CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC]
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NBP1-28238

Conjugate
Catalog #
Forumulation
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Porcine
Applications
Flow Cytometry
Label
FITC (Excitation = 495 nm, Emission = 519 nm)
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG2a Kappa Clone # 76-2-11
Concentration
Please see the vial label for concentration. If unlisted please contact technical services.
Product Specifications
Immunogen
CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC] was developed against fresh dd miniature swine thymocytes
Specificity
CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) recognizes Porcine CD8a, Mr 32-34 kDa
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG2a Kappa
Theoretical MW
26 kDa.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Disclaimer note: The observed molecular weight of the protein may vary from the listed predicted molecular weight due to post translational modifications, post translation cleavages, relative charges, and other experimental factors.
Scientific Data Images for CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC]
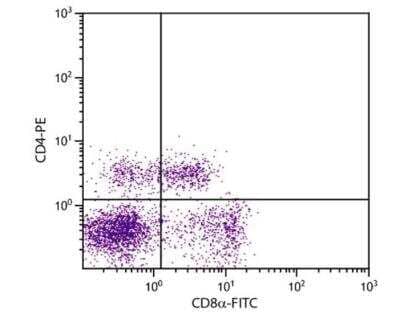
Flow Cytometry: CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC] [NBP1-28238] - Porcine peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with Mouse Anti-Porcine CD8 alpha-FITC and Mouse Anti-Porcine CD4-PE.
Flow Cytometry: CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC] [NBP1-28238] - CD8 alpha Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC] [NBP1-28238] - CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC] 1 ug/10^6 Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from heparinized pig blood on Ficoll-Hypaque density gradients and double stained with mouse anti-pig CD8-FITC and mouse anti-pig CD4a-R-PE. Lymphocytes were gated and analyzed on a flow cytometer
Applications for CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC]
Application
Recommended Usage
Flow Cytometry
Optimal dilutions of this antibody should be experimentally determined.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein A or G purified
Formulation
PBS
Preservative
0.05% Sodium Azide
Concentration
Please see the vial label for concentration. If unlisted please contact technical services.
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at 4C. Do not freeze.
Background: CD8
Given its role in the immune system, CD8-deficiency in T-cells is a hallmark of many diseases and pathologies (8-10). Specifically, CD8+ T-cell deficiency is prevalent in chronic autoimmune diseases including multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and Graves' disease (8). Furthermore, cancers or chronic infection can lead to CD8 T-cell exhaustion as the continual antigen presentation and inflammatory signals eventually cause the CD8+ T-cells to lose functionality (9, 10). However, animal models and clinical studies have suggested that T-cells are capable of being reinvigorated using inhibitory receptor blockade resulting in better disease outcomes and these exhausted T-cells may be a potential therapeutic target (9, 10).
Alternative names for CD8 includes CD antigen: CD8a, CD8 antigen, alpha polypeptide (p32), CD8a molecule, CD8A, Leu2 T-lymphocyte antigen, LEU2, MAL, OKT8 T-cell antigen, p32, T cell co-receptor, T8 T-cell antigen, T-cell antigen Leu2, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain, and T-lymphocyte differentiation antigen T8/Leu-2.
References
1. Littman D. R. (1987). The structure of the CD4 and CD8 genes. Annual review of immunology. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.003021
2. Naeim F. (2008). Chapter 2- Principles of Immunophenotyping. Hematopathology. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-370607-2.00002-8.
3. Gao, G. F., & Jakobsen, B. K. (2000). Molecular interactions of coreceptor CD8 and MHC class I: the molecular basis for functional coordination with the T-cell receptor. Immunology today. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-5699(00)01750-3
4. UniProt (P01732)
5. UniProt (P01731)
6. Kappes D. J. (2007). CD4 and CD8: hogging all the Lck. Immunity. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2007.11.002
7. Gangadharan, D., & Cheroutre, H. (2004). The CD8 isoform CD8alphaalpha is not a functional homologue of the TCR co-receptor CD8alphabeta. Current opinion in immunology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2004.03.015
8. Pender M. P. (2012). CD8+ T-Cell Deficiency, Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, Vitamin D Deficiency, and Steps to Autoimmunity: A Unifying Hypothesis. Autoimmune diseases. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/189096
9. Kurachi M. (2019). CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Seminars in immunopathology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-019-00744-5
10. Hashimoto, M., Kamphorst, A. O., Im, S. J., Kissick, H. T., Pillai, R. N., Ramalingam, S. S., Araki, K., & Ahmed, R. (2018). CD8 T Cell Exhaustion in Chronic Infection and Cancer: Opportunities for Interventions. Annual review of medicine. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-med-012017-043208
Alternate Names
CD8, CD8A
Gene Symbol
CD8A
Additional CD8 Products
Product Documents for CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC]
Product Specific Notices for CD8 Antibody (76-2-11) [FITC]
Protect conjugated forms from light.
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
