Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 (108-261), Animal-Free
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AFL617

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Glu108-Leu261, with an N-terminal Met
Produced using non-animal reagents in an animal-free laboratory.
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
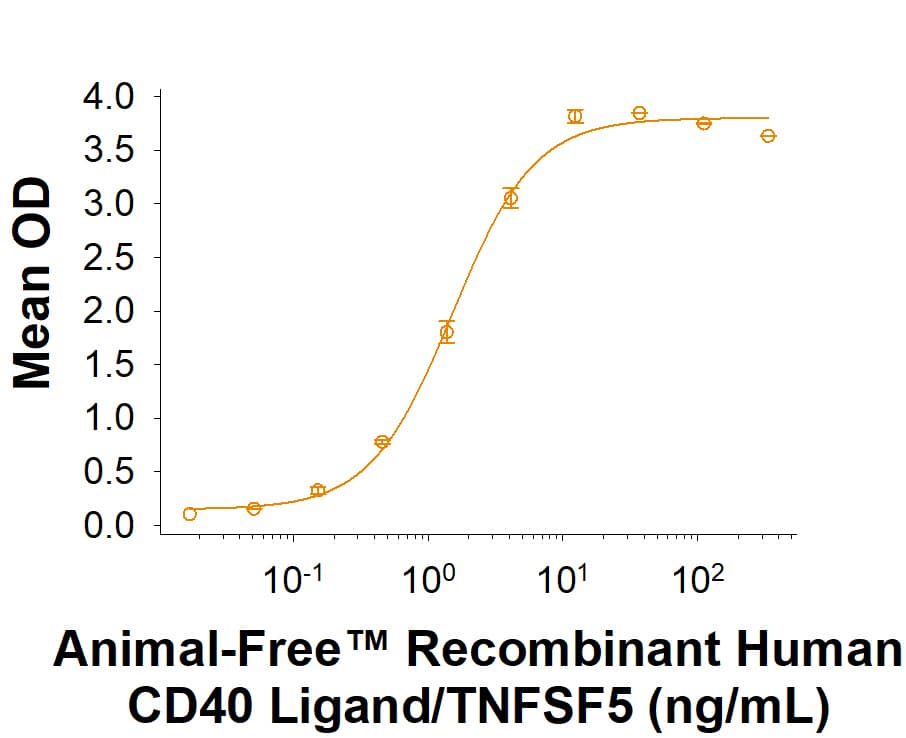
Animal-Free™ Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 aa 108‑261 (Catalog # AFL617) binds to Recombinant Human CD40/TNFRSF5 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 1493-CDB) with an ED50 of 0.300-3.60 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 (108-261), Animal-Free
Animal-Free™ Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 (aa 108‑261) Protein Binding Activity.
In a functional ELISA, Animal-Free™ Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 (aa 108-261) (Catalog # AFL617) binds to Recombinant Human CD40/TNFRSF5 Fc Chimera (1493-CDB) with an ED50 of 0.300-3.60 ng/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AFL617
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in NaH2PO4, NaCl and EDTA. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.2 mg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5
CD40 Ligand, also known as TNFSF, CD154, TRAP, and gp39, is a 34-39 kDa type II transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the TNF superfamily (1-3). Mature human CD40 Ligand consists of a 22 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a transmembrane segment, and an 215 aa extracellular region (4, 5). The extracellular domain of human CD40 Ligand shares 74% and 76% aa sequence identity with mouse and rat CD40 Ligand, respectively. Similar to other TNF superfamily members, CD40 Ligand forms a bioactive homotrimer, both as membrane bound and soluble forms (6-9). The 18 kDa soluble form (aa 113-261) arises from proteolytic processing. Mutation and alternative splicing generate additional forms of CD40 Ligand that are often truncated or non-trimerizable (8). CD40 Ligand is expressed on platelets, as well as on activated T cells and B cells, basophils, eosinophils, fibroblasts, mast cells, monocytes, natural killer cells, vascular endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells. CD40 Ligand binds to CD40, which is expressed on the surface of B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, platelets, endothelial, and epithelial cells (10). The interaction of CD40 Ligand with CD40 initiates signaling in both CD40 and CD40 Ligand expressing cells (11). CD40 ligation by CD40 Ligand promotes B cell activation and T cell-dependent humoral responses (12, 13). CD40 Ligand dysregulation on T cells and antigen presenting cells contributes to the immune deficiency associated with HIV infection and AIDS (14, 15). It is also implicated in the pathology of multiple cardiovascular diseases including atherosclerosis, atherothrombosis, and restenosis (16, 17).
References
- Zhang, G. (2004) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 14:154.
- Hehlgans, T. and K. Pfeffer (2005) Immunology 115:1.
- Quezada, S.A. et al. (2004) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:307.
- Graf, D. et al. (1992) Eur. J. Immunol. 22:3191.
- Hollenbaugh, D. et al. (1992) EMBO J. 11:4313.
- Khandekar, S.S. et al. (2001) Protein Expr. Purif. 23:301.
- Pietravalle, F. et al. (1996) J. Biol. Chem. 271:5965.
- Garber, E. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274:33545.
- Vakkalanka, R.K. et al. (1999) Arthritis Rheum. 42:871.
- van Kooten, C. and J. Banchereau (1997) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 9:330.
- Eissner, G. et al. (2004) Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 15:353.
- Rickert, R.C. et al. (2011) Immunol. Rev. 244:115.
- Elgueta, R. et al. (2009) Immunol. Rev. 229:152.
- Kornbluth, R.S. (2000) J. Leukoc. Biol. 68:373.
- Chougnet, C. (2003) J. Leukoc. Biol. 74:702.
- Pamukcu, B. et al. (2011) Ann. Med. 43:331.
- Hassan, G.S. et al. (2012) Immunobiology 217:521.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Products
- All Products for CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 cDNA Clones
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 ELISA Kits
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Luminex Assays
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Lysates
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Primary Antibodies
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Proteins and Enzymes
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Simple Plex
- CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 Small Molecules and Peptides
Product Documents for Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 (108-261), Animal-Free
Manufacturing Specifications
Animal-Free Manufacturing ConditionsOur dedicated controlled-access animal-free laboratories ensure that at no point in production are the products exposed to potential contamination by animal components or byproducts. Every stage of manufacturing is conducted in compliance with R&D Systems' stringent Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). Production and purification procedures use equipment and media that are confirmed animal-free.
Production
- All molecular biology procedures use animal-free media and dedicated labware.
- Dedicated fermentors are utilized in committed animal-free areas.
Purification
- Protein purification columns are animal-free.
- Bulk proteins are filtered using animal-free filters.
- Purified proteins are stored in animal-free containers in a dedicated cold storage room.
- Low Endotoxin Level.
- No impairment of biological activity.
- High quality product obtained under stringent conditions.
- For ex vivo research or bioproduction, additional documentation can be provided.
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human CD40 Ligand/TNFSF5 (108-261), Animal-Free
For research use or further manufacturing only