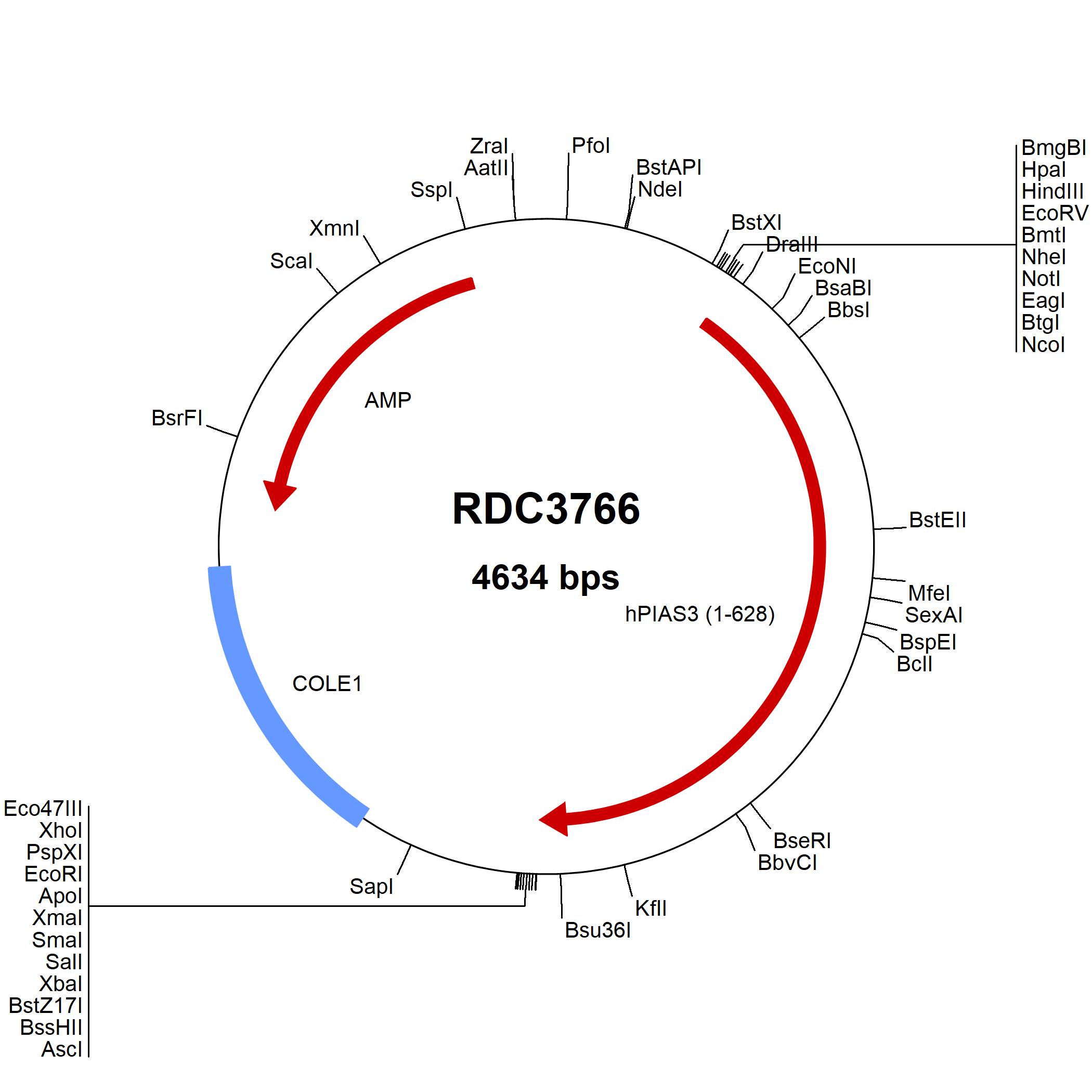
PIAS3: cDNA Clones
Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT, 3 (PIAS3) is one member of the PIAS family of molecules. It is 628 amino acids (aa) in length and has a predicted molecular weight of 68.0 kDa. Human PIAS3 shares 97% aa sequence identity with the mouse and rat orthologs. It contains several domains conserved among all PIAS family members. These domains include an N-terminal SAP domain that contains the LXXLL signature motif, a PINIT motif, a RING finger-like zinc binding domain, and a highly acidic region that contains a putative SUMO-interaction motif. The LXXLL motif mediates interactions between nuclear receptors and regulatory proteins, and the PINIT motif has been shown to be critical for nuclear retention of PIAS3. PIAS proteins function as RING-type small Ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) ligases. They regulate intracellular signaling by modulating the activity of many transcription factors. PIAS3 was first identified as a inhibitor of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). It has now been shown to regulate numerous transcription factors including Ets-1, EGR1, PXR/NR1I2, GATA-1, MITF, ELK4, and the Androgen Receptor. As a consequence, PIAS3 regulates a vast array of biological processes such as immune responses, melanocyte development, and osteoclastogenesis. In addition, PIAS3 appears to control carcinogenesis. Interestingly, STAT3 phosphorylation has been shown to promote tumor development, and PIAS3 protein expression is reduced or nonexistant in many cancer types including gastric, lung, breast, and brain carcinomas.
1 result for "PIAS3 cDNA Clones" in Products
1 result for "PIAS3 cDNA Clones" in Products
PIAS3: cDNA Clones
Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT, 3 (PIAS3) is one member of the PIAS family of molecules. It is 628 amino acids (aa) in length and has a predicted molecular weight of 68.0 kDa. Human PIAS3 shares 97% aa sequence identity with the mouse and rat orthologs. It contains several domains conserved among all PIAS family members. These domains include an N-terminal SAP domain that contains the LXXLL signature motif, a PINIT motif, a RING finger-like zinc binding domain, and a highly acidic region that contains a putative SUMO-interaction motif. The LXXLL motif mediates interactions between nuclear receptors and regulatory proteins, and the PINIT motif has been shown to be critical for nuclear retention of PIAS3. PIAS proteins function as RING-type small Ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) ligases. They regulate intracellular signaling by modulating the activity of many transcription factors. PIAS3 was first identified as a inhibitor of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). It has now been shown to regulate numerous transcription factors including Ets-1, EGR1, PXR/NR1I2, GATA-1, MITF, ELK4, and the Androgen Receptor. As a consequence, PIAS3 regulates a vast array of biological processes such as immune responses, melanocyte development, and osteoclastogenesis. In addition, PIAS3 appears to control carcinogenesis. Interestingly, STAT3 phosphorylation has been shown to promote tumor development, and PIAS3 protein expression is reduced or nonexistant in many cancer types including gastric, lung, breast, and brain carcinomas.