Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Cytokines

Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Cytokines, Receptors and Signaling Pathways
IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21 form a family of cytokines known as the common cytokine receptor gamma chain family. Cytokines belonging to this family signal through receptor complexes that contain a shared subunit, known as the common cytokine receptor gamma chain subunit. This subunit associates with either IL-4 R alpha, IL-7 R alpha, IL-9R, or IL-21R to form heterodimeric receptors for IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, or IL-21 respectively, or it associates with both IL-2 R alpha and IL-2/IL-15 R beta or IL-15 R alpha and IL-2/IL-15 R beta to form heterotrimeric receptor complexes for IL-2 or IL-15. In addition to sharing a common receptor subunit, members of the common cytokine receptor gamma chain family are all class I short chain four alpha-helix bundle cytokines with similar structural features. Following receptor binding, they activate similar intracellular signaling pathways, including Jak-STAT signaling, PI 3-K-Akt signaling, and Ras-MAPK signaling, leading to the expression of specific target genes.
Common Cytokine Gamma Chain Family Cytokines Regulate Immune Cell Development and Functions
Functionally, cytokines belonging to the common cytokine receptor gamma chain family are involved in regulating the development, survival, proliferation, differentiation and functions of different immune cell types. As a result, they affect the activities of multiple cell types, including natural killer cells, innate lymphoid cells, T cells, and B cells. Cytokines in this family can also have both unique and overlapping effects. Their unique functions are primarily determined by differences in their expression patterns or the expression of their unique receptor subunits, or by activation of different STAT proteins. The importance of common cytokine receptor gamma chain signaling for immune system development and maintenance is emphasized by the fact that mutations in the human common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma are associated with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (XSCID). XSCID is a life-threatening disease in which patients lack T cells and natural killer cells and have nonfunctional B cells that produce significantly reduced levels of immunoglobulin. Importantly, it was discovered that IL-2 knockout mice and patients deficient in IL-2 do not mimic the XSCID phenotype, leading to the realization that the common cytokine receptor gamma chain must serve as a receptor component for other cytokines as well.
IL-2
IL-2 is produced primarily by CD4+ T cells, although it can also be produced at lower levels by CD8+ T cells, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, NKT cells, and B cells. It signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-2 R alpha/CD25, IL-2 R beta, and the common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma subunit. IL-2 plays a central role in stimulating CD4+ and CD8+ T cell proliferation, and it regulates peripheral self-tolerance by promoting activation-induced cell death (AICD) in CD4+ T cells. IL-2 promotes Th1, Th2, and Th9 cell differentiation, while inhibiting the differentiation of Th17 and T follicular helper (Tfh) cells. Additionally, IL-2 stimulates the proliferation and cytotoxicity of natural killer cells, enhances B cell functions, and promotes the development and maintenance of regulatory T cells (Tregs). IL-2 has been approved as an anti-cancer treatment for melanoma and renal cancer, and it is being evaluated as a potential treatment for autoimmune diseases due to its ability to promote regulatory T cell homeostasis.
IL-4
IL-4 is produced primarily by T cells, NKT cells, mast cells, and eosinophils. It signals through two different receptor complexes, a type I receptor complex consisting of IL-4 R alpha and the common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma subunit, and a type II receptor complex consisting of IL-4 R alpha and IL-13 R alpha 1. The type I receptor complex is expressed on hematopoietic cells and is specific for IL-4, while the type II receptor complex is expressed on nonhematopoietic cells and some hematopoietic cells and can be activated by either IL-4 or IL-13. IL-4 is a signature cytokine for Th2-type immune responses and is essential for providing protection against large extracellular parasites. It also promotes B cell differentiation and immunoglobulin class switching, Th2 and Th9 cell differentiation, M2 macrophage activation, and mast cell survival and proliferation. Due to its central role in regulating Th2-type immune responses, IL-4 is thought to play a central role in mediating the development of allergic inflammation and asthma.
IL-7
IL-7 is produced primarily by stromal cells, epithelial cells, and keratinocytes, and it signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-7 R alpha and the common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma subunit. IL-7 signaling is required for T cell development and homeostasis in both mice and humans, mouse B cell development, and the generation and survival of CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cells. The requirement of IL-7 for the maintenance of T cell survival has in part been attributed to its ability to induce the expression of the anti-apoptotic proteins, Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Mcl-1. Additionally, IL-7 is required for maintaining the homeostasis of thymic natural killer cells and is involved in regulating V(D)J recombination at the TCR and distal Ig heavy chain loci.
IL-9
IL-9 is produced primarily by Th9 cells, mast cells, ILC2 cells, and NKT cells, and it signals through a receptor complex consisting of IL-9 R alpha and the common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma subunit. IL-9 was originally thought to be produced by Th2 cells, but it was later discovered to be the signature cytokine of Th9 cells. IL-9 promotes mast cell proliferation, enhances IL-4-induced IgG and IgE production by B cells, and promotes goblet cell hyperplasia and mucus production. It is thought to contribute to the development of allergic inflammation and asthma, but it as also been shown to have anti-cancer activity.
IL-15
IL-15 is produced primarily by dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and stromal cells. It binds with high affinity to IL-15 R alpha, which then associates with IL-2/IL-15 R beta and the common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma, either in cis (on the same cell) or in trans (on a different cell). IL-15 signaling is required for the development and maintenance of natural killer cells and memory CD8+ T cells. Similar to IL-2, IL-15 can stimulate the cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells and natural killer cells, but in contrast to IL-2, it inhibits activation-induced cell death. Additionally, IL-15 promotes the expansion and homeostasis of NKT cells and intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. IL-15 is considered to be a promising anti-cancer agent, particularly when used in combination with other anti-cancer agents such as immune checkpoint inhibitors or agonistic anti-CD40 antibodies.
IL-21
IL-21 is produced primarily by Th17 cells, T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, NKT cells, and gamma delta T cells. It binds to a receptor complex consisting of IL-21 R and the common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma subunit. IL-21 signaling promotes Th17 and T follicular helper cell differentiation, while inhibiting the differentiation of Th9 cells and regulatory T cells (Tregs). Additionally, IL-21 enhances the cytotoxicity of CD8+ cells, natural killer cells, and NKT cells, regulates B cell proliferation and apoptosis in a context-dependent manner, and promotes B cell differentiation and immunoglobulin production, in the presence of IL-4. IL-21 has been shown to have anti-tumor activity, but it is also associated with the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease in mouse models of type I diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and experimental autoimmune uveitis.
Bio-Techne offers a wide selection of proteins, antibodies, and immunoassays for cytokines belonging to the common cytokine receptor gamma chain family. Our catalog includes research-grade, Animal-FreeTM, and GMP-grade bioactive IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21. Additionally, we offer antibodies validated for blocking/neutralization, flow cytometry, ICC, or Western blot, and immunoassays for measuring these cytokines in various sample types.
Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Cytokines - Products by Molecule
Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Receptors - Products by Molecule
| CD25/IL-2 R alpha | Common gamma chain/IL-2 R gamma | IL-2 R beta | IL-4 R alpha | IL-7 R alpha/CD127 |
| IL-9 R | IL-15 R alpha | IL-21 R |
Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Intracellular Signaling - Products by Molecule
Cell Proliferation Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Mouse IL-4 and Neutralization by a Rat Anti-Mouse IL-4 Monoclonal Antibody

