Human EphB4 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF3038


Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Leu16-Ala539
Accession # P54760
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human EphB4 Antibody
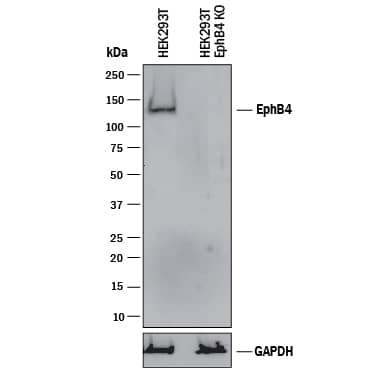
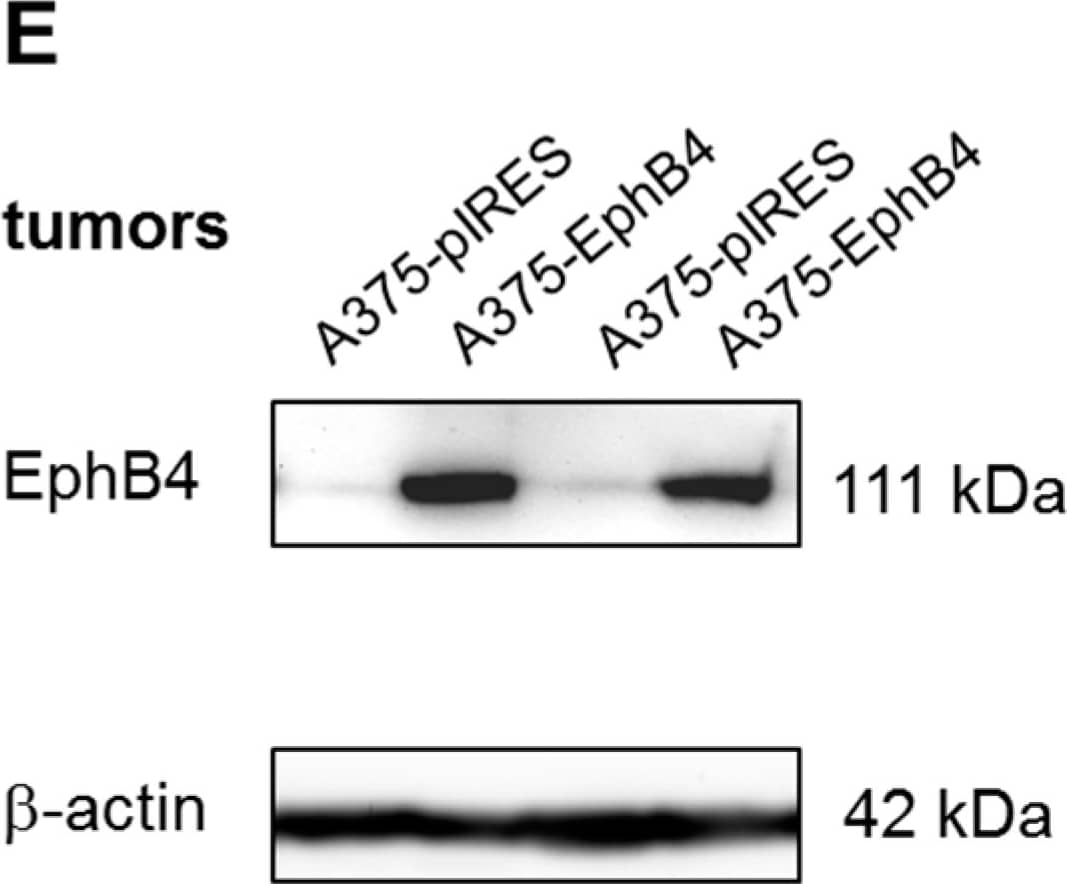
Detection of Human EphB4 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line, COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line, ZR-75 human breast cancer cell line, and HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells. PVDF membrane was probed with 2 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human EphB4 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3038) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for EphB4 at approximately 120 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of EphB4 in MCF‑7 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
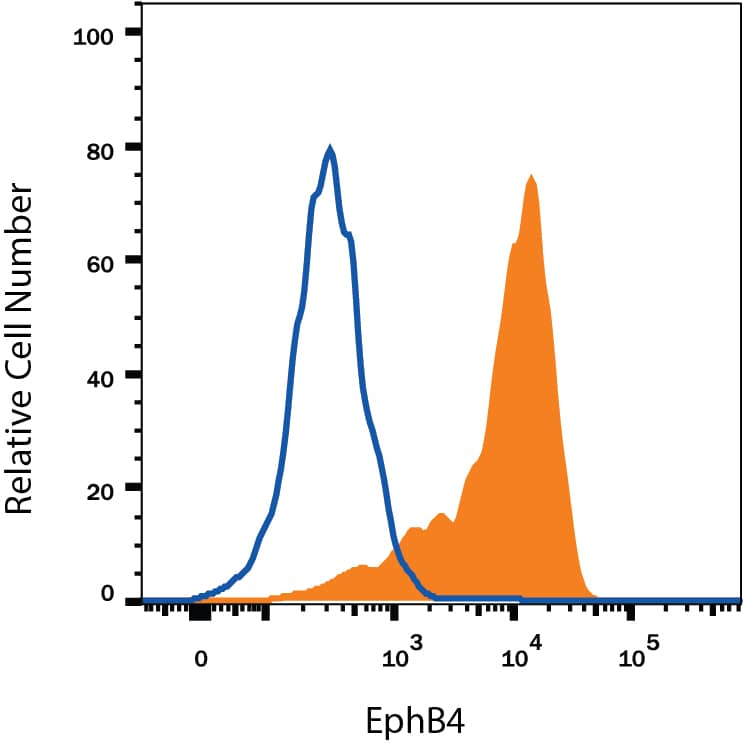
MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line was stained with Goat Anti-Human EphB4 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3038, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # AB-108-C, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0107). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.EphB4 in Human Kidney.
EphB4 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney using 15 µg/mL Goat Anti-Human EphB4 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF3038) overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained with the Anti-Goat HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS008) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.Applications for Human EphB4 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human kidney
Knockout Validated
Simple Western
Sample: HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Western Blot
Sample: K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line, COLO 205 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line, ZR‑75 human breast cancer cell line, and HUVEC human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using AF3038 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: EphB4
