Human SR-AI/MSR Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB2708


Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Lys77-Leu451
Accession # P21757
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human SR-AI/MSR Antibody
Detection of Human SR‑AI/MSR by Western Blot.
Western blot shows lysates of THP-1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line untreated (-) or treated (+) with 80 nM PMA for 72 hours. PVDF membrane was probed with 1 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-Human SR-AI/MSR Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2708) followed by HRP-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # HAF018). A specific band was detected for SR-AI/MSR at approximately 80 kDa (as indicated). This experiment was conducted under reducing conditions and using Immunoblot Buffer Group 1.Detection of SR-AI/MSR in M2 macrophages cells by Flow Cytometry.
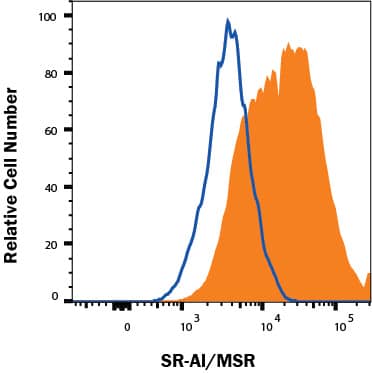
M2 macrophages cells treated with 50 ng/mL Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein (216-MC) for 6 days followed by an overnight polarization with 20 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein (204-IL) and 20 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-13 Protein (213-ILB) were stained with Mouse Anti-Human SR-AI/MSR Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB2708, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # MAB004, open histogram), followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (Catalog # F0102B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human SR-AI/MSR Antibody
CyTOF-reported
Flow Cytometry
Sample: M2 macrophages cells treated with 50 ng/mL Recombinant Human M-CSF Protein (Catalog # 216-MC) for 6 days followed by an overnight polarization with 20 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein (Catalog # 204-IL) and 20 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-13 Protein (Catalog # 213-ILB)
Western Blot
Sample: THP‑1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line treated with PMA
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using MAB2708 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: SR-AI/MSR
The type I class A macrophage scavenger receptor (SR-AI; also MSR-AI) is a 70-80 kDa protein that belongs to the scavenger receptor superfamily (1‑3). Receptors of this family contain characteristic extracellular domains and bind to a series of generally unrelated, but negatively-charged/polyanionic ligands (1, 3). Human SR-AI is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein that is 451 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains a 50 aa cytoplasmic tail, a 26 aa transmembrane segment and a 375 aa extracellular region (4, 5). The extracellular region contains four definitive domains, with a membrane proximal spacer of 33 aa, an alpha-helical coiled-coil domain of 163 aa, a collagen-like domain of 69 aa, and a cysteine-rich C-terminus of 110 aa (4, 6). The cysteine-rich domain (CRD) forms three intrachain disulfide bonds (7). The functional form of the molecule is a 220‑230 kDa membrane-associated trimer that, in human, apparently has two disulfide bonded chains and a third noncovalently associated subunit (8, 9). Human extracellular region is 73% and 72% aa identical to bovine and mouse SR-AI extracellular region, respectively. The human gene for SR-A gives rise to three isoforms; the I isoform of 451 aa, the II isoform of 358 aa, and the III isoform of 388 aa (4, 5, 10). All are identical through the first 344 aa which includes the cytoplasmic tail through the collagenous domain. Isoform II (SR-AII) shows a severe truncation of the CRD, but is expressed on the cell surface. Isoform III (SR-AIII) has a modest truncation of the CRD, and cannot be expressed on the cell surface. However, relative to SR-AI, SR-AII is known to show differential sensitivity to LPS and receptor binding to gram‑negative bacteria (9, 11), while SR-AIII is known to be a dominant-negative isoform (10). SR-AIII may achieve this by either heterotrimerizing with SR-AI, or simply eliminating the production of SR-AI mRNA.
References
- Platt, N. and S. Gordon (2001) J. Clin. Invest. 108:649.
- Linton, M.F. and S. Fazio (2001) Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 12:489.
- Platt, N. and S. Gordon (1998) Chem. Biol. 5:R193.
- Matsumoto, A. et al. (1990) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:9133.
- Emi, M. et al. (1993) J. Biol. Chem. 268:2120.
- Naito, M. et al. (1992) Am. J. Pathol. 141:591.
- Resnick, D. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:26924.
- Ashkenas, J. et al. (1993) J. Lipid Res. 34:983.
- Penman, M. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:23985.
- Gough, P.J. et al. (1998) J. Lipid Res. 39:531.
- Peiser, L. et al. (2000) Inf. Immun. 68:1953.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional SR-AI/MSR Products
Product Documents for Human SR-AI/MSR Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human SR-AI/MSR Antibody
For research use only