Mouse IL-4 MAb (Clone 30340)
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB404

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
His23-Ser140
Accession # P07750
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Mouse IL-4 MAb (Clone 30340)
Cell Proliferation Induced by IL-4 and Neutralization by Mouse IL-4 Antibody.
Recombinant Mouse IL-4 (Catalog # 404-ML) stimulates proliferation in the HT-2 mouse T cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Proliferation elicited by Recombinant Rat Anti-Mouse IL-4 (7.5 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Rat Anti-Mouse IL-4 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB404). The ND50 is typically 0.1-0.6 µg/mL.Detection of Mouse IL-4 by Flow Cytometry
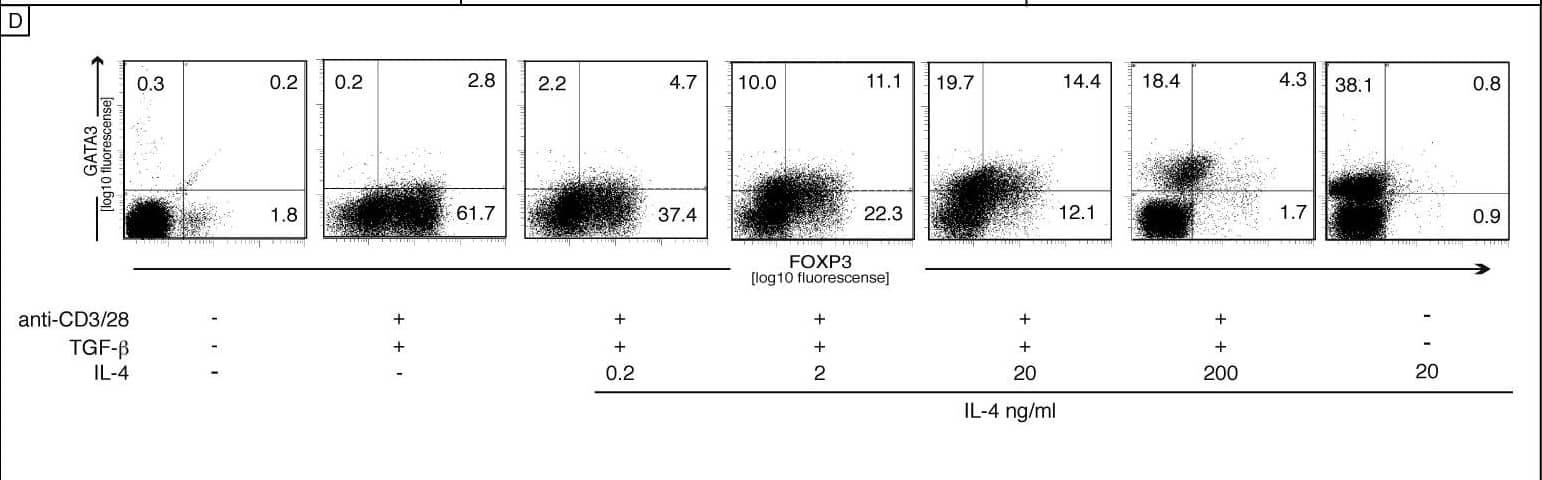
Effect of IL-4 on FOXP3 Induction(A) A statistical analysis was performed with six donors on day 5 (TGF-beta (10 ng/ml) and with or without IL-4 (100 ng/ml)); Shown is the mean, and error bars indicated the SD of six donors. Statistical analysis was performed using the Dunnett test. Statistical significance is indicated by asterisks (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, Dunnett).(B) CD4+CD45RA+ cells were activated in the presence of a constant concentration of TGF-beta (5 ng/ml) with an increasing concentration of IL-4, as indicated. Cells were harvested for mRNA quantification after 5 d.(C) CD4+CD45RA+ cells were stimulated in vitro with plate-bound anti-CD3/CD28, TGF-beta (10ng/ml), and IL-4 (100 ng/ml) as indicated. After 1 h, cell lysates were prepared and analyzed by Western blot for phosphorylated SMAD2 and STAT6. Total STAT6 and GAPDH served as internal control.(D) Intracellular GATA3 and FOXP3 staining are shown after exposure of CD4+CD45RA+ T cells to IL-4 as described for panel B. Data are representative of three independent experiments. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18162042), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse IL-4 MAb (Clone 30340)
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse IL-4 (Catalog # 404-ML)
under non-reducing conditions only
Neutralization
Mouse IL-4 Sandwich Immunoassay
Reviewed Applications
Read 2 reviews rated 5 using MAB404 in the following applications:
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: IL-4
Interleukin-4 (IL-4), also known as B cell-stimulatory factor-1, is a monomeric, approximately 13-18 kDa Th2 cytokine that shows pleiotropic effects during immune responses (1‑4). It is a glycosylated polypeptide that contains three intrachain disulfide bridges and adopts a bundled four alpha-helix structure (5). Mouse IL-4 is synthesized with a 24 amino acid (aa) signal sequence. Mature mouse IL-4 shares 39%, 39%, and 59% aa sequence identity with bovine, human, and rat IL-4, respectively. Human, mouse, and rat IL-4 are species-specific in their activities (6-8). IL-4 exerts its effects through two receptor complexes (9, 10). The type I receptor, which is expressed on hematopoietic cells, is a heterodimer of the ligand binding IL-4 R alpha and the common gamma chain (a shared subunit of the receptors for IL-2, -7, -9, -15, and -21). The type II receptor on nonhematopoietic cells consists of IL-4 R alpha and IL-13 R alpha1. The type II receptor also transduces IL-13 mediated signals. IL-4 is primarily expressed by Th2-biased CD4+ T cells, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils (1, 2). It promotes cell proliferation, survival, and immunoglobulin class switch to IgG1 and IgE in mouse B cells, acquisition of the Th2 phenotype by naïve CD4+ T cells, priming and chemotaxis of mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils, and the proliferation and activation of epithelial cells (11‑14). IL-4 plays a dominant role in the development of allergic inflammation and asthma (13, 15).
References
- Benczik, M. and S.L. Gaffen (2004) Immunol. Invest. 33:109.
- Chomarat, P. and J. Banchereau (1998) Int. Rev. Immunol. 17:1.
- Lee, F. et al. (1986) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83:2061.
- Noma, Y. et al. (1986) Nature 319:640.
- Redfield, C. et al. (1991) Biochemistry 30:11029.
- Ramirez, F. et al. (1988) J. Immunol. Meth. 221:141.
- Leitenberg, D. and T.L. Feldbush (1988) Cell. Immunol. 111:451.
- Mosman, T.R. et al. (1987) J. Immunol. 138:1813.
- Mueller, T.D. et al. (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1592:237.
- Nelms, K. et al. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:701.
- Paludan, S.R. (1998) Scand. J. Immunol. 48:459.
- Corthay, A. (2006) Scand. J. Immunol. 64:93.
- Ryan, J.J. et al. (2007) Crit. Rev. Immunol. 27:15.
- Grone, A. (2002) Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 88:1.
- Rosenberg, H.F. et al. (2007) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119:1303.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IL-4 Products
Product Documents for Mouse IL-4 MAb (Clone 30340)
Product Specific Notices for Mouse IL-4 MAb (Clone 30340)
For research use only