Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein, CF Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # BT-004

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
His25-Ser153, with an N-terminal Met
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
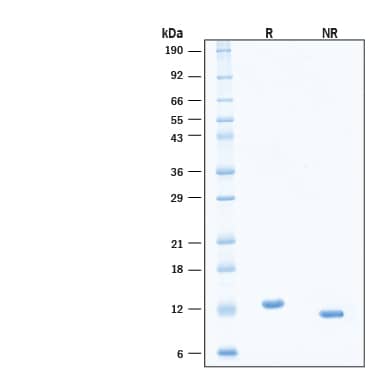
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
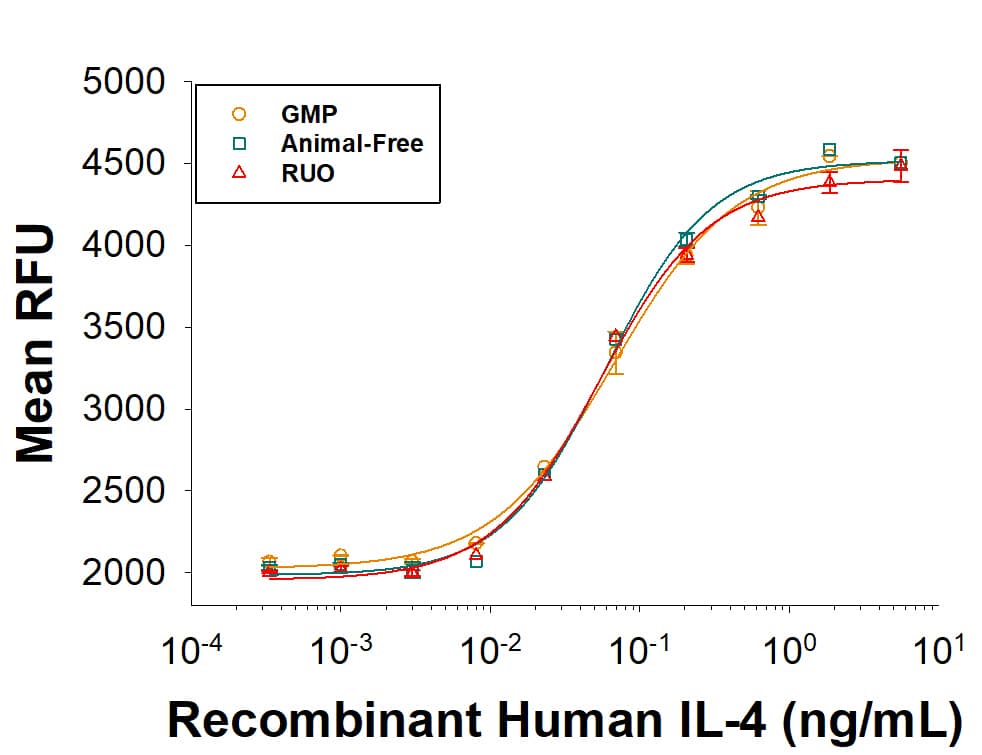
The ED50 for this effect is 0.0400-0.320 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein, CF
Recombinant Human IL‑4 Protein SEC-MALS.
Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein (Catalog # BT-004) has a molecular weight (MW) of 15.2 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a monomer.Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein Bioactivity Comparison.
As an alternative, please consider our next generation Recombinant Human IL-4 Proteins, (BT-004-AFL) and (BT-004-GMP). They have equivalent bioactivity to Recombinant Human IL-4 (Catalog # BT-004). These combine R&D Systems quality with scalability that allows for a solid supply chain. All Recombinant Human IL-4 proteins are measured in a cell proliferation assay using TF-1 human erythroleukemic cell line.Recombinant Human IL‑4 Protein Bioactivity.
