Recombinant Human Dkk-1 N-Terminal Fragment Protein, CF
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 9837-DK

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line, CHO-derived human Dkk-1 protein
Thr32-Ser141, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Thr32-Ser141, with a C-terminal 6-His tag
Purity
>95%, by SDS-PAGE visualized with Silver Staining and quantitative densitometry by Coomassie® Blue Staining.
Endotoxin Level
<0.10 EU per 1 μg of the protein by the LAL method.
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Thr32, Ser35 & Ser39
Predicted Molecular Mass
12 kDa
SDS-PAGE
13 - 21 kDa, reducing conditions
Activity
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA.
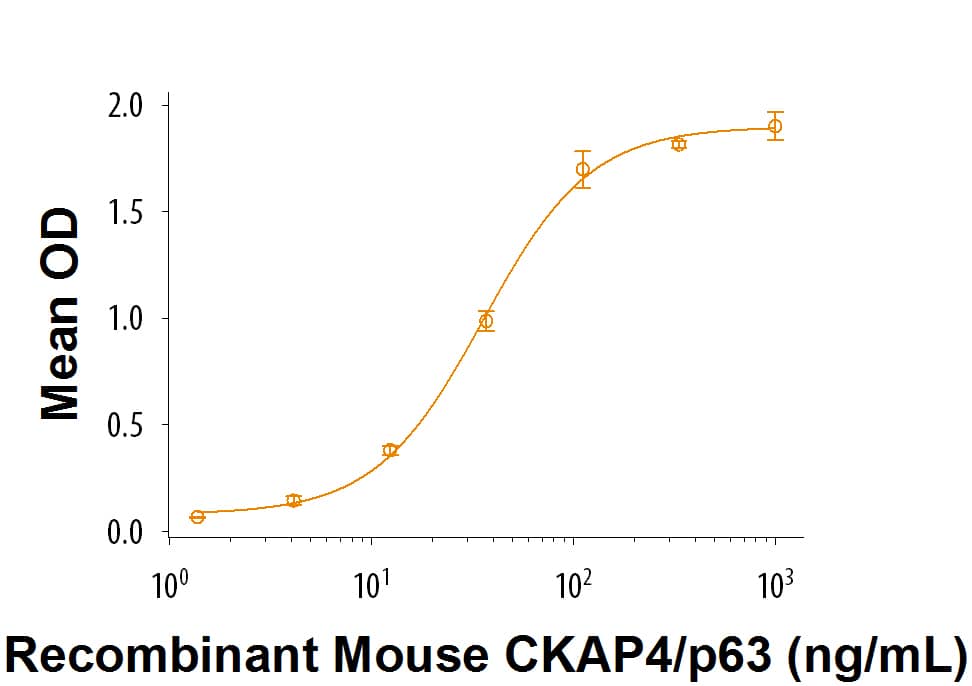
When Recombinant Human Dkk‑1 N-Terminal Fragment is coated at 1 μg/mL, Mouse CKAP4/p63 (Catalog # 9734-CK) binds with an ED50 of 9-54 ng/mL.
When Recombinant Human Dkk‑1 N-Terminal Fragment is coated at 1 μg/mL, Mouse CKAP4/p63 (Catalog # 9734-CK) binds with an ED50 of 9-54 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 N-Terminal Fragment Protein, CF
Recombinant Human Dkk-1 N-Terminal Fragment Protein Binding Activity
When Recombinant Human Dkk-1 N-Terminal Fragment (Catalog # 9837-DK) is immobilized at 1 µg/mL, 100 µL/well, Recombinant Mouse CKAP4/p63 (Catalog # 9734-CK) binds with an ED50 of 9-54 ng/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
9837-DK
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution |
Reconstitute at 500 μg/mL in PBS.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped with polar packs. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Dkk-1
References
- Krupnik, V.E. et al. (1999) Gene 238:301.
- Niehrs, C. (2006) Oncogene 25:7469.
- Bullock, C.M. et al. (2004) Mol. Pharmacol. 65:582.
- Mao, B. et al. (2001) Nature 411:321.
- Brott, B.K. and S.Y. Sokol (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:6100.
- Kimura, H. et al. (2016) J. Clin. Invest. 126:7.
- Chen, S. et al. (2011) Dev. Cell 21:848.
- Bourhis, E. et al. (2011) Structure 19:1433.
- Cheng, Z. et al. (2011) Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 18:1204.
- Mao, B. et al. (2002) Nature 417:664.
- Kemp, C. et al. (2005) Dev. Dyn. 233:1064.
- Adamska, M. et al. (2004) Dev. Biol. 272:134.
- Li, J. et al. (2006) Bone 39:754.
- Verani, R. et al. (2007) J. Neurochem. 100:242.
- Pinzone, J.J. et al. (2009) Blood 113:517.
- Morvan, F. et al. (2006) J. Bone Miner. Res. 21:934.
- Cappuccio, I. et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25:2647.
- Menezes, M.E. et al. (2012) Int. J. Cancer 130:1477.
- Li, S. et al. (2013) PLoS One 8:e84944.
- Chen, L. et al. (2013) Mol. Cancer 12:157.
Long Name
Dickkopf-1
Alternate Names
Dkk1
Gene Symbol
DKK1
UniProt
Additional Dkk-1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 N-Terminal Fragment Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 N-Terminal Fragment Protein, CF
For research use only
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...