Recombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1, Animal-Free Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AFL232

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Phe16-Asp155, with an N-terminal Met
Produced using non-animal reagents in an animal-free laboratory.
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
Activity
The ED50 for this effect is 0.0150-0.150 ng/mL in the presence of 10 µg/mL of heparin.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1, Animal-Free Protein
Recombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1, Animal-Free Protein Bioactivity
Animal-FreeTMRecombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1 (Catalog # AFL232) stimulates cell proliferation in the NR6R‑3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 0.1-0.3 ng/mL in the presence of 10 μg/mL heparin.Recombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1, Animal-Free Protein SDS-PAGE
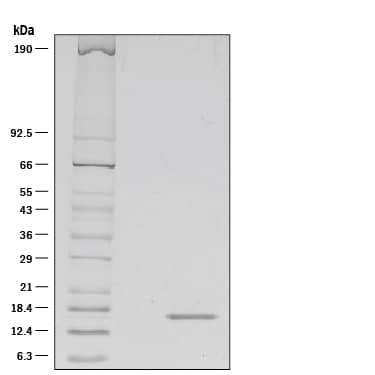
1 μg/lane of Animal-FreeTMRecombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1 (Catalog # AFL232) was resolved with SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) conditions and visualized by silver staining, showing a single band at 16 kDa.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
AFL232
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in MOPS, Na2SO4 and EDTA. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 0.2 mg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: FGF acidic/FGF1
FGF acidic, also known as FGF1, ECGF, and HBGF-1, is a 17 kDa nonglycosylated member of the FGF family of mitogenic peptides. FGF acidic, which is produced by multiple cell types, stimulates the proliferation of all cells of mesodermal origin and many cells of neuroectodermal, ectodermal, and endodermal origin. It plays a number of roles in development, regeneration, and angiogenesis (1-3). Human FGF acidic shares 54% amino acid sequence identity with FGF basic and 17%-33% with other human FGFs. It shares 92%, 96%, 96%, and 96% aa sequence identity with bovine, mouse, porcine, and rat FGF acidic, respectively, and exhibits considerable species cross-reactivity. Alternate splicing generates a truncated isoform of human FGF acidic that consists of the N-terminal 40% of the molecule and functions as a receptor antagonist (4). During its nonclassical secretion, FGF acidic associates with S100A13, copper ions, and the C2A domain of synaptotagmin 1 (5). It is released extracellularly as a disulfide-linked homodimer and is stored in complex with extracellular heparan sulfate (6). The ability of heparan sulfate to bind FGF acidic is determined by its pattern of sulfation, and alterations in this pattern during embryogenesis thereby regulate FGF acidic bioactivity (7). The association of FGF acidic with heparan sulfate is a prerequisite for its subsequent interaction with FGF receptors (8, 9). Ligation triggers receptor dimerization, transphosphorylation, and internalization of receptor/FGF complexes (10). Internalized FGF acidic can translocate to the cytosol with the assistance of Hsp90 and then migrate to the nucleus by means of its two nuclear localization signals (11-13). The phosphorylation of FGF acidic by nuclear PKC delta triggers its active export to the cytosol where it is dephosphorylated and degraded (14, 15). Intracellular FGF acidic functions as a survival factor by inhibiting p53 activity and proapoptotic signaling (16).
References
- Jaye, M. et al. (1986) Science 233:541.
- Galzie, Z. et al. (1997) Biochem. Cell Biol. 75:669.
- Presta, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:159.
- Yu, Y.L. et al. (1992) J. Exp. Med. 175:1073.
- Rajalingam, D. et al. (2007) Biochemistry 46:9225.
- Guerrini, M. et al. (2007) Curr. Pharm. Des. 13:2045.
- Allen, B.L. and A.C. Rapraeger (2003) J. Cell Biol. 163:637.
- Robinson, C.J. et al. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280:42274.
- Mohammadi, M. et al. (2005) Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 16:107.
- Wiedlocha, A. and V. Sorensen (2004) Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 286:45.
- Wesche, J. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:11405.
- Imamura, T. et al. (1990) Science 249:1567.
- Wesche, J. et al. (2005) Biochemistry 44:6071.
- Wiedlocha, A. et al. (2005) Mol. Biol. Cell 16:794.
- Nilsen, T. et al. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282:26245.
- Bouleau, S. et al. (2005) Oncogene 24:7839.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional FGF acidic/FGF1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1, Animal-Free Protein
Manufacturing Specifications
Animal-Free Manufacturing ConditionsOur dedicated controlled-access animal-free laboratories ensure that at no point in production are the products exposed to potential contamination by animal components or byproducts. Every stage of manufacturing is conducted in compliance with R&D Systems' stringent Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). Production and purification procedures use equipment and media that are confirmed animal-free.
Production
- All molecular biology procedures use animal-free media and dedicated labware.
- Dedicated fermentors are utilized in committed animal-free areas.
Purification
- Protein purification columns are animal-free.
- Bulk proteins are filtered using animal-free filters.
- Purified proteins are stored in animal-free containers in a dedicated cold storage room.
- Low Endotoxin Level.
- No impairment of biological activity.
- High quality product obtained under stringent conditions.
- For ex vivo research or bioproduction, additional documentation can be provided.
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human FGF acidic/FGF1, Animal-Free Protein
For research use or further manufacturing only