Human ACE-2 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB10823


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln18-Ser740
Accession # Q9BYF1
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human ACE-2 Antibody
Detection of Human ACE-2 by Western Blot.
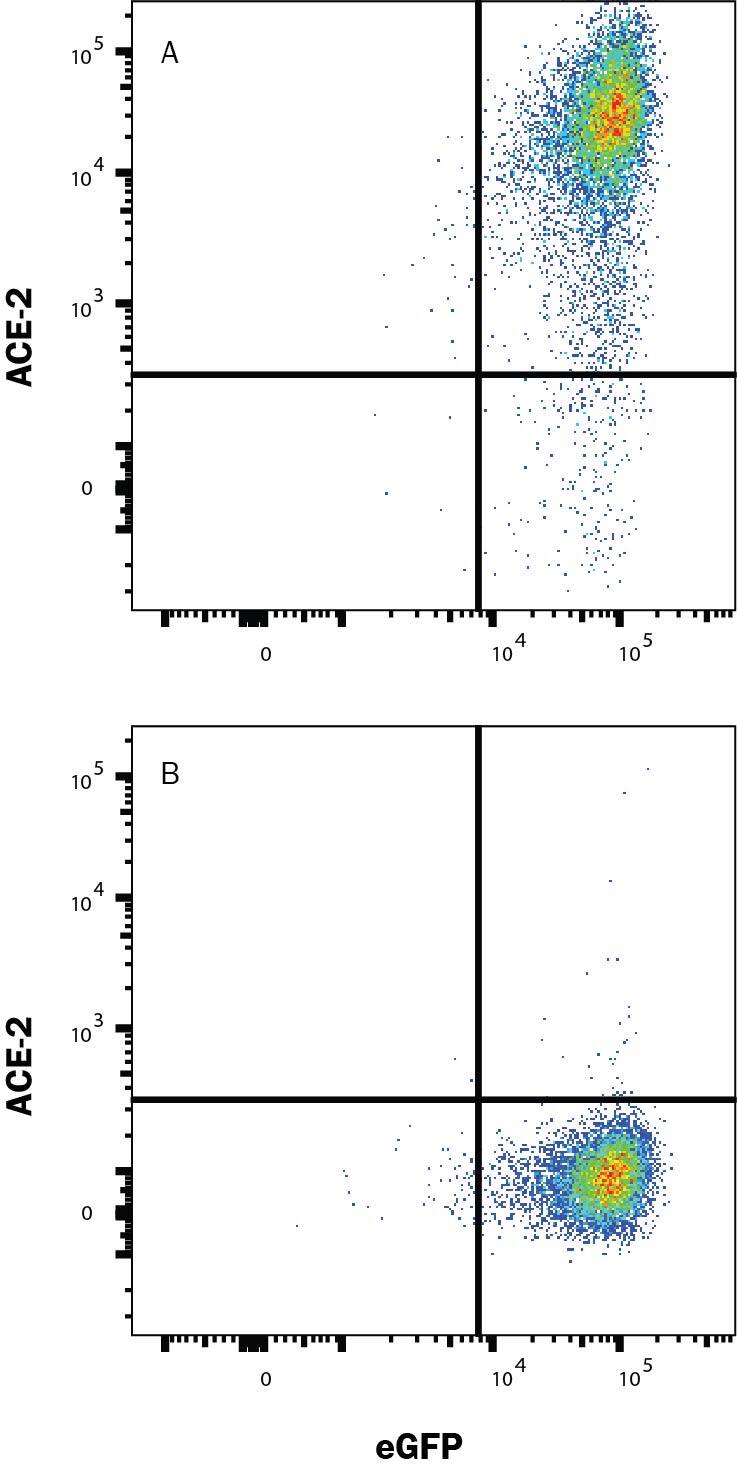
Western blot shows lysates of human kidney and human testis. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Rabbit Anti-Human ACE-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB10823) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (HAF008). A specific band was detected for ACE-2 at approximately 120 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Western Blot Buffer Group 1.Detection of ACE-2 in HEK293 Human Cell Line Transfected with Human ACE-2 and eGFP by Flow Cytometry.
HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with (A) human ACE-2 or (B) irrelevant protein, and eGFP was stained with Rabbit Anti-Human ACE-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB10823) followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Rabbit IgG Secondary Antibody (F0111). Quadrant markers were set based on Rabbit IgG Isotype Control (MAB1050). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane-associated Proteins protocol.ACE-2 in Human Kidney.
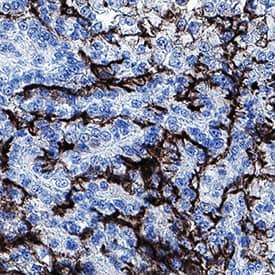
ACE-2 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using Rabbit Anti-Human ACE-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB10823) at 0.3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Rabbit IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (VC003). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane in convoluted tubules. Staining was performed using our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human ACE-2 Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HEK293 Human Cell Line Transfected with Human ACE-2 and eGFP
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney
Western Blot
Sample: Human kidney and human testis
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: ACE-2
Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE-2), also called ACEH (ACE homologue), is a dimeric, zinc-dependent metalloprotease of the ACE family that also includes somatic and germinal ACE (1, 2). ACE-2 mRNA is found at high levels in heart, testis, and kidney and at lower levels in a wide variety of tissues (1, 3). ACE-2 is the SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV2 Spike protein receptor in vivo (4-6), functions catalytically as a carboxypeptidase to cleave several substrates including angiotensins I and II, and acts as a partner for B0AT1-family amino acid transporters (1, 2). Through these functions, ACE-2 has been shown to be involved in several diseases including SARS, COVID19, acute lung injury (4, 7), heart disease (8), liver and lung fibrosis (9), inflammatory lung disease (10), and cardiopulmonary disease (11). Full length ACE-2 protein includes an extracellular region composed of a single N-terminal peptidase domain and C-terminal collectrin-like domain (CLD), a transmembrane domain, and a short cytoplasmic tail (12). The N-terminal peptidase region is required for binding to SARS-CoV and SARSCoV2 spike proteins, while the CLD contains a region that promotes dimerization and association with amino acid transporters (2). The peptidase domain contains a long deep cleft that undergoes a large hinge-bending movement at substrate and inhibitor binding (12). Classical ACE inhibitors such as captopril and lisinopril do not inhibit ACE-2 activity and inhibitors of ACE-2 do not inhibit ACE activity (13).
References
- Kuba, K. et al. (2010) Pharmacol. Ther. 128:119.
- Yan, et al. (2020) Science 367:1444.
- Tipnis, S.R. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:33238.
- Kuba, K. et al. (2005) Nature Med. 11:875.
- Hoffmann, M. et al. (2020) Cell.181:1.
- Wrapp, et al. (2020) Science 367:1260.
- Imai, Y. et al. (2005) Nature 436:112.
- Huang, L. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:15532.
- Schrom, E. et al. (2017) Mol. Therapy Nuc. Acid 7:350.
- Jia, H. et al. (2016) Shock. 46:239.
- Cole-Jeffrey, C.T. et al. (2015) J. Cadiovasc. Pharmacol. 66:540.
- Towler, P. et al. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279:17996.
- Crackower, M.A. et al. (2002) Nature 417:822.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional ACE-2 Products
Product Documents for Human ACE-2 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human ACE-2 Antibody
For research use only