EphB4, also known as Htk, Myk1, Tyro11, and Mdk2, is a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family and binds Ephrin-B2. The A and B class Eph proteins have a common structural organization (1-4). The human EphB4 cDNA encodes a 987 amino acid (aa) precursor that includes a 15 aa signal sequence, a 524 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 427 aa cytoplasmic domain (5). The ECD contains an N-terminal globular domain, a cysteine-rich domain, and two fibronectin type III domains. The cytoplasmic domain contains a juxtamembrane motif with two tyrosine residues which are the major autophosphorylation sites, a kinase domain, and a conserved sterile alpha motif (SAM) (5). Activation of kinase activity occurs after membrane-bound or clustered ligand recognition and binding. The ECD of human EphB4 shares 89% aa sequence identity with mouse EphB4 and 42-45% aa sequence identity with human EphB1, 2, and 3. EphB4 is expressed preferentially on venous endothelial cells (EC) and inhibits cell-cell adhesion, chemotaxis, and angiogenesis. Opposing effects are induced by signaling through Ephrin-B2 expressed on arterial EC: adhesion, endothelial cell migration, and vessel sprouting (6). EphB4 singaling contributes to new vascularization by guiding venous EC away from Ephrin-B2 expressing EC. Ephrin-B2 signaling induces arterial EC to migrate towards nascent EphB4 expressing vessels (6). The combination of forward signaling through EphB4 and reverse signaling through Ephrin-B2 promotes in vivo mammary tumor growth and
tumor-associated angiogenesis (7). EphB4 promotes the differentiation of megakaryocytic and erythroid progenitors but not granulocytic or monocytic progenitors (8, 9).
References
- Poliakov, A. et al. (2004) Dev. Cell 7:465.
- Surawska, H. et al. (2004) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:419.
- Pasquale, E.B. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:462.
- Davy, A. and P. Soriano (2005) Dev. Dyn. 232:1.
- Bennett, B.D. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:14211.
- Fuller, T. et al. (2003) J. Cell Sci. 116:2461.
- Noren, N.K. et al. (2004) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:5583.
- Wang, Z. et al. (2002) Blood 99:2740.
- Inada, T. et al. (1997) Blood 89:2757.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional EphB4 Products
Product Documents for Human EphB4 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human EphB4 Antibody
For research use only