IL-4-induced Cell Proliferation is Neutralized Using a Rat Anti-Mouse IL-4 Monoclonal Antibody. The HT-2 mouse T cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Mouse IL-4 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 404-ML) and cell proliferation was measured (orange line). The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.3-1.5 ng/mL. Proliferation induced by 7.5 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse IL-4 was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Rat Anti-Mouse IL-4 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB404; green line). The ND50 for this effect is typically 0.1-0.6 ug/mL.
Assessment of the Bioactivity and Lot-to-Lot Consistency of R&D Systems GMP-grade Recombinant Human IL-2
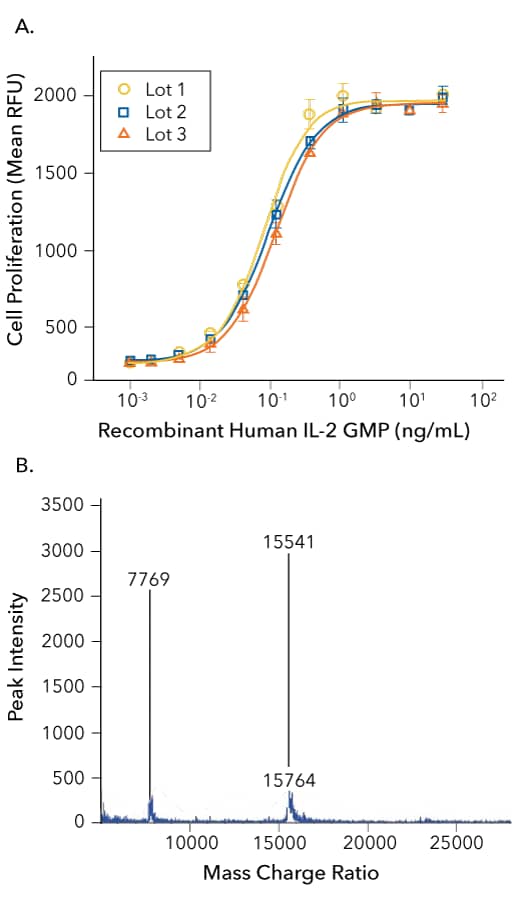
Analysis of the Bioactivity, Lot-to-Lot Consistency, and Mass of R&D Systems GMP-grade Recombinant Human IL-2. (A) Three independent lots of GMP-grade Recombinant Human IL-2 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 202-GMP) were tested for their ability to stimulate proliferation of the CTLL-2 mouse cytotoxic T cell line. The ED50 for this effect is 0.05-0.25 ng/mL. Each trace on the graph represents data obtained from GMP-grade Recombinant Human IL-2 from a different manufacturing run, demonstrating the lot-to-lot consistency of the protein. (B) MALDI-TOF analysis of GMP-grade Recombinant Human IL-2 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 202-GMP). The major peak corresponds to the calculated molecular mass of the protein, 15549 Da. The minor peak at 15764 Da is a matrix-associated artifact of the MALDI-TOF.
Detection of IL-7 R alpha/CD127 on Human Blood Lymphocytes by Flow Cytometry

