Human EphB6 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB33841

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Val17-Thr579
Accession # O15197
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human EphB6 Antibody
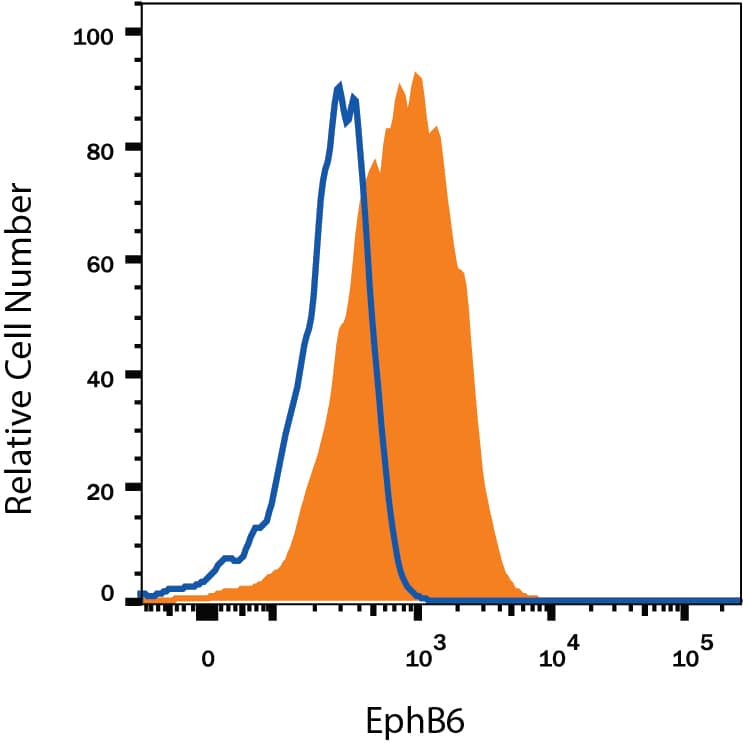
Detection of EphB6 in MOLT‑4 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
MOLT-4 human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human EphB6 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB33841, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB002, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human EphB6 Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: MOLT‑4 human acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: EphB6
EphB6, also known as Hep and Mep, is a 110 kDa member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family. The A and B classes of Eph proteins are distinguished by ligand preference and have a common structural organization (1‑4). The human EphB6 cDNA encodes a 1006 amino acid (aa) precursor that includes a 16 aa signal sequence, a 563 aa extracellular domain (ECD), a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 406 aa cytoplasmic domain. The ECD contains serine- and cysteine-rich regions and two fibronectin type-III domains. The cytoplasmic domain contains one non-catalytic protein kinase-like, one proline-rich, one SAM, and one PDZ-binding domain (5, 6). Within the ECD, human EphB6 shares 91% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat EphB6. It shares 38‑45% aa sequence identity with human EphB1, 2, 3, 4, and 6. Human EphB5 has not been characterized. Two secreted splice variants have been described in mouse but not in human (6). EphB6 is primarily expressed in brain, pancreas, thymus, and peripheral T cells (5, 7, 8). EphB6 forms stable heterodimers with EphB1 and participates in signal transduction by association with other enzymatically active molecules (9‑11). Ephrin-B2 is the dominant ligand for EphB6, although Ephrin-B1 and Ephrin-B3 can also trigger responses (12‑14). High concentrations of Ephrin-B2 inhibit cell adhesion and migration as well as tyrosine phosphorylation of EphB6. Conversely, low concentrations of Ephrin-B2 promote adhesion and migration and do not lead to EphB6 phosphorylation (15). The level of EphB6 expression is inversely correlated with tumor aggressiveness in a variety of malignancies (1). EphB6 also functions as a T cell co-stimulatory molecule (8, 11, 13). EphB6 clusters with the T cell receptor and participates in the subsequent attenuation of the T cell response (8, 10, 11, 13).
References
- Surawska, H. et al. (2004) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:419.
- Poliakov, A. et al. (2004) Dev. Cell 7:465.
- Wu, J. and H. Luo (2005) Curr. Opin. Hematol. 12:292.
- Pasquale, E.B. (2005) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6:462.
- Matsuoka, H. et al. (1997) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235:487.
- Gurniak, C.B. and L.J. Berg (1996) Oncogene 13:777.
- Hafner, C. et al. (2004) Clin. Chem. 50:490.
- Luo, H. et al. (2002) J. Clin. Invest. 110:1141.
- Freywald, A. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:3823.
- Freywald, A. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:10150.
- Luo, H. et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 167:1362.
- Munthe, E. et al. (2000) FEBS Lett. 466:169.
- Luo, H. et al. (2004) J. Clin. Invest. 114:1762.
- Shimoyama, M. et al. (2002) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 298:87.
- Matsuoka, H. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:29355.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional EphB6 Products
Product Documents for Human EphB6 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human EphB6 Antibody
For research use only