RAGE/AGER Products
RAGE (Receptor for Advanced Glycation End product) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that binds advanced glycation end products (AGEs), beta-amyloid peptides, HMGB1/Amphoterin, and several S100 family proteins. AGEs are adducts formed by the non-enzymatic glycation and oxidation of proteins and lipids. A soluble form can also be generated by MMP-mediated shedding.
RAGE is expressed in the CNS during development as well as in adult endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, pericytes, monocytes, and neurons. It is locally upregulated in vascular inflammation (e.g. diabetes, atherosclerosis, vascular injury, Alzheimer’s disease). At these sites, RAGE binding to S100A1, EN-RAGE/S100A12, or S100B induces inflammatory immune cell adhesion and infiltration as well as vascular smooth muscle proliferation, neointimal expansion, atherosclerotic plaque development, and transport of A-beta into the cerebrospinal fluid. In cancer, RAGE binding to HMGB1, S100A8, or S100A9 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in addition to inflammatory cell infiltration.
Products:
41 results for "RAGE/AGER" in Products
41 results for "RAGE/AGER" in Products
RAGE/AGER Products
RAGE (Receptor for Advanced Glycation End product) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that binds advanced glycation end products (AGEs), beta-amyloid peptides, HMGB1/Amphoterin, and several S100 family proteins. AGEs are adducts formed by the non-enzymatic glycation and oxidation of proteins and lipids. A soluble form can also be generated by MMP-mediated shedding.
RAGE is expressed in the CNS during development as well as in adult endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, pericytes, monocytes, and neurons. It is locally upregulated in vascular inflammation (e.g. diabetes, atherosclerosis, vascular injury, Alzheimer’s disease). At these sites, RAGE binding to S100A1, EN-RAGE/S100A12, or S100B induces inflammatory immune cell adhesion and infiltration as well as vascular smooth muscle proliferation, neointimal expansion, atherosclerotic plaque development, and transport of A-beta into the cerebrospinal fluid. In cancer, RAGE binding to HMGB1, S100A8, or S100A9 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in addition to inflammatory cell infiltration.
Products:
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, Block |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC, Block |
| Reactivity: | Canine |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody.
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #JF0975 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Rat |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Block |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Amphibian, Squirrel |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Reactivity: | Canine |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Rat |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Monoclonal Clone #005 |
| Applications: | ELISA |

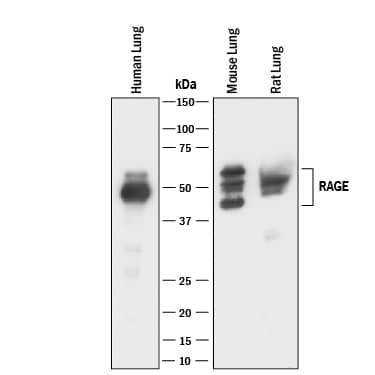

![Western Blot: AGER Antibody (JF0975) [NBP2-67095] Western Blot: AGER Antibody (JF0975) [NBP2-67095]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/AGER-Antibody-JF0975-Western-Blot-NBP2-67095-img0005.jpg)
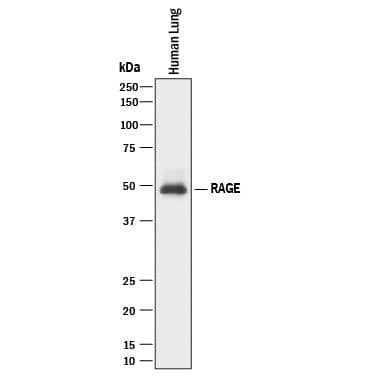
![Western Blot: AGER Antibody [NBP3-13484] Western Blot: AGER Antibody [NBP3-13484]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/AGER-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP3-13484-img0003.jpg)
![Western Blot: AGER Antibody [NBP3-18000] Western Blot: AGER Antibody [NBP3-18000]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/AGER-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP3-18000-img0001.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: AGER Antibody [NBP3-16981] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: AGER Antibody [NBP3-16981]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/AGER-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP3-16981-img0002.jpg)
