Human Kynureninase Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF4887

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Met1-Asn465
Accession # Q16719
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human Kynureninase Antibody
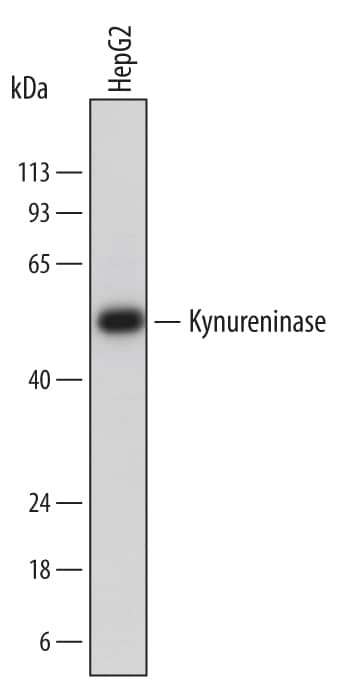
Detection of Human Kynureninase by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Goat Anti-Human Kynureninase Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF4887) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF017). A specific band was detected for Kynureninase at approximately 50 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Applications for Human Kynureninase Antibody
Immunoprecipitation
Sample: Conditioned cell culture medium spiked with Recombinant Human Kynureninase (Catalog # 4887-KH), see our available Western blot detection antibodies
Western Blot
Sample: HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Kynureninase
Kynureninase is a pyridoxal-5 (-phosphate-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolytic cleavage of the amino acids L-kynurenine and L-3-hydroxykynurenine to give either anthranilic acid or 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid and alanine (1). The enzyme is a member of the “kynurenine pathway” enzymes, through which the majority of dietary tryptophan is degraded in the liver, and is involved in the de novo biosynthesis of NAD+ (2, 3). Kynurenine pathway genes are expressed in immune system cells such as macrophages and microglia. During inflammatory responses, the kynurenine pathway in these cells produces quinolinic acid (QA) and not NAD+. QA excites neurons via the activation of NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptors resulting in neuronal damage. The tissue-damaging process has been demonstrated in AIDS-related dementia complex, Alzheimer’s, stroke, epilepsy, and Huntington’s disease. Because Kynureninase is one of the key enzymes of QA production, its inhibitors may be useful for the treatment of neurological disorders. The recombinant Kynureninase has been shown to possess specificity for 3-hydroxykynurenine over kynurenine (4, 5).
References
- Lima, S. et al. (2007) Biochemistry 46:2735.
- Botting, N. P. (1995) Chem. Soc. Rev. 24:401.
- Stone, T. W. (2000) Trends in Pharm. Sci. 21:149.
- Walsh, H. et al. (2002) Eur. J. Chem. 269:2069.
- Toma, S. et al. (1997) FEBS Lett. 408:5.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Kynureninase Products
Product Documents for Human Kynureninase Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human Kynureninase Antibody
For research use only