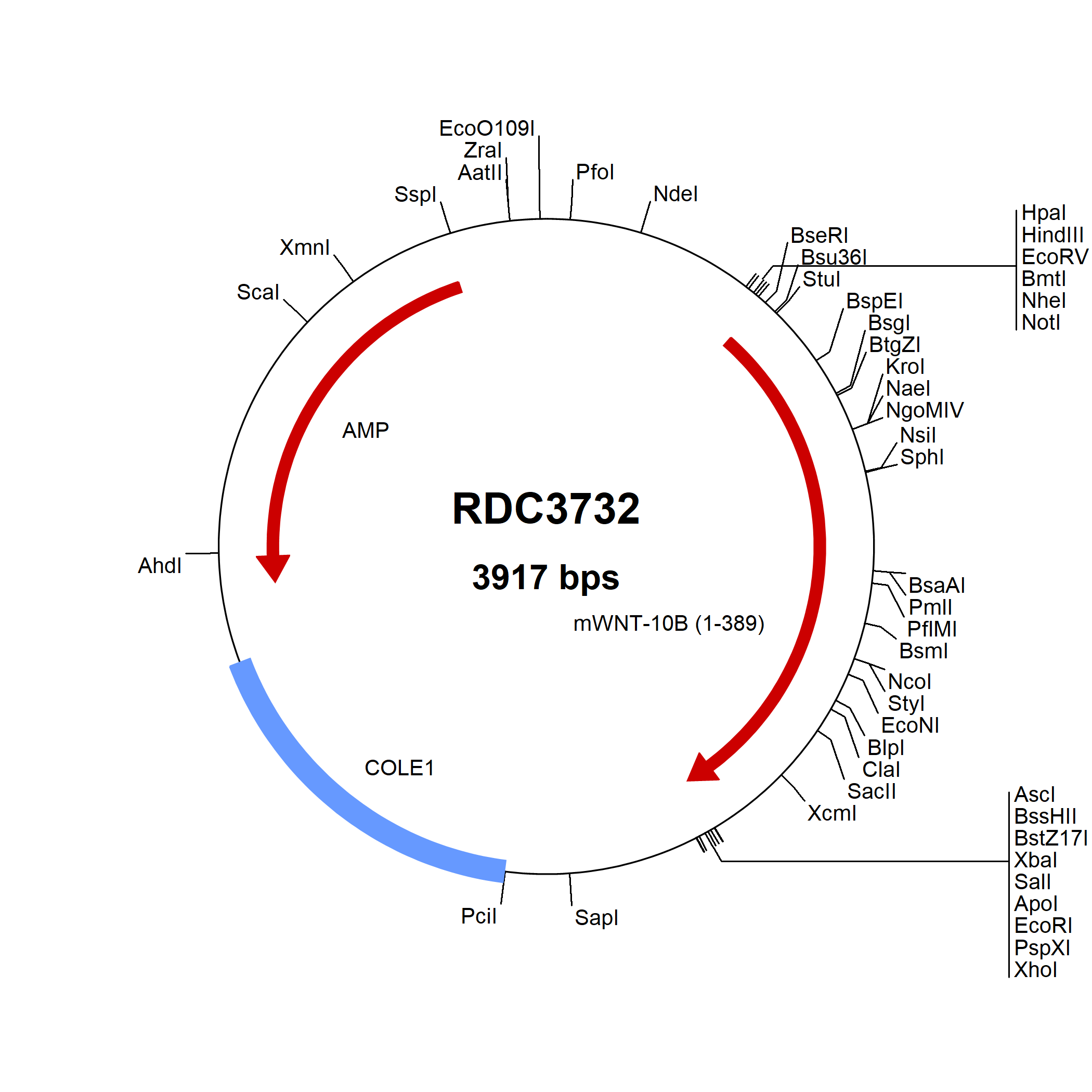
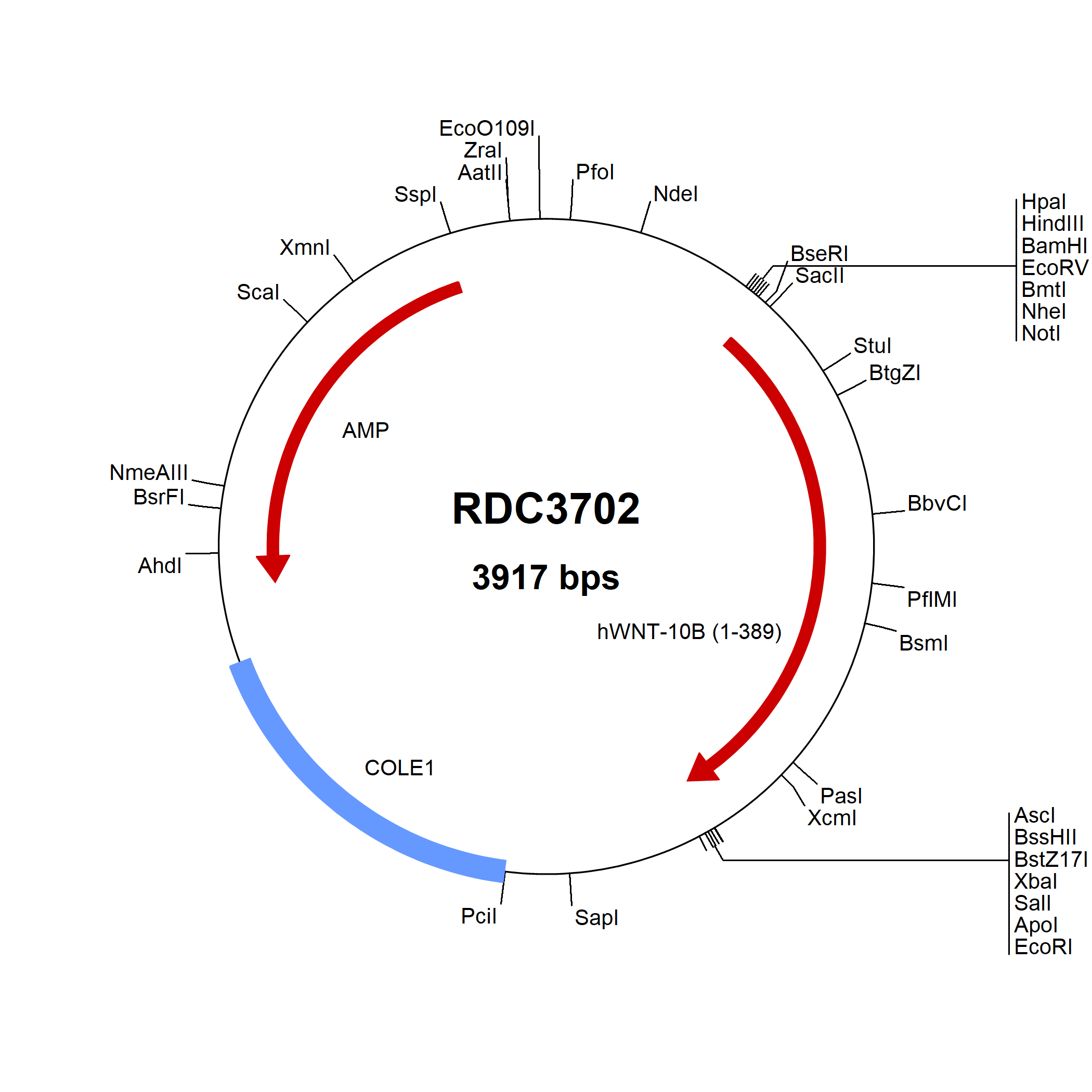
Wnt-10b: cDNA Clones
Wnt-10b (also known as Wnt-12) is a 45 kDa glycoprotein involved in fetal limb bud development and adult hematopoiesis. Wnt-10b has been shown to promote epithelial cell differentiation and hair shaft growth. In addition, Wnt-10b may play an important role in hair follicle development by inducing differentiation of epithelial cells. Wnt-10b is less than 60% amino acid (aa) identical to other Wnts, but mouse to human, Wnt-10b shows greater than 97% aa sequence identity.
The Wnts make up a large family of secreted proteins with roles in pattern formation, cell fate decision, axon guidance, and tumor formation. Wnt family members vary in length between 350 and 400 aa, possess 22 to 24 conserved cysteines, are highly hydrophobic, and show 20 - 85% aa identity within the Wnt family. In general, there are three signaling pathways associated with Wnt-receptor interaction. The first is commonly called the canonical pathway and ultimately culminates in beta-Catenin accumulation and TCF/LEF-1-mediated gene transcription. The other two less well-defined non-canonical pathways include the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway.
2 results for "Wnt-10b cDNA Clones" in Products
2 results for "Wnt-10b cDNA Clones" in Products
Wnt-10b: cDNA Clones
Wnt-10b (also known as Wnt-12) is a 45 kDa glycoprotein involved in fetal limb bud development and adult hematopoiesis. Wnt-10b has been shown to promote epithelial cell differentiation and hair shaft growth. In addition, Wnt-10b may play an important role in hair follicle development by inducing differentiation of epithelial cells. Wnt-10b is less than 60% amino acid (aa) identical to other Wnts, but mouse to human, Wnt-10b shows greater than 97% aa sequence identity.
The Wnts make up a large family of secreted proteins with roles in pattern formation, cell fate decision, axon guidance, and tumor formation. Wnt family members vary in length between 350 and 400 aa, possess 22 to 24 conserved cysteines, are highly hydrophobic, and show 20 - 85% aa identity within the Wnt family. In general, there are three signaling pathways associated with Wnt-receptor interaction. The first is commonly called the canonical pathway and ultimately culminates in beta-Catenin accumulation and TCF/LEF-1-mediated gene transcription. The other two less well-defined non-canonical pathways include the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and the planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway.