Porcine TNF-alpha Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF690


Key Product Details
Validated by
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Arg78-Leu232
Accession # P23563
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Porcine TNF-alpha Antibody
Cytotoxicity Induced by TNF-alpha and Neutralization by Porcine TNF-alpha Antibody.
Recombinant Porcine TNF-a (Catalog # 690-PT) induces cytotoxicity in the the PK-15 porcine kidney epithelial cell line in a dose-dependent manner (orange line), as measured by crystal violet staining. Cytotoxicity elicited by Recombinant Porcine TNF-a (0.05 ng/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Porcine TNF-a Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF690). The ND50 is typically 0.2-0.8 µg/mL in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D (1 µg/mL).TNF‑ alpha in Porcine PBMCs.
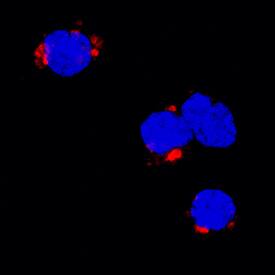
TNF-a was detected in immersion fixed porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) treated with calcium ionomycin and PMA using Goat Anti-Porcine TNF-a Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF690) at 15 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL001) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Non-adherent Cells.Detection of Porcine TNF-alpha by Western Blot
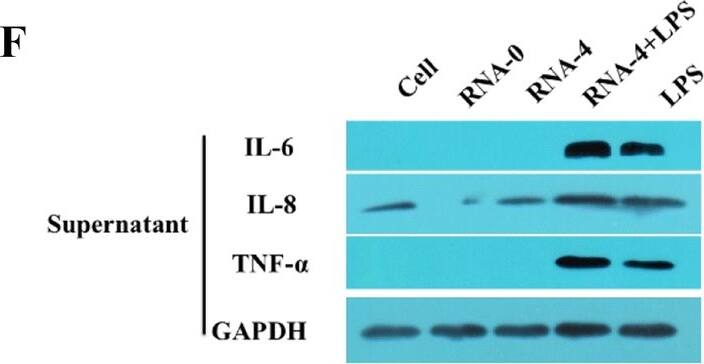
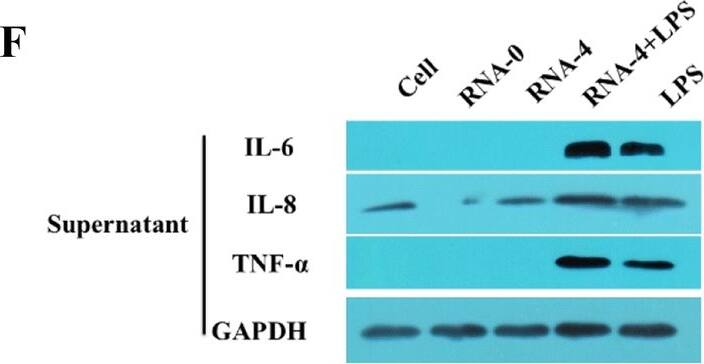
Inflammatory response in PAMs induced by PRRSV 5′UTR RNA and LPS. A, B PAMs were transfected with different doses of 5′UTR RNA (1, 2, and 4 μg/well) along with 1 μg/mL LPS. qRT-PCR and Western blot results showed that compared with PAMs in other groups, PAMs in the 4 μg 5′UTR RNA and 1 μg/mL LPS co-stimulation group produced higher levels of IL-1 beta (p < 0.05). C After co-stimulation, the relative expression level of IL-1 beta mRNA obtained was similar at the 12 and 24 h time-points. D 5′UTR RNA and LPS co-stimulation induced IL-1 beta expression in cells and supernatants. E, F 5′UTR RNA and LPS co-stimulation induced increased levels of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-alpha mRNA and protein. Expression was normalized to that of GAPDH. Different letters (a, b, c, d, and e) on data indicate significant differences between groups (p < 0.05). Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31300043), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Porcine TNF-alpha Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed porcine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) treated with calcium ionomycin and PMA
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Porcine TNF-alpha (Catalog # 690-PT)
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: TNF-alpha
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), also known as cachectin and TNFSF2, is the prototypic ligand of the TNF superfamily. It is a pleiotropic molecule that plays a central role in inflammation, apoptosis, and immune system development. TNF-alpha is produced by a wide variety of immune and epithelial cell types (1, 2). Porcine TNF-alpha consisits of a 35 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 176 aa extracellular domain (ECD) (3). Within the ECD, porcine TNF-alpha shares 69%‑86% aa sequence identity with bovine, canine, cotton rat, equine, feline, human, mouse, rat, and rhesus TNF-alpha. The 26 kDa type 2 transmembrane protein is assembled intracellularly to form a noncovalently linked homotrimer (4). Ligation of this complex induces reverse signaling that promotes lymphocyte costimulation but diminishes monocyte responsiveness (5). Cleavage of membrane bound TNF-alpha by TACE/ADAM17 releases a 55 kDa soluble trimeric form of TNF-alpha (6, 7). TNF-alpha trimers bind the ubiquitous TNF RI and the hematopoietic cell-restricted TNF RII, both of which are also expressed as homotrimers (1, 8). TNF-alpha regulates lymphoid tissue development through control of apoptosis (2). It also promotes inflammatory responses by inducing the activation of vascular endothelial cells and macrophages (2). TNF-alpha is a key cytokine in the development of several inflammatory disorders (9). It contributes to the development of type 2 diabetes through its effects on insulin resistance and fatty acid metabolism (10, 11).
References
- Idriss, H.T. and J.H. Naismith (2000) Microsc. Res. Tech. 50:184.
- Hehlgans, T. and K. Pfeffer (2005) Immunology 115:1.
- Pauli, U. et al. (1989) Gene 81:185.
- Tang, P. et al. (1996) Biochemistry 35:8216.
- Eissner G. et al. (2004) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:353.
- Black, R.A. et al. (1997) Nature 385:729.
- Moss, M.L. et al. (1997) Nature 385:733.
- Loetscher, H. et al. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266:18324.
- Clark, I.A. (2007) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 18:335.
- Romanatto, T. et al. (2007) Peptides 28:1050.
- Hector, J. et al. (2007) Horm. Metab. Res. 39:250.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional TNF-alpha Products
Product Documents for Porcine TNF-alpha Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Porcine TNF-alpha Antibody
For research use only