Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF1999

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Trp20-Arg184
Accession # Q9QYY7
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antibody
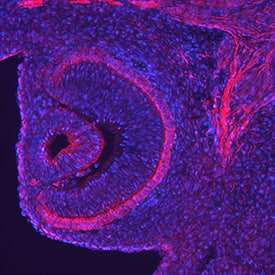
Endocan/ESM‑1 in Mouse Embryo.
Endocan/ESM-1 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (13 d.p.c.) using Goat Anti-Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1999) at 5 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to the retina. View our protocol for Fluorescent IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Cell Adhesion Mediated by Endocan/ESM‑1 and Neutralization by Mouse Endocan/ESM‑1 Antibody.
Recombinant Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 (Catalog # 1999-EC), immobilized onto a microplate, supports the adhesion of the Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Adhesion elicited by Recombinant Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 (25 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1999). The ND50 is typically 1-5 µg/mL.Detection of Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 by Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence
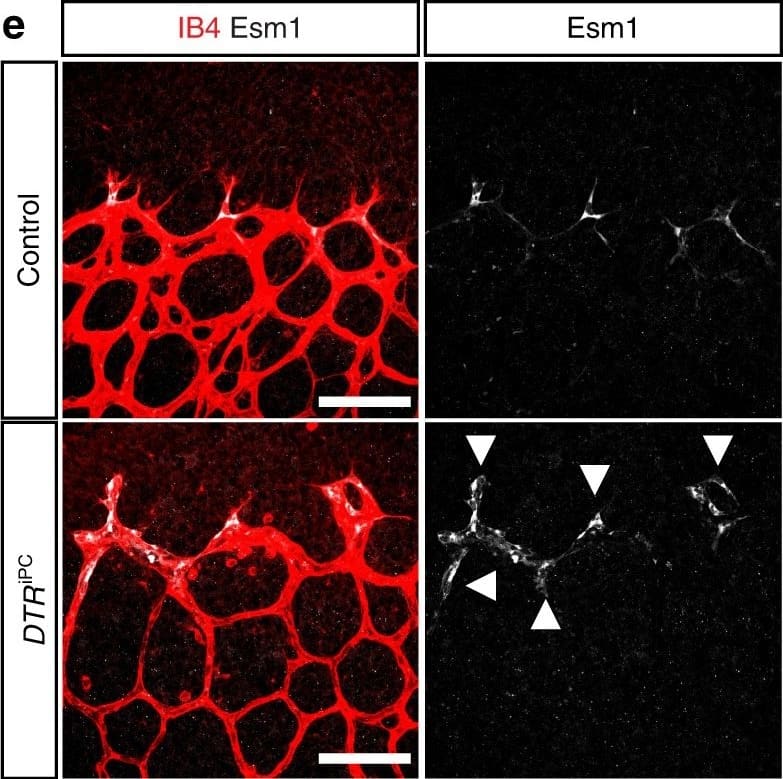
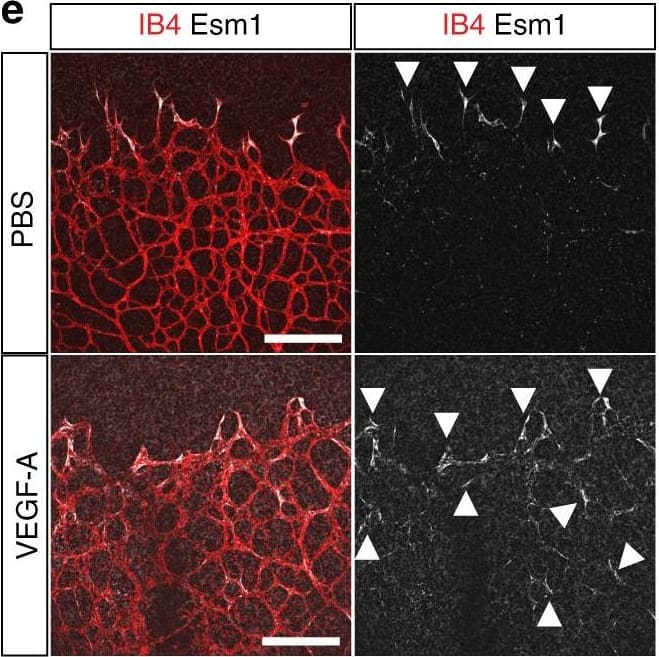
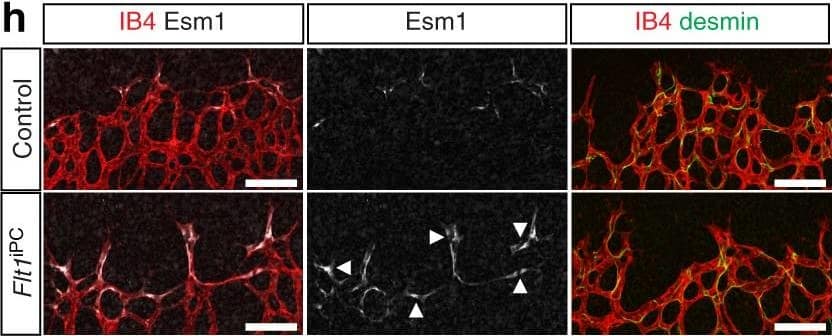
Endothelial changes after pericyte depletion. a–f Maximum intensity projection of confocal images from control and DTRiPC P6 retinas stained for IB4 (red) in combination with VEGF-A a, VEGFR2 b, VEGFR3 c, Tie2 d, Esm1 e, and Dll4 f (all in white), as indicated. Note local increase of VEGFR2, VEGFR3, and Esm1 (arrowheads in b, c, e) but not Tie2 or VEGF-A at the edge of the vessel plexus. Dll4 expression in DTRiPC sprouts is increased in some regions (arrowheads) but absent in others (arrows). Scale bar, 100 µm. g–j Quantitation of VEGF-A immunosignals area and intensity g, signal intensity for VEGFR2 h and VEGFR3 i and proportion of Esm1+ area with respect to vascular area j in the P6 control and DTRiPC angiogenic front. Error bars, s.e.m. p-values, Student’s t-test Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29146905), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample:
Perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (13 d.p.c.)
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 (Catalog # 1999-EC)
