Human ACE/CD143 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF929

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Leu30-Leu1261
Accession # P12821
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human ACE/CD143 Antibody
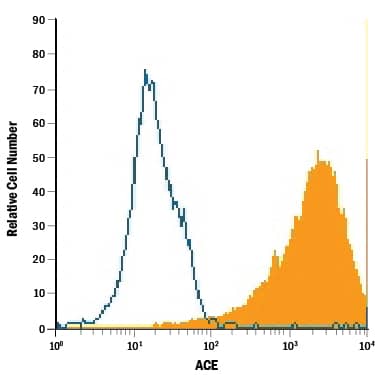
Detection of ACE/CD143 in Human Mature Monocyte-derived Dendritic Cells by Flow Cytometry.
Human mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells were stained with Goat Anti-Human ACE/CD143 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF929, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Allophycocyanin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0108).ACE/CD143 in Human Kidney.
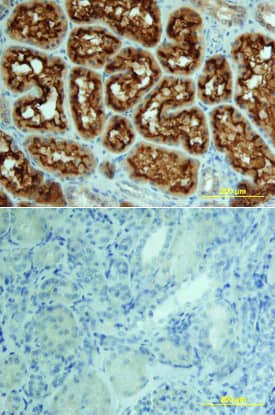
ACE/CD143 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using 15 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human ACE/CD143 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF929) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.ACE/CD143 in Human Kidney.
ACE/CD143 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney array using Goat Anti-Human ACE/CD143 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF929) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Lower panel shows a lack of labeling if primary antibodies are omitted and tissue is stained only with secondary antibody followed by incubation with detection reagents. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Applications for Human ACE/CD143 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human mature monocyte-derived dendritic cells
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human ACE/CD143 Somatic Form (Catalog # 929-ZN)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: ACE/CD143
ACE (also known as peptidyl-dipetidase A) is a zinc metallopeptidase important for blood pressure control and water and salt metabolism (2). It cleaves the C-terminal dipeptide from angiotensin I to produce the potent vasopressor octapeptide angiotensin II and inactivates bradykinin by the sequential removal of two C-terminal dipeptides. In addition to the two physiological substrates, ACE cleaves C-terminal dipeptides from various oligopeptides with a free C-terminus. Because of its location and specificity, ACE plays additional roles in immunity, reproduction and neuropeptide regulation. For example, ACE degrades Alzheimer amyloid beta-peptide (A beta), retards A beta aggregation, deposition, fibril formation, and inhibits cytotoxicity (3).
ACE is a type I membrane protein and exists in two isoforms (2). Somatic ACE, found in endothelial, epithelial and neuronal cells, comprises two highly similar domains called N- and C-domains, each of which contains the HExxH consensus sequence for zinc binding. Germinal ACE, found exclusively in the testes, comprises a single catalytically active domain identical to the C-domain of somatic ACE except for an N-terminal 67 residue germinal ACE-specific sequence. Physiological functions of the two tissue-specific isozymes are not interchangeable (4). For example, sperm-specific expression of the germinal ACE, not the somatic ACE, in ACE knockout male mice restored fertility.
Soluble ACE is present in many biological fluids, such as serum, seminal fluid, amniotic fluid and cerebrospinal fluid (2). The soluble ACE is derived from the membrane forms by actions of secretases or sheddases. The identities of the secretases have not been revealed, although they belong to the family of zinc metallopeptidases (5, 6).
References
- Soubrier, et al. (1988) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:9386.
- Corvol, P. and T.A. Williams (1998) in Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Barrett, A.J. et al. (eds): San Diego, Academic Press, p. 1066.
- Hu, et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:47863.
- Kessler, et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:26259.
- Eyries, et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:5525.
- Alfalah, et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:21105.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional ACE/CD143 Products
Product Documents for Human ACE/CD143 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human ACE/CD143 Antibody
For research use only