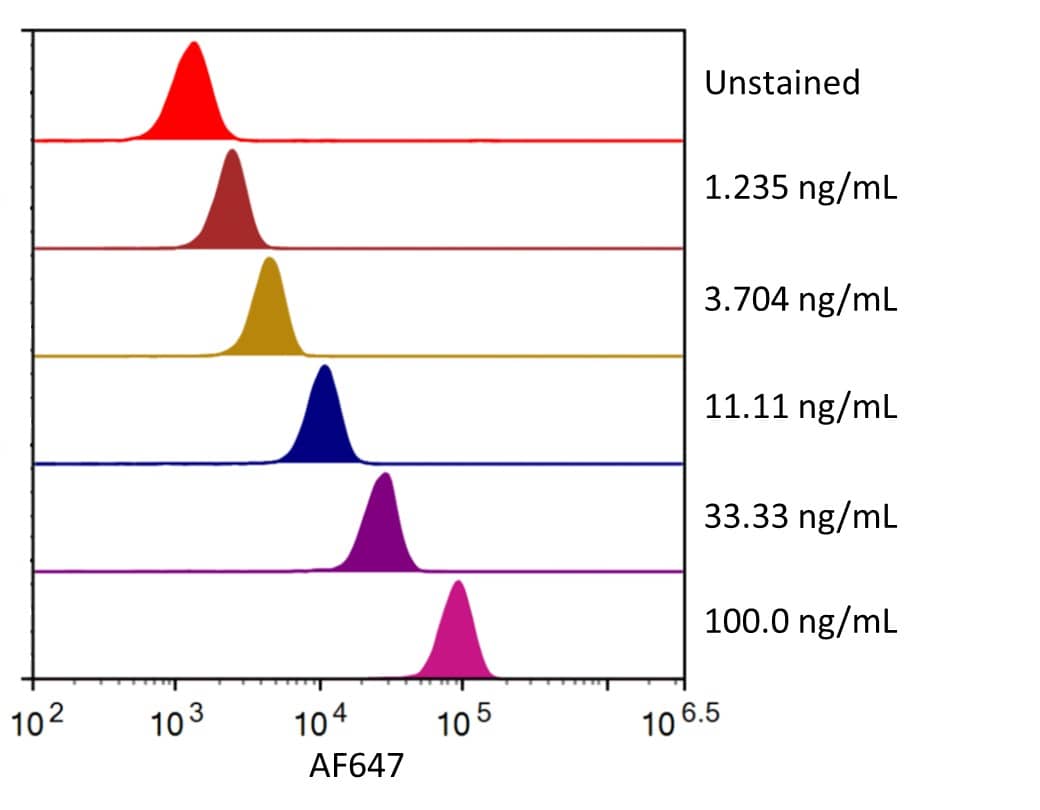
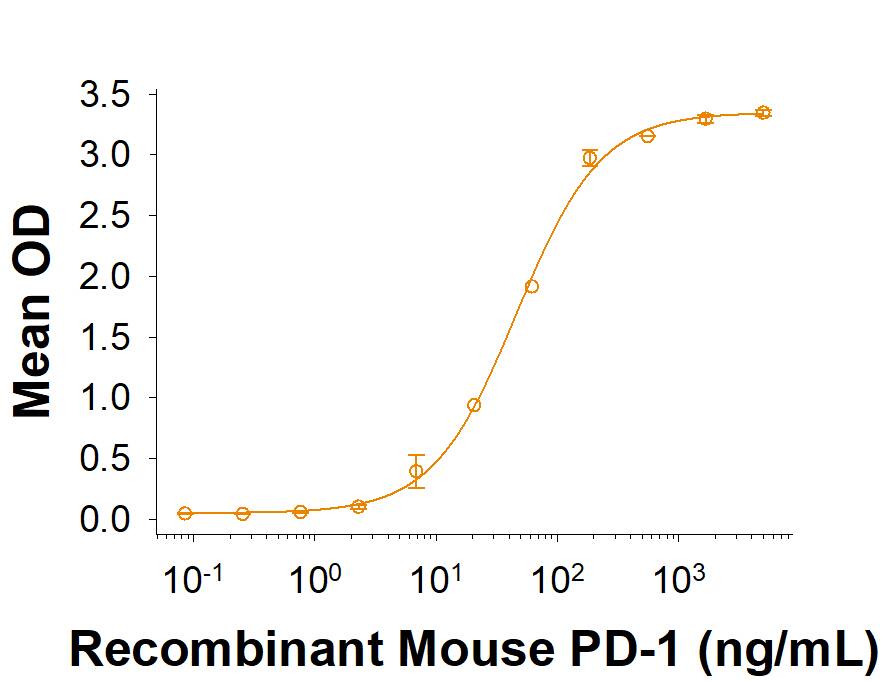
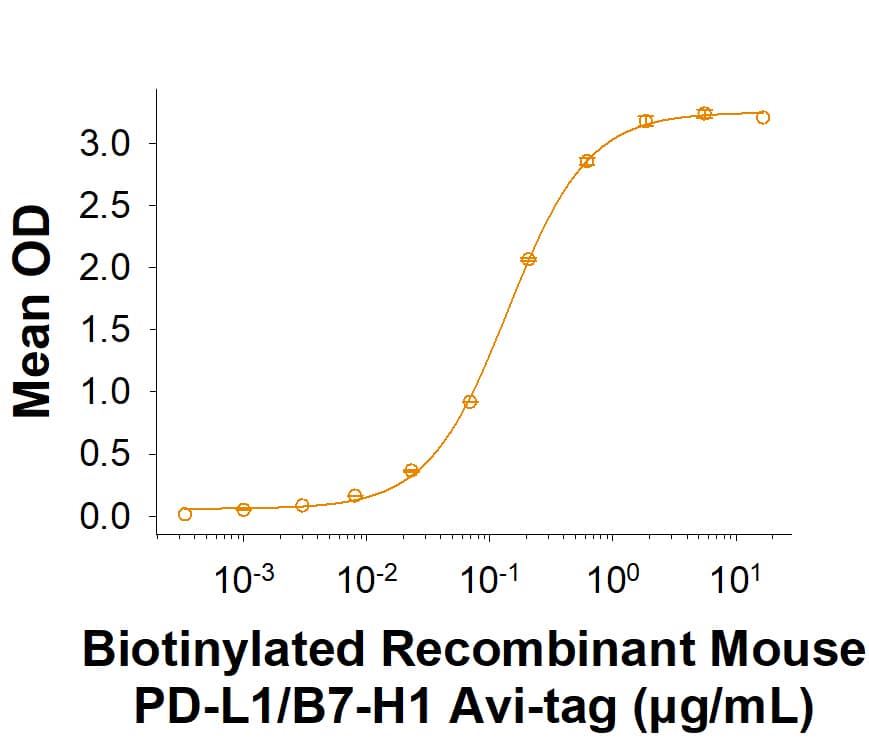
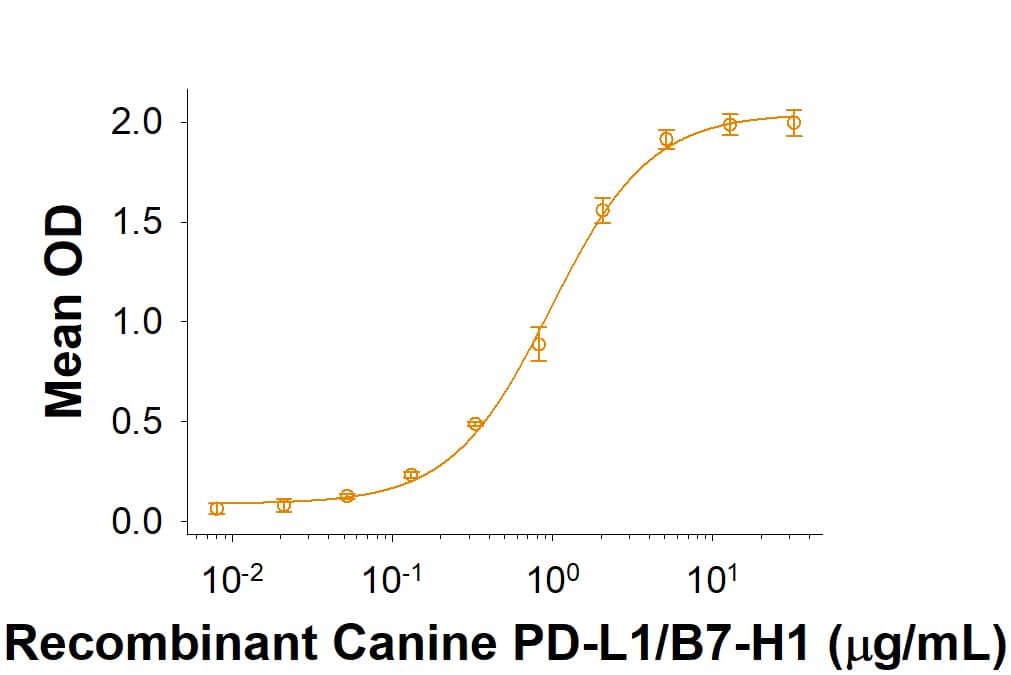
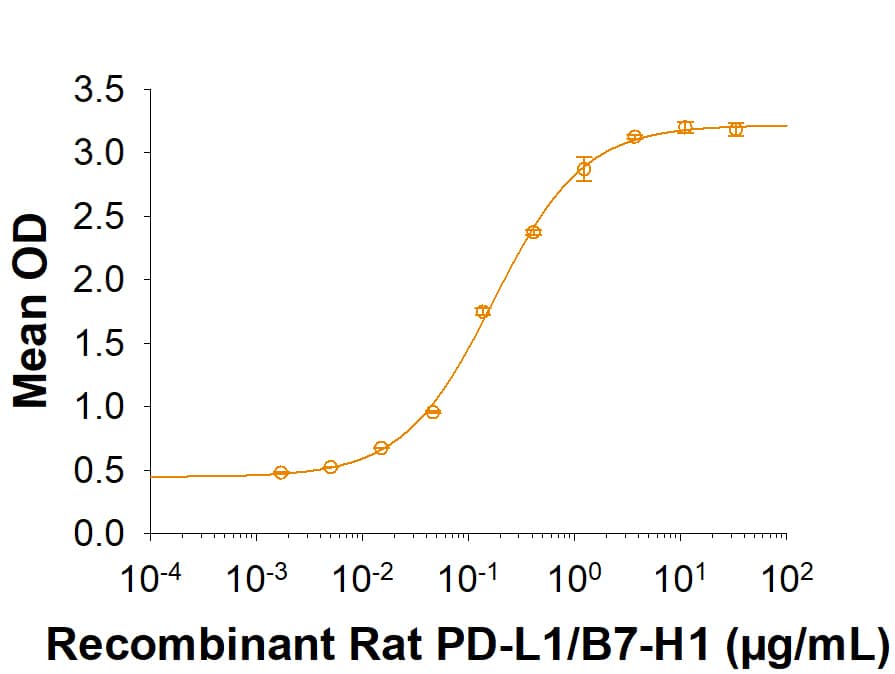
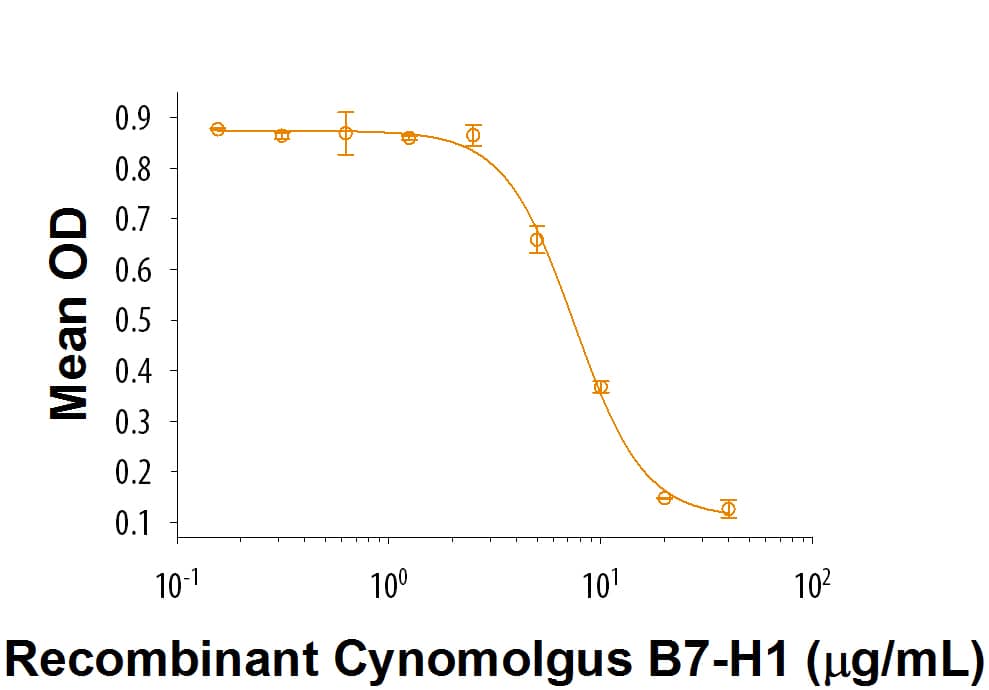

![SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human PD-L1 His Protein [NBP1-98984] SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human PD-L1 His Protein [NBP1-98984]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Recombinant-Human-B7-H1-PD-L1-CD274-Protein-SDS-Page-NBP1-98984-img0002.jpg)
![SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Mouse PD-L1 His Protein [NBP1-98887] SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Mouse PD-L1 His Protein [NBP1-98887]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Recombinant-Mouse-PD-L1-B7-H1-Protein-SDS-Page-NBP1-98887-img0001.jpg)