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Endocan/ESM-1
Endocan (endothelial cell proteoglycan; also known as endothelial-cell specific molecule-1 [ESM-1]), is a 50 kDa, monomeric, secreted, cysteine-rich proteoglycan identified initially in endothelial cells of the kidney and lung (1). Mouse Endocan is synthesized as a 184 amino acid (aa) precursor that contains a 21 aa signal sequence and a 20 kDa, 163 aa mature region (2). The N-terminal 2/3 of the molecule contains 18 cysteine residues and there are no potential N-linked glycosylation sites. Based on human Endocan, there are at least two potential O-linked glycosylation sites, one of which will likely be utilized on Ser at position # 136 of the mature molecule (3). The posttranslational modification is approximately 30 kDa in size. It consists of a single dermatan sulfate chain that contains 4-O sulfated N-acetyl galactosamine with alpha-iduronate. This chain is suggested to bind HGF and contribute to HGF mitogenic activity (4). Mature mouse Endocan is 96% and 74% aa identical to rat and human Endocan, respectively. In human, there is a potential for an alternate splice variant. It shows a deletion of aa’s 82 through 131, a range which would not remove the dermatan sulfate attachment site (4). It is not known if such a splice form exists in mouse. Endocan is expressed by endothelial cells, adipocytes, bronchial epithelium and distal renal tubular epithelium (1, 5, 6). It is upregulated by TNF-alpha and VEGF, (1, 7) and is known to bind to LFA-1 ( alphaL beta2) on the surface of PBMCs, blocking LFA-1 interaction with ICAM-1 (8). Normal circulating levels of Endocan are approximately 1 ng/mL (6).
References
- Lassalle, P. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:20458.
- Lassalle, P. (1999) Genbank Accession #: Q9QYY7.
- Bechard, D. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:48341.
- Aitkenhead, M. et al. (2002) Microvasc. Res. 63:159.
- Wellner, M. et al. (2003) Horm. Metab. Res. 35:217
- Bechard, D. et al. (2000) J. Vasc. Res. 37:417.
- Tsai, J.C. et al. (2002) J. Vasc. Res. 39:148.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Endocan/ESM-1 Products
Product Documents for Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Endocan/ESM-1 Antibody
For research use only