Mouse IL-13 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF-413-NA


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ser26-Phe131
Accession # P20109
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse IL-13 Antibody
Cell Proliferation Induced by IL‑13 and Neutralization by Mouse IL‑13 Antibody.
Recombinant Mouse IL-13 (413-ML) stimulates proliferation in the TF-1 human erythroleukemic cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Mouse IL-13 (10 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Mouse IL-13 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-413-NA). The ND50 is typically 0.05-0.15 µg/mL.IL‑13 in Mouse Splenocytes.
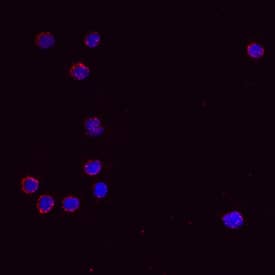
IL-13 was detected in immersion fixed mouse splenocytes using Goat Anti-Mouse IL-13 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF-413-NA) at 10 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.Detection of Mouse IL-13 by Immunohistochemistry
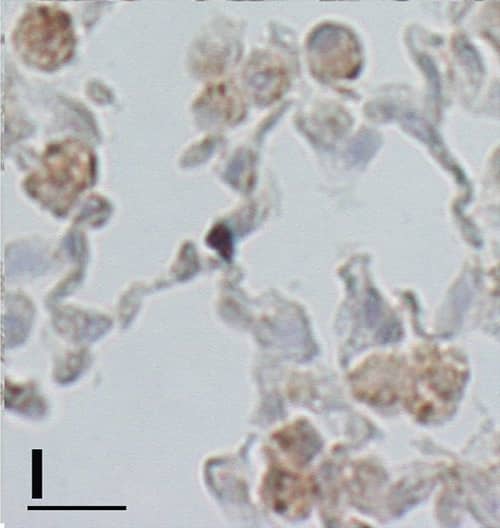
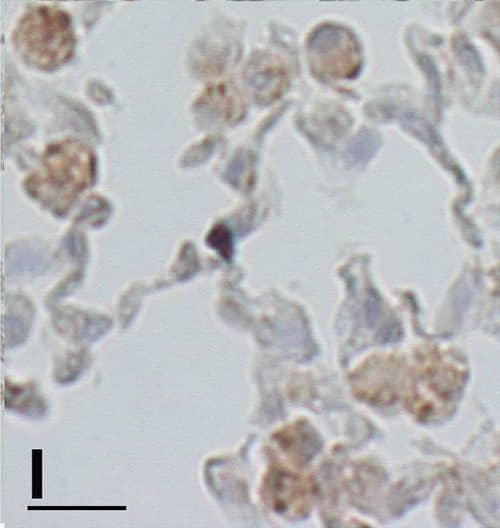
Histological lung sections of a p66Shc−/− mouse at 7 months after CS exposure.(A) Positive immunostaining for MAC-3 confirms that the free alveolar cells are predominantly macrophages. A small number of macrophages are also present in the peribronchiolar infiltrates. (B) Representative lung section showing alveolar multinucleated macrophages containing fine granular brown cytoplasmic particles that stain with Perls’ Prussian blue (C). (D) The peribronchiolar areas of inflammation are characterized by a large amount of lymphocytes and a small number of pigmented cells that also stain with Perl’s Prussian blue (E). (F) Many fascin positive cells (histiocytes) are present in the peribronchiolar areas. (A) and (F): Scale bars = 80 μm; (B-E): Scale bars = 40 μm. Immunohistochemistry of CD4 (G), IL-4 (H), IL-13 (I), Arginase I (J), Chitinase (K) and iNOS (L) in the lung tissue of p66Shc−/− mice at 7 months after CS exposure. In Fig. 4L, a M1 macrophage (iNOS positive)(arrowhead) is present together iNOS negative macrophages. (G-L): Scale bars = 40 μm. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119797), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse IL-13 Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed mouse splenocytes
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse IL-13 (Catalog # 413-ML)
Neutralization
Reviewed Applications
Read 1 review rated 5 using AF-413-NA in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: IL-13
IL-13 is a 17 kDa immunoregulatory cytokine that plays a key role in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma and atopy. It is secreted by Th1 and Th2 CD4+ T cells, NK cells, visceral smooth muscle cells, eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils (1-3). IL-13 circulates as a monomer with two internal disulfide bonds that contribute to a bundled four alpha-helix configuration (4, 5). Mature mouse IL-13 shares 57%, 75%, and 58% amino acid sequence identity with human, rat, and rhesus IL-13, respectively. Despite the low homology, it exhibits cross-species activity between human, mouse, and rat (6, 7). IL-13 has diverse activities on numerous cell types (8). On macrophages, IL-13 suppresses the production of proinflammatory cytokines and other cytotoxic substances. On B cells, IL-13 induces immunoglobulin class switching to IgE, upregulates the expression of MHC class II, CD71, CD72, and CD23, and costimulates proliferation. IL-13 upregulates IL-6 while downregulating IL-1 and TNF-alpha production by fibroblasts and endothelial cells. IL-13 binds with low affinity to IL-13 R alpha1, triggering IL-13 R alpha1 association with IL-4 R alpha. This high affinity receptor complex also functions as the type 2 IL-4 receptor complex (9, 10). Additionally, IL-13 binds with high affinity to IL-13 R alpha2 which is expressed intracellularly, on the cell surface, and as a soluble molecule (11-14). IL-13 R alpha2 regulates the bioavailability of both IL-13 and IL-4 and is overexpressed in glioma and several bronchial pathologies (10, 15, 16). Compared to wild type IL-13, the atopy-associated R110Q variant of IL-13 elicits increased responsiveness from eosinophils that express low levels of IL-13 R alpha2 (17).
References
- Wills-Karp, M. (2004) Immunol. Rev. 202:175.
- Nakajima, H. and K. Takatsu (2007) Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 142:265.
- Brown, K.D. et al. (1989) J. Immunol. 142:679.
- Moy, F.J. et al. (2001) J. Mol. Biol. 310:219.
- Eisenmesser, E.Z. et al. (2001) J. Mol. Biol. 310:231.
- Ruetten, H. and C. Thiemermann (1997) Shock 8:409.
- Lakkis, F.G. et al. (1997) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235:529.
- Wynn, T.A. (2003) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21:425.
- Andrews, A.L. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:46073.
- Tabata, Y. et al. (2007) Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 7:338.
- Chiaramonte, M.G. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 197:687.
- Daines, M.O. and G.K. Hershey (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 227:10387.
- Matsumura, M. et al. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 360:464.
- Tabata, Y. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 177:7905.
- Andrews, A.L. et al. (2006) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 118:858.
- Joshi, B.H. et al. (2006) Vitam. Horm. 74:479.
- Andrews, A-L. et al. (2007) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 120:91.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IL-13 Products
Product Documents for Mouse IL-13 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse IL-13 Antibody
For research use only