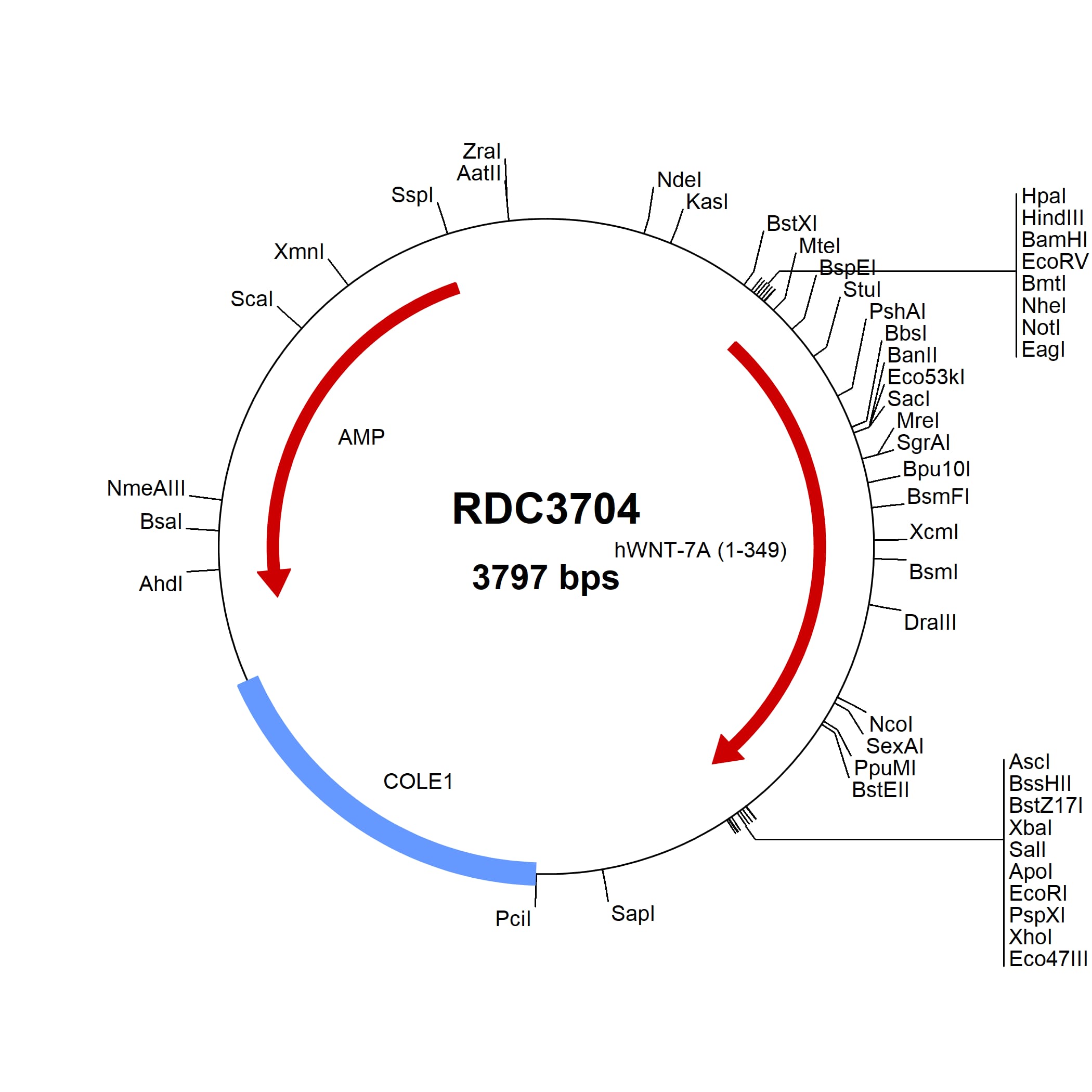
Wnt-7a: cDNA Clones
Wnt-7a is one of about 19 vertebrate members of the Wingless-type MMTV integration site (Wnt) family of highly conserved cysteine-rich secreted glycoproteins important for normal developmental processes. During development, Wnt7a is expressed by the dorsal ectoderm and drives expression of homeodomain transcription factors that control effectors important in patterning and cell fates in adjacent mesenchyme. When Wnt-7a is deleted, mice show disruption of dorsalization and anterior/posterior patterning during limb development and abnormalities in the reproductive tract. Wnt-7a is frequently downregulated in leukemia and lung cancers, potentially affecting homeobox (HOX) gene expression, differentiation state, and growth control. Roles for Wnt-7a have also been shown during formation of neural synapses, response of the uterus to estrogen, and inflammatory cartilage destruction. In addition, Wnt-7a has been shown to modulate synaptic transmission and induces presynaptic colocalization of alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
Human Wnt-7a is a 48 kDa secreted glycoprotein containing 24 cysteine residues that is expressed by epithelial and epithelially-derived cells of the placenta, kidney, testis, uterus, fetal lung and fetal and adult brain. Palmitate modification of a cysteine residue has been shown for Wnt-3a; this site is conserved on all Wnts and is Cys73 on Wnt7a. When modified, increased hydrophobicity and activity is expected. Human Wnt-7a shows 97% aa identity with mouse, rat and canine Wnt-7a and 92% aa identity with chicken Wnt-7a.
1 result for "Wnt-7a cDNA Clones" in Products
1 result for "Wnt-7a cDNA Clones" in Products
Wnt-7a: cDNA Clones
Wnt-7a is one of about 19 vertebrate members of the Wingless-type MMTV integration site (Wnt) family of highly conserved cysteine-rich secreted glycoproteins important for normal developmental processes. During development, Wnt7a is expressed by the dorsal ectoderm and drives expression of homeodomain transcription factors that control effectors important in patterning and cell fates in adjacent mesenchyme. When Wnt-7a is deleted, mice show disruption of dorsalization and anterior/posterior patterning during limb development and abnormalities in the reproductive tract. Wnt-7a is frequently downregulated in leukemia and lung cancers, potentially affecting homeobox (HOX) gene expression, differentiation state, and growth control. Roles for Wnt-7a have also been shown during formation of neural synapses, response of the uterus to estrogen, and inflammatory cartilage destruction. In addition, Wnt-7a has been shown to modulate synaptic transmission and induces presynaptic colocalization of alpha 7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.
Human Wnt-7a is a 48 kDa secreted glycoprotein containing 24 cysteine residues that is expressed by epithelial and epithelially-derived cells of the placenta, kidney, testis, uterus, fetal lung and fetal and adult brain. Palmitate modification of a cysteine residue has been shown for Wnt-3a; this site is conserved on all Wnts and is Cys73 on Wnt7a. When modified, increased hydrophobicity and activity is expected. Human Wnt-7a shows 97% aa identity with mouse, rat and canine Wnt-7a and 92% aa identity with chicken Wnt-7a.