Human GDF-15 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF957

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala197-Ile308
Accession # Q99988
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human GDF-15 Antibody
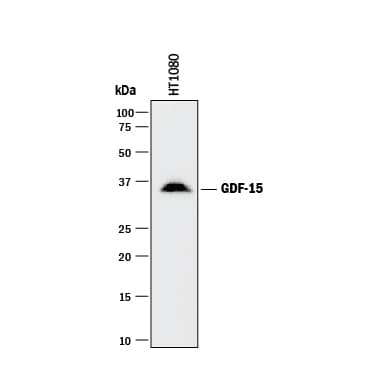
Detection of Human GDF‑15 by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysate of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 0.5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human GDF-15 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF957) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for GDF-15 at approximately 35 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of Human GDF‑15 by Simple WesternTM.
Simple Western lane view shows lysate of HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line, loaded at 0.2 mg/mL. A specific band was detected for GDF-15 at approximately 47 kDa (as indicated) using 5 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human GDF-15 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF957) followed by 1:50 dilution of HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF109). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using the 12-230 kDa separation system.Detection of Human GDF-15 by Western Blot
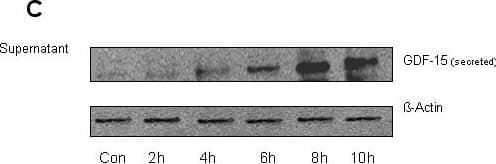
Upregulation of GDF-15 by hypoxia in endothelial cells. Human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMEC) were subjected to hypoxia for various time periods (2 h to 24 h). The mRNA and protein levels of GDF-15 (secreted form) were determined either by quantitative RT-PCR (panel A), immunoradiometric sandwich assay - IRMA (panel B) or Western Blot analysis (panel C). Hypoxia increased GDF-15 expression in a time dependent manner, which was initially detected after 2 hours on mRNA level and after 4 hours on protein level. Data from n = 4 each group are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 compared to control. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21548946), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human GDF-15 Antibody
Simple Western
Sample: HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line
Western Blot
Sample: HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 5 using AF957 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: GDF-15
Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15), also called Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1), placental transforming growth factor-beta, prostate-derived factor, and placental bone morphogenetic protein, is a divergent member of the transforming growth factor beta(TGF-beta) superfamily. GDF-15 is highly expressed in placenta and is expressed at lower levels in kidney, pancreas, prostate and colon. It is also widely expressed in brain. Similar to other TGF-beta family proteins, GDF-15 is synthesized as a large precursor protein that is cleaved at the dibasic cleavage site (RXXR) to release the carboxy-terminal domain. The carboxy-terminal domain of GDF-15 contains the characteristic seven conserved cysteine residues necessary for the formation of the cysteine knot and the single interchain disulfide bond. Furthermore, the carboxy-terminal domain contains two additional cysteine residues that form a fourth intrachain disulfide bond. Biologically active GDF-15 is a disulfide-linked homodimer of the carboxy-terminal 112 amino acid residues. Mature human GDF-15 shares 66.1% and 68.7% amino acid sequence similarity with rat and mouse GDF-15, respectively, which are remarkably low homologies between species in TGF-beta superfamily. GDF-15 has been shown to have various functions, including inhibition of production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages, induction of cartilage formation, early-stage endochonadal bone formation, and promotion of neuronal survival.
References
- Bootcov, M.R. et al. (1997) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:11514.
- Böttner, M. et al. (1999) Gene 237:105.
- Fairlie, W.D. et al. (1998) J. Leukoc. Biol 65:2.
- Fairlie, W.D. et al. (2001) J B.C 20:16911.
- Bauskin, A.R. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19:2212.
- Strelau, J. et al. (2000) J. Neurosci. 20:8597.
- Schober, A. et al. (2001) J. Comp. Neurol. 439:32.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional GDF-15 Products
Product Documents for Human GDF-15 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human GDF-15 Antibody
For research use only