VEGF Antibody (VG1) - Azide and BSA Free
Novus Biologicals, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # NBP2-81007


Conjugate
Catalog #
Forumulation
Catalog #
Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine, Canine
Applications
CyTOF-ready, ELISA, Flow Cytometry, Immunocytochemistry, Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunohistochemistry-Frozen, Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin, Western Blot
Label
Unconjugated
Antibody Source
Monoclonal Mouse IgG1 kappa Clone # VG1
Format
Azide and BSA Free
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Recombinant VEGF 189 protein.
Clonality
Monoclonal
Host
Mouse
Isotype
IgG1 kappa
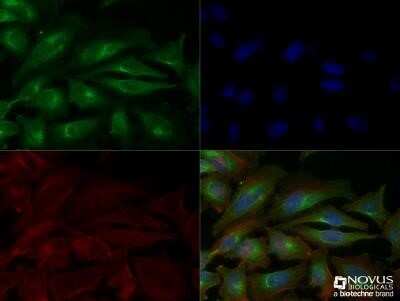
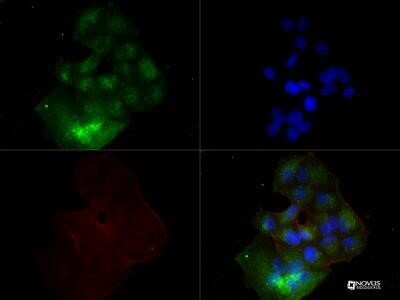
Scientific Data Images for VEGF Antibody (VG1) - Azide and BSA Free
Western Blot Analysis of VEGF in Transfected Cell Lines
HUVEC and 293T cells transfected with a plasmid expressing human VEGF165 at 1:1000. Image provided by verified customer review. Image from the standard format of this antibody.Immunohistochemical Analysis of VEGF in Paraffin Embedded Human Angiosarcoma Tissue
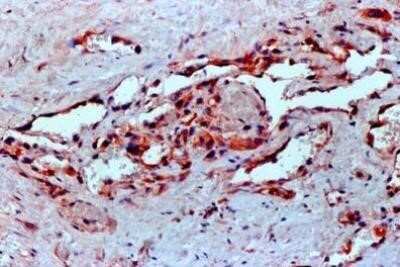
FFPE human angiosarcoma tissue section using VEGF antibody (clone VG1). The endothelial cells of the blood vessels and most of the cancer cells showed strong positivity for VEGF protein. Image from the standard format of this antibody.Flow Cytometry of HUVEC Cells Stained with PerCP Conjugated VEGF Antibody
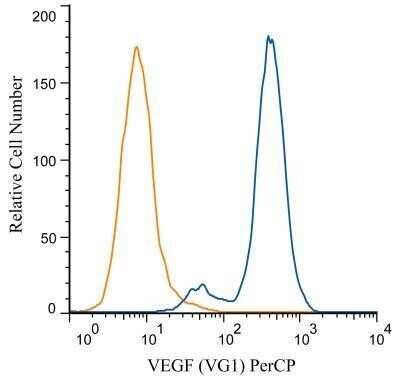
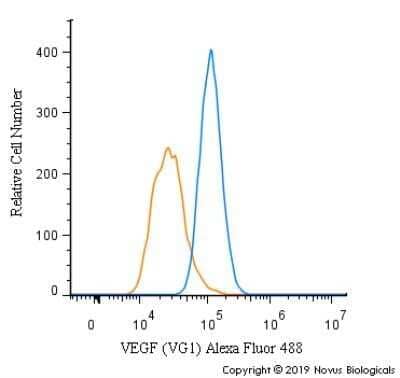
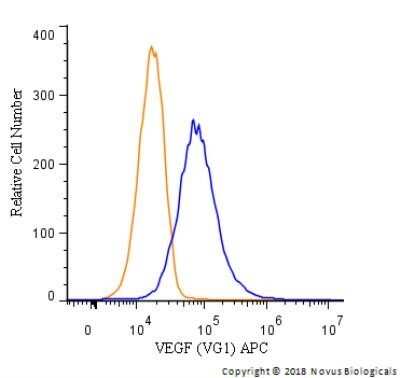
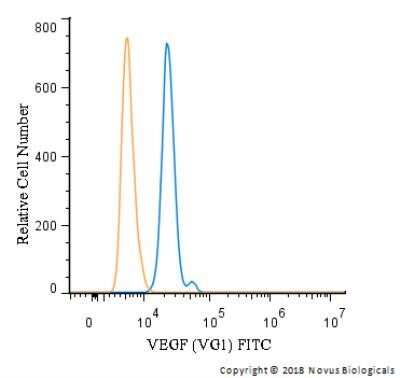
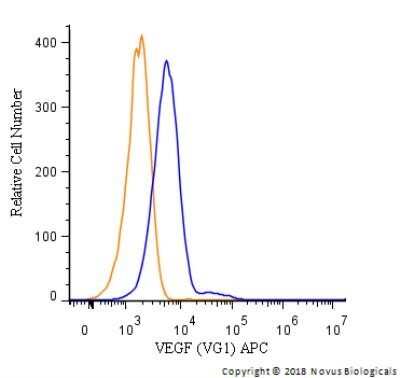
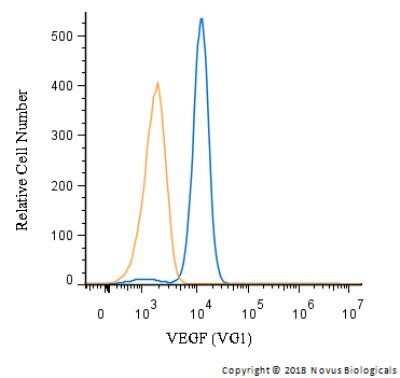
Analysis of PerCP conjugate of NB100-664. An intracellular stain was performed on HUVEC cells with VEGF (VG1) antibody NB100-664PCP (blue) and a matched isotype control NBP2-27287PCP (orange). Cells were fixed with 4% PFA and then permeablized with 0.1% saponin. Cells were incubated in an antibody dilution of 10 ug/mL for 30 minutes at room temperature. Both antibodies were directly conjugated to PerCP.Applications for VEGF Antibody (VG1) - Azide and BSA Free
Application
Recommended Usage
Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence
1:10 - 1:500
Immunohistochemistry
1:20 - 1:100
Immunohistochemistry-Frozen
1:20 - 1:100
Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin
1:20 - 1:100
Western Blot
1 - 2 ug/ml
Application Notes
In IHC a dilution of 1:20-1:50 was used in an ABC method. However, depending on the staining conditions employed, we suggest that the final dilution should be determined by the user. We suggest an incubation period of 30-60 minutes at room temperature. High temperature treatment of formalin-fixed tissue sections using 1mM EDTA, pH 8.0 must be performed prior to the immunostaining. This antibody is CyTOF ready.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Protein G purified
Formulation
PBS
Format
Azide and BSA Free
Preservative
No Preservative
Concentration
1 mg/ml
Shipping
The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below.
Stability & Storage
Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Background: VEGF
References
1. Melincovici CS, Bosca AB, susman S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2018;59(2):455-467.
2. Shaik F, Cuthbert GA, Homer-Vanniasinkam S, Muench SP, Ponnambalam S, Harrison MA. Structural Basis for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Activation and Implications for Disease Therapy. Biomolecules. 2020;10(12):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121673
3. Apte RS, Chen DS, Ferrara N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.021
4. Matsumoto K, Ema M. Roles of VEGF-A signalling in development, regeneration, and tumours. J Biochem. 2014;156(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvu031
5. Itatani Y, Kawada K, Yamamoto T, Sakai Y. Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in Cancer-Alterations to Anti-VEGF Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1232. Published 2018 Apr 18. doi:10.3390/ijms19041232
6. Uniprot (P15692)
7. Hamilton JL, Nagao M, Levine BR, Chen D, Olsen BR, Im HJ. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2828
Long Name
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
Alternate Names
MVCD1, VAS, Vasculotropin, VEGF-A, VEGFA, VPF
Gene Symbol
VEGFA
Additional VEGF Products
Product Documents for VEGF Antibody (VG1) - Azide and BSA Free
Product Specific Notices for VEGF Antibody (VG1) - Azide and BSA Free
This product is for research use only and is not approved for use in humans or in clinical diagnosis. Primary Antibodies are guaranteed for 1 year from date of receipt.
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...