SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB11294

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
SARS-CoV-2
Applications
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction, Immunocytochemistry, Neutralization
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG1 Clone # 1049417
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Human embryonic kidney cell, HEK293-derived sars-cov-2 Spike S1 Subunit protein
Val16-Pro681
Accession # YP_009724390.1
Val16-Pro681
Accession # YP_009724390.1
Specificity
Detects SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD in ELISA.
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG1
Scientific Data Images for SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody
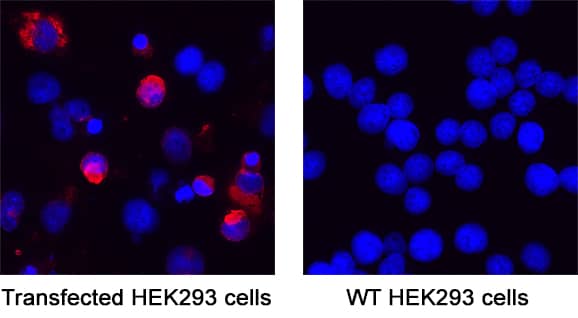
Detection of Spike RBD in Transfected & Wild Type HEK293 Human Embryonic Kidney Cell Line.
Spike RBD was detected in immersion fixed Transfected & absent in Wild Type HEK293 Human Embryonic Kidney Cell Line using Mouse Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB11294) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red; Catalog # NL007) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Cells on Coverslips.SARS-CoV-2 variant protein (named 20A.EU2) binding to ACE-2-transfected Human Cell Line is Blocked by SARS2-20A.EU2 S1 Antibody.
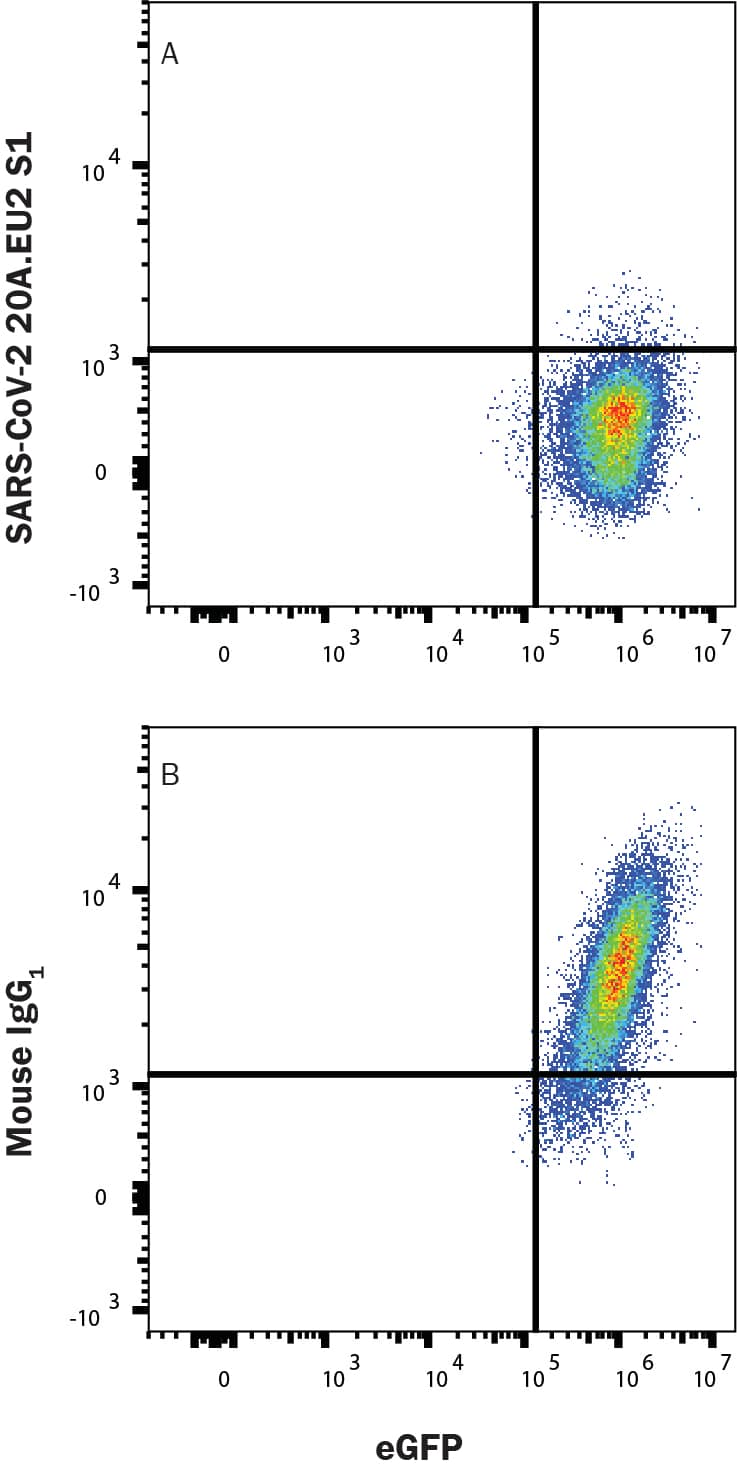
In a functional flow cytometry test, Recombinant SARS-CoV2 20A.EU2 S1 His-tagged protein (10780-CV) binds to HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with recombinant human ACE-2 and eGFP. (A) Binding is completely blocked by 25 µg/mL of Mouse Anti-SARS2-20A.EU2 S1 Antibody (Catalog # MAB11294) but not by (B) Mouse IgG1 Isotype Control (MAB002). Protein binding was detected with Mouse Anti-His APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (IC050A). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane-associated Proteins protocol.Applications for SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody
Application
Recommended Usage
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
In a functional flow cytometry test, 25 μg/mL of MsxSARS2-20A.EU2 S1 Antibody (Catalog # MAB11294) will block the binding of Recombinant SARS-CoV2 20A.EU2 S1 Protein (Catalog # 10780-CV) to HEK293 human embryonic kidney cell line transfected with recombinant human ACE-2.
Immunocytochemistry
8-25 µg/mL
Sample: Immersion fixed Transfected & Wild Type HEK293 Human Embryonic Kidney Cell Line
Sample: Immersion fixed Transfected & Wild Type HEK293 Human Embryonic Kidney Cell Line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein A or G purified from hybridoma culture supernatant
Reconstitution
Reconstitute at 0.5 mg/mL in sterile PBS. For liquid material, refer to CoA for concentration.
Formulation
Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. *Small pack size (SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Shipping
Lyophilized product is shipped at ambient temperature. Liquid small pack size (-SP) is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Spike RBD
References
- Wu, F. et al. (2020) Nature 579:265.
- Tortorici, M.A. and D. Veesler (2019) Adv. Virus Res. 105:93.
- Bosch, B.J. et al. (2003). J. Virol. 77:8801.
- Belouzard, S. et al. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106:5871.
- Millet, J.K. and G.R. Whittaker (2015) Virus Res. 202:120.
- Ortega, J.T. et al. (2020) EXCLI J. 19:410.
- Yuan, Y. et al. (2017) Nat. Commun. 8:15092.
- Tai, W. et al. (2020) Cell. Mol. Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2020.03.007.
- Wang, X. et al. (2020) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-020-0424-9.
- Wang, K. et al. (2020) bioRxiv https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.03.14.988345v1.
- Hodcroft, E.B. et al. (2020) medRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.25.20219063.
Long Name
Spike Receptor Binding Domain
Gene Symbol
S
UniProt
Additional Spike RBD Products
Product Documents for SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody
Product Specific Notices for SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD Antibody
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...