Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 Protein Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 623-AN

Key Product Details
Source
Accession #
Structure / Form
Conjugate
Applications
Product Specifications
Source
Tyr19-Phe496, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
0.2 μg/mL of Recombinant Human Angiopoietin‑2 significantly induces phosphorylation of human Tie-2.
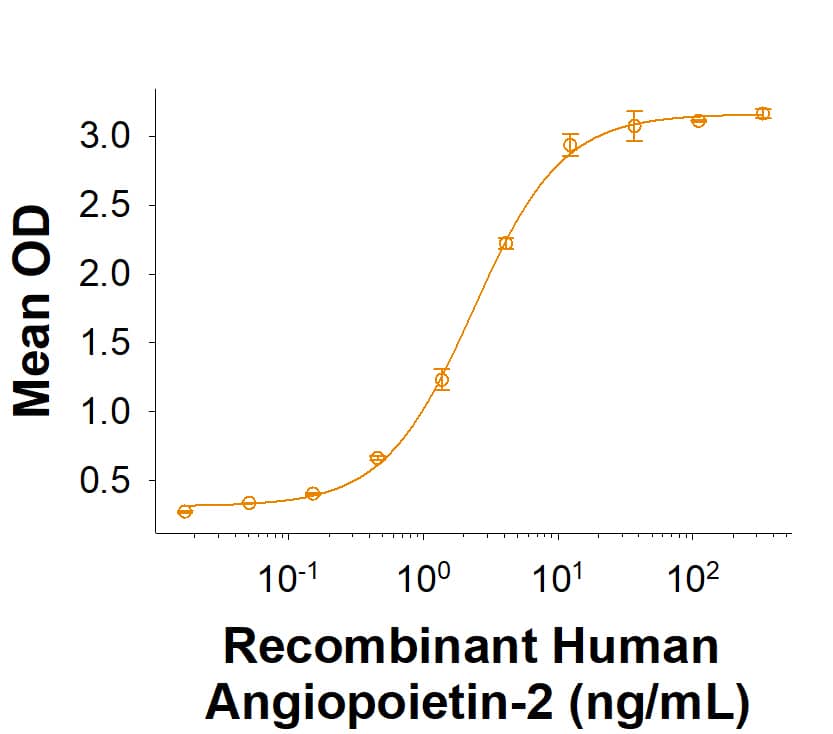
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
When Recombinant Human Tie-2 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 313-TI) is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Human Angiopoietin‑2 (Catalog # 623-AN) binds with an ED50 of 0.5-4 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 5 reviews rated 4.8 using 623-AN in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 Protein
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 Protein Binding Activity
When Recombinant Human Tie-2 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 313-TI) is immobilized at 0.5 µg/mL (100 µL/well), Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (Catalog # 623-AN) binds with an ED50 of 0.5-4 ng/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 623-AN
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MOPS, NaCl, CHAPS and PEG with BSA as a carrier protein and Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 623-AN/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MOPS, NaCl, CHAPS and PEG with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Angiopoietin-2
Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2; also ANGPT2) is a secreted glycoprotein that plays a complex role in angiogenesis and inflammation (1, 2). Mature Ang-2 is 478 amino acids (aa) in length. It contains one coiled‑coil domain (aa 166-248) that mediates multimerization, and a C-terminal fibrinogen-like domain (aa 275-495) that mediates receptor binding. Under reducing conditions, secreted monomeric Ang-2 is 65-66 kDa in size. Under non‑reducing conditions, both natural and recombinant Ang-2 form 140 kDa dimers, 200 kDa trimers, and 250-300 kDa tetramers and pentamers (3-6). Alternate splicing generates a short isoform that lacks 52 amino acids (aa) preceding the coiled‑coil domain (4). Mature human Ang-2 shares 86% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat Ang-2. Ang-2 is widely expressed during development, but it is restricted postnatally to highly angiogenic tissues such as the placenta, ovaries, and uterus (3). It is particularly abundant in vascular endothelial cells (EC) where it is stored in intracellular Weibel-Palade bodies (1, 3, 7). Both Ang-2 and the related Angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) are ligands for the receptor tyrosine kinase Tie-2 (2). While Ang-1 is a potent Tie‑2 agonist, Ang-2 may act as either a Tie-2 antagonist or agonist, depending upon its state of multimerization. The higher the order of oligomer, the more effective Ang-2 becomes as a Tie-2 agonist (3, 8‑11). The short isoform appears to block the binding of either Ang-1 or full-length Ang-2 to Tie-2 (4). Ang-2 functions as a pro-angiogenic factor, although it can also induce EC death and vessel regression (12, 13). Upon its release from quiescent EC, it regulates vascular remodeling by promoting EC survival, proliferation, and migration and destabilizing the interaction between EC and perivascular cells (8, 13, 14). Ang-2 is required for postnatal vascular remodeling, and it cooperates with Ang-1 during lymphatic vessel development (7, 15). It mediates the up‑regulation of ICAM‑1 and VCAM‑1 on EC, which facilitates the adhesion of leukocytes during inflammation (16). Ang-2 is up‑regulated in both the endothelium and tumor cells of several cancers as well as in ischemic tissue (17-20). Its direct interaction with Integrins promotes tumor cell invasion (21, 22). Ang-2 also promotes the neuronal differentiation and migration of subventricular zone progenitor cells (20).
References
- Augustin, H.G. et al. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10:165.
- Murdoch, C. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:7405.
- Maisonpierre, P.C. et al. (1997) Science 27:55.
- Kim, I. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:18550.
- Procopio, W.N. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:30196.
- Kim, K-T. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:20126.
- Gale, N.W. et al. (2002) Dev. Cell 3:411.
- Yuan, H.T. et al. (2009) Mol. Cell. Biol. 29:2011.
- Falcon, B.L. et al. (2009) Am. J. Pathol. 175:2159.
- Kim, H-Z. et al. (2009) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1793:772.
- Kim, I. et al. (2001) Cardiovasc. Res. 49:872.
- Lobov, I.B. et al. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99:11205.
- Cao, Y. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:3835.
- Nasarre, P. et al. (2009) Cancer Res. 69:1324.
- Dellinger, M. et al. (2008) Dev. Biol. 319:309.
- Fiedler, U. et al. (2006) Nat. Med. 12:235.
- Koga, K. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:6248.
- Etoh, T. et al. (2001) Cancer Res. 61:2145.
- Tressel, S.L. et al. (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:1989.
- Liu, X.S. et al. (2009) J. Biol. Chem. 284:22680.
- Hu, B. et al. (2006) Cancer Res. 66:775.
- Imanishi, Y. et al. (2007) Cancer Res. 67:4254.
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Angiopoietin-2 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 Protein
For research use only