Recombinant Human IL‑4 Protein (Catalog # BT-004) stimulates cell proliferation of TF‑1 human erythroleukemic cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.0400-0.320 ng/mL.Formulation, Preparation and Storage
BT-004
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with Trehalose. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute the 10 μg size at 100 μg/mL in PBS. Reconstitute all other sizes at 500 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: IL-4
Interleukin-4 (IL-4), also known as B cell-stimulatory factor-1, is a monomeric, approximately 13 kDa‑18 kDa Th2 cytokine that shows pleiotropic effects during immune responses (1‑3). It is a glycosylated polypeptide that contains three intrachain disulfide bridges and adopts a bundled four alpha-helix structure (4). Human IL-4 is synthesized with a 24 aa signal sequence. Alternate splicing generates an isoform with a 16 aa internal deletion. Mature human IL-4 shares 55%, 39% and 43% aa sequence identity with bovine, mouse, and rat IL-4, respectively. Human, mouse, and rat IL-4 are species-specific in their activities (5‑7). IL-4 exerts its effects through two receptor complexes (8, 9). The type I receptor, which is expressed on hematopoietic cells, is a heterodimer of the ligand binding IL-4 R alpha and the common gamma chain (a shared subunit of the receptors for IL-2, -7, -9, -15, and ‑21). The type II receptor on nonhematopoietic cells consists of IL-4 R alpha and IL‑13 R alpha1. The type II receptor also transduces IL-13 mediated signals. IL-4 is primarily expressed by Th2-biased CD4+ T cells, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils (1, 2). It promotes cell proliferation, survival, and immunoglobulin class switch to IgG4 and IgE in human B cells, acquisition of the Th2 phenotype by naïve CD4+ T cells, priming and chemotaxis of mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils, and the proliferation and activation of epithelial cells (10‑13). IL-4 plays a dominant role in the development of allergic inflammation and asthma (12, 14).
Due to its role in the differentiation of certain immune cell types, IL-4 is commonly used in combination with other growth factors to transform induced pluripotent stem cells into dendritic cells in high numbers. These dendritic cells can then be used for research or clinical applications to improve disease modeling, for screening and cell therapies (15). Study of IL-4 signaling has led to the development of monoclonal antibodies that can block the signaling pathway at various steps to mitigate the inflammatory response in certain autoimmune diseases (16, 17). While IL-4 has the capacity to improve immune functions, treatments involving IL-4 have not been utilized due to the dangerous side effects that may result from IL-4 signaling in non-immune cells (16). Blockade of IL-4 signaling also has been studied as a therapeutic target to suppress inflammation in the tumor microenvironment (18). Use of IL-4 suppressors can also improve the efficacy of anti-tumor immunotherapies, as blocking IL-4 enhances activity of tumor-specific T lymphocytes (19, 20).
References
- Benczik, M. and S.L. Gaffen (2004) Immunol. Invest. 33:109.
- Chomarat, P. and J. Banchereau (1998) Int. Rev. Immunol. 17:1.
- Yokota, T. et al. (1986) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 83:5894.
- Redfield, C. et al. (1991) Biochemistry 30:11029.
- Ramirez, F. et al. (1988) J. Immunol. Meth. 221:141.
- Leitenberg, D. and T.L. Feldbush (1988) Cell. Immunol. 111:451.
- Mosman, T.R. et al. (1987) J. Immunol. 138:1813.
- Mueller, T.D. et al. (2002) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1592:237.
- Nelms, K. et al. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:701.
- Paludan, S.R. (1998) Scand. J. Immunol. 48:459.
- Corthay, A. (2006) Scand. J. Immunol. 64:93.
- Ryan, J.J. et al. (2007) Crit. Rev. Immunol. 27:15.
- Grone, A. (2002) Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 88:1.
- Rosenberg, H.F. et al. (2007) J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 119:1303.
- Flosdorf, N. & Zenke, M. (2022) Eur. J. Immunol. 52:1880.
- Junttila, I.S. (2018) Front Immunol. 9:888.
- Keegan, A.D. et al. (2021) Fac Rev. 10:71.
- Bankaitis, K.V. & Fingleton, B. (2016) Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 32:847.
- Mirlekar, B. (2022) SAGE Open Med. 10:1.
- Ilto, S. E. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Immunother. 66:1485.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional IL-4 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein, CF
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human IL-4 Protein, CF
For research use only