Detection of IL-7 R alpha/CD127 on Human Blood Lymphocytes by Flow Cytometry. Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with an APC-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human CD3 epsilon Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB100A) and either a (A) PE-conjugated Mouse Anti-Human IL-7 R alpha/CD127 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB306P) or a (B) PE-conjugated Mouse IgG1 Isotype Control Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # IC002P).
Measurement of Anti-Human CD5-Induced IL-2 Production by Human T Cells Using the Human IL-2 Quantikine™ ELISA Kit

Measurement of Anti-Human CD5-Induced IL-2 Production by Human T Cells. Freshly prepared human T cells were added to a plate coated with suboptimal amounts of a Mouse Anti-Human CD3 epsilon Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB100) and a Mouse Anti-Human CD28 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB342), plus the indicated concentrations of a Goat Anti-Human CD5 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF1636). Following incubation at 37 ˚C, the levels of IL-2 in the cell culture supernatants were measured using the Human IL-2 Quantikine ELISA Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # D2050).
Featured Products for Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family

Preclinical Animal-Free™ and GMP-grade Recombinant Proteins
Preclinical Animal-Free™ and GMP-grade Recombinant Proteins
To simplify the transition from basic research to preclinical applications and ex vivo cell manufacturing, we offer research-grade, Pre-clinical Animal-Free, and Animal-Free GMP-grade IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21. Our GMP-grade proteins frequently originate from the same clone, sequence, and expression system as our traditional research-grade materials to make the switch to a GMP protein as seamless as possible.

Custom Protein Libraries
Custom Protein Libraries
Are you spending valuable research time aliquoting proteins into plates? Let us help. We offer Custom Protein Libraries, which come with the proteins that you select already aliquoted into the wells of a 96-well plate. This custom product allows you to select the proteins that you need from a portfolio of over 5,000 R&D SystemsTM bioactive proteins and will significantly reduce the amount of time needed to set-up your experiments.

Bulk Proteins
Bulk Proteins
If your experiments require large quantities of a particular protein, contact us for a bulk quote. We have the capacity and the expertise to scale up the production of any protein to meet your needs, and we offer economical pricing on bulk orders.
Featured Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Resources

Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Product Guide
Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Product Guide
Explore this guide to learn more about the cytokines belonging to the common cytokine receptor gamma chain family and the signaling pathways that they activate. This guide includes a complete listing of products for this cytokine family and provides multiple data examples to demonstrate the testing our scientists have performed to ensure that our products will provide superior performance and lot-to-lot consistency.

Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cytokines activate a diverse array of intracellular signaling pathways that can induce processes such as development, survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Explore the signaling pathways that are activated by different cytokine families, the primary target cells that they affect, and the biological effects that they mediate using our interactive signaling pathways.

Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Cytokines Poster
Common Cytokine Receptor Gamma Chain Family Cytokines Poster
Cytokines belonging to the common cytokine receptor gamma chain family play a major role in regulating the development, survival, proliferation, differentiation, and/or function of different immune cell types. Use this poster to learn more about the unique and overlapping effects of these cytokines on T cells, natural killer cells, dendritic cells, B cells, and more.