Human LDLR PE-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB2148P

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala22-Arg788
Accession # P01130
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human LDLR PE-conjugated Antibody
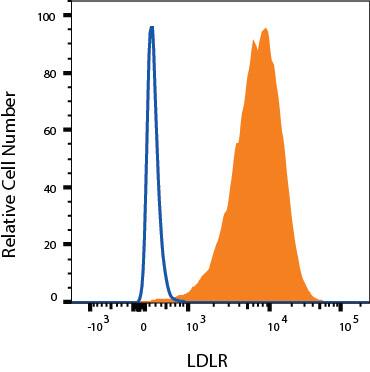
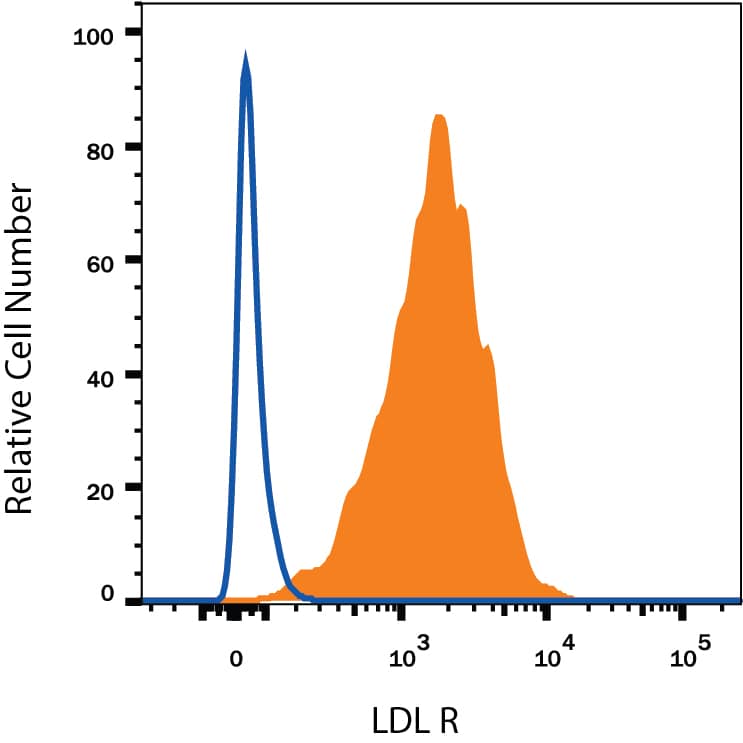
Detection of LDL R in HepG2 Human Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line was stained with Mouse Anti-Human LDL R PE-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB2148P, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (IC002P, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of Human LDLR by Flow Cytometry
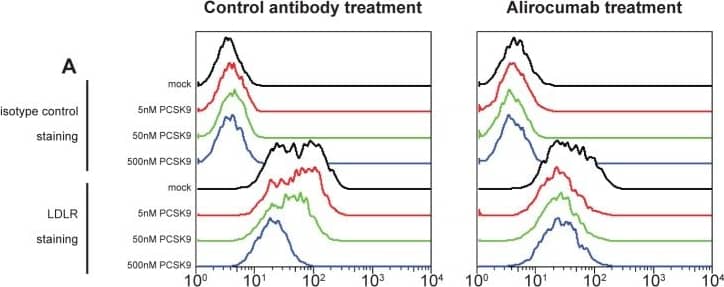
Flow cytometry quantification of surface levels of LDLR (parts A and C) and CD81 (parts B and D) on Huh-7 cells, following incubation with the indicated concentrations of wild-type PCSK9 (parts A and B) or the gain-of-function PCSK9 D374Y mutant (parts C and D) and 300 nM alirocumab (monoclonal antibody to PCSK9; right panels) or isotype control monoclonal antibody (left panels) for 6 hours.LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154498), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Human LDLR by Flow Cytometry
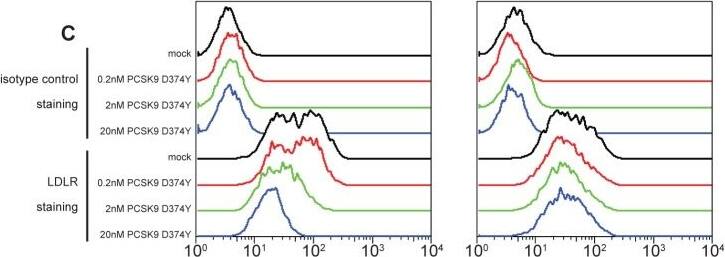
Flow cytometry quantification of surface levels of LDLR (parts A and C) and CD81 (parts B and D) on Huh-7 cells, following incubation with the indicated concentrations of wild-type PCSK9 (parts A and B) or the gain-of-function PCSK9 D374Y mutant (parts C and D) and 300 nM alirocumab (monoclonal antibody to PCSK9; right panels) or isotype control monoclonal antibody (left panels) for 6 hours.LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154498), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Human LDLR PE-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line and U-118-MG human glioblastoma/astrocytoma cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: LDLR
The Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor (LDL R) is the founding member of the LDL R family of scavenger receptors (1, 2). This family contains transmembrane molecules that are characterized by the presence of EGF repeats, complement-like repeats, and YWTD motifs that form beta-propellers. Although members of the family were originally thought to be endocytic receptors, it is now clear that some members interact with adjacent cell-surface molecules, expanding their range of activities (2). Human LDL R is synthesized as an 860 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 21 aa signal sequence, a 767 aa extracellular region, a 22 aa transmembrane segment and a 50 aa cytoplasmic tail (3). The extracellular region is complex. It consists of seven N-terminal complement-like cysteine-rich repeats that bind ligand. Cysteine residues in this region participate in intrachain disulfide bonds. This region is followed by three EGF-like repeats with a beta-propeller YWTD containing motif. The EGF-like repeats are responsible for ligand bonding and dissociation. Finally, there is a 50 aa membrane proximal Ser/Thr-rich region that serves as a carbohydrate attachment point (1, 3, 4). There is extensive O-linked and modest N-linked glycosylation. Thus the receptor’s predicted molecular weight of 93 kDa is increased to a native molecular weight of 120-160 kDa (3, 4). Within the 50 aa cytoplasmic tail, there is an NPXY motif that links the receptor to clathrin pits (1). The extracellular region of human LDL R is 51% aa identical to the extracellular region of human VLDL R, and 79% aa identical to the extracellular region of mouse LDL R. LDL R is constitutively expressed and binds ApoB of LDL and ApoE of VLDL (5). It is responsible for clearing 70% of plasma LDL in liver (5). Mutations in the LDL R gene cause the autosomal dominant disorder, familial hypercholesterolemia (6).
References
- Strickland, D.K. et al. (2002) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 13:66.
- Nykjaer, A. and T.E. Willnow (2002) Trends Cell Biol. 12:273.
- Yamamoto, T. et al. (1984) Cell 39:27.
- Davis, C.G. et al. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261:2828.
- Defesche, J.C. (2004) Semin. Vasc. Med. 4:5.
- Varret, M. et al. (2008) Clin Genet. 73:1.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional LDLR Products
Product Documents for Human LDLR PE-conjugated Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human LDLR PE-conjugated Antibody
For research use only