TGF-beta Superfamily

TGF-beta Signaling Pathway
TGF-beta Superfamily Ligands
The transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) superfamily consists of over 30 highly pleiotropic molecules that regulate a diverse range of biological processes during embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis. Members of the TGF-beta superfamily include Activins, Inhibins, Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) Growth Differentiation Factors (GDFs), Glial-derived Neurotrophic Factors (GDNFs), Lefty, Mullerian Inhibiting Substance (MIS), Nodal, and TGF-beta proteins. Proteins in this family share approximately 25-40% amino acid sequence identity and a conserved cysteine knot structure. They are initially synthesized as precursor proteins with an N-terminal signal peptide, a prodomain that regulates folding, secretion, and localization, and a C-terminal mature peptide. Following removal of the signal peptide and proteolytic cleavage, the mature segments typically form dimers, which are held together in most cases, by a single disulfide bond. While most TGF-beta superfamily proteins form homodimers, some can also form natural heterodimers with biological activity.
TGF-beta Superfamily Receptors
Activins, BMPs, GDFs, and TGF-beta proteins signal through serine/threonine kinase receptors. They bind to heterotetrameric receptor complexes composed of two type I and two type II receptor subunits, which all contain extracellular ligand-binding domains and intracellular serine/threonine kinase domains. The type I receptor also contains an approximately 30-residue intracellular, juxtamembrane domain, called the GS domain, which contains the sequence SGSGSG. This domain is phosphorylated by the type II receptor following ligand binding and receptor oligomerization, resulting in activation of type I receptor serine/threonine kinase activity and subsequent Smad protein phosphorylation. In humans, there are 7 type I receptors in the TGF-beta family, known as activin-like receptors 1-7 (ALK1-7), and 5 type II receptors, known as TGF-beta RII, BMPR-II, Activin RIIA, Activin RIIB, and MIS RII or AMHR II. Additionally, a type III TGF-beta receptor, TGF-beta RIII/Betaglycan, has been identified as a co-receptor, which is thought to enhance or inhibit TGF-beta superfamily signaling in a context-dependent manner.
Members of the GDNF family, including GDNF, Artemin, Neurturin, and Persephin, are distantly-related to the other TGF-beta superfamily proteins. They form homodimers, but do not signal through serine/threonine kinase receptors. Instead, GDNF family ligands initially bind to a specific GPI-anchored GDNF family receptor alpha (GFR), which then binds to the receptor tyrosine kinase, Ret, to mediate downstream signaling. There are 4 GFRalpha receptors, GFRalpha1, GFRalpha2, GFRalpha3, and GFRalpha4, which bind to GDNF, Neurturin, Artemin, and Persephin, respectively.
TGF-beta Superfamily Signaling
Binding of TGF-beta superfamily proteins to heterotetrameric serine-threonine kinase receptors results in phosphorylation of the type I receptor by the type II receptor. This leads to activation of the type I receptor and phosphorylation of a receptor-activated Smad (R-Smad) protein. In general, the R-Smad is typically R-Smad2/3 in the case of TGF-beta and Activin signaling, while the R-Smad for BMP and GDF signaling is typically R-Smad1/5/8. R-Smad phosphorylation induces its dissociation from the receptor and formation of a complex with the common Smad4 protein, which subsequently moves into the nucleus where it interacts with sequence-specific transcription factors, transcriptional co-activators or co-repressors, and/or chromatin remodeling factors that regulate gene expression. In addition to Smad-dependent signaling, TGF-beta proteins, BMPs, and some GDFs can also activate several non-canonical, Smad-independent signaling pathways in a cell- and context-dependent manner. These pathways include the Ras/MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K/Akt pathway, the RhoA/ROCK pathway, and TRAF6-mediated p38 MAPK and JNK activation.
In contrast to other TGF-beta superfamily proteins, GDNF family ligands do not signal through serine/threonine kinase receptors. Conversely, they initially bind to a specific GFRalpha, which then associates with two Ret receptor tyrosine kinase receptor subunits. Formation of this 2:2:2 complex of GDNF ligand-GFR-Ret induces Ret autophosphorylation, creating docking sites for adaptor proteins that activate a series of intracellular signaling pathways. These include the Ras/MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K/Akt pathway, the PLC-gamma/PKC pathway, and the p38 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways. In addition to Ret-dependent signaling, GDNF-GFRalpha1 can also activate downstream signaling pathways independent of Ret. GDNF-GFRalpha1 has been shown to bind to NCAM to activate downstream signaling pathways, and it has also been suggested to signal through another unidentified receptor, in the absence of Ret, to activate Src.
Functions of the TGF-beta Superfamily Proteins
TGF-beta superfamily proteins are ubiquitously expressed and they regulate the expression of hundreds of genes. During embryogenesis, these proteins are involved in regulating processes such as dorso-ventral patterning, limb bud formation, mesoderm induction and patterning, neuron differentiation, organogenesis, and bone formation, while in adult organisms, they also participate in immune responses, tissue healing, and the maintenance of tissue homeostasis in a wide variety of tissues. As a result, misregulation of signaling pathways activated by TGF-beta superfamily proteins have not only been associated with developmental disorders, but also with cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
Differentiation of hESCs into Endoderm Using R&D Systems Recombinant Human Activin A

Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells in Media Supplemented with R&D Systems Recombinant Human Activin A. BG01V human embryonic stem cells were (A) cultured in media without any protein added or (B) differentiated into endoderm using media supplemented with Recombinant Human Activin A (R&D Systems, Catalog # 338-AC). Differentiation into endoderm was confirmed by positive staining for Claudin-6 (red) and Sox17 (green) using the Mouse Anti-Human Claudin-6 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB3656) and the Goat Anti-Human Sox17 Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF1924), respectively. BG01V human embryonic stem cells are licensed from ViaCyte, Inc.
Inhibin A-Mediated Neutralization of Activin A-Induced Erythroid Differentiation of K562 Human Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cells

Recombinant Human Inhibin A Neutralizes Activin A-induced Erythroid Differentiation of K562 Human Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Cells. Activin A-induced erythroid differentiation of K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cells was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human Inhibin A (R&D Systems, Catalog # 8506-AB). The ED50 for this effect is 3-18 ng/mL.
Bone Morphogenetic Proteins and Growth Differentiation Factors - Products by Molecule
BMP Receptors - Products by Molecule
| BMPR-IA/ALK-3 | BMPR-IB/ALK-6 | BMPR-II | BMP and Other Activin Receptor Activators |
| BMP and Other Activin Receptor Inhibitors | RGM-A | RGM-B | RGM-C/Hemojuvelin |
BMP Modulators - Products by Molecule
Assessment of the Bioactivity of R&D Systems Recombinant Human BMP-4
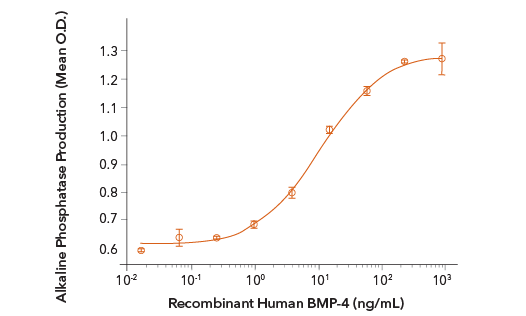
Recombinant Human BMP-4 Induces Alkaline Phosphatase Production. The ATDC5 mouse chondrogenic cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of E. coli-expressed Recombinant Human BMP-4 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 314-BPE) and alkaline phosphatase production was assessed. The ED50 for this effect is 6-48 ng/mL.
Hemoglobin Expression Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human/Mouse GDF-8 and Neutralization by a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse GDF-8 Polyclonal Antibody

GDF-8/Myostatin-Induced Hemoglobin Expression is Neutralized Using a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse GDF-8/Myostatin Polyclonal Antibody. The K562 human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human/Mouse GDF-8/Myostatin (R&D Systems, Catalog # 788-G8) and hemoglobin expression was assessed using the pseudoperoxidase assay (orange line). The ED50 for this effect is 2-10 ng/mL. Hemoglobin expression elicited by 30 ng/mL Recombinant Human/Mouse GDF-8/Myostatin was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Goat Anti-Human/Mouse GDF-8/Myostatin Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF788; blue line). The ND50 is typically 0.6-3 ug/mL.
GDNF Family Ligands - Products by Molecule
GDNF Family Receptors - Products by Molecule
R&D Systems Recombinant Human GDNF Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s GDNF Protein

R&D Systems Recombinant Human GDNF Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human GDNF Protein. The bioactivity of R&D Systems Recombinant Human GDNF (Catalog # 212-GD; orange line) or recombinant human GDNF from another company (blue line) was assessed by measuring the ability of the proteins to stimulate proliferation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells, in the presence of Recombinant Human GFR alpha-1 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 714-GR). The activity of the R&D Systems GDNF protein was approximately 9-fold greater than the leading competitor’s GDNF protein.
Protein Characterization Using SEC-MALS Analysis
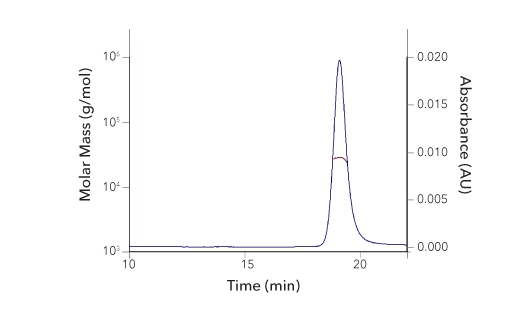
Recombinant Human GDNF Protein SEC-MALS. Recombinant human GDNF (Catalog # 212-GD) has a molecular weight (MW) of 27.5 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a homodimer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).
| SEC-MALS Data | Result |
| Retention Time | 18.8-19.4 min |
| MW-Predicted (Monomer) | 11.6 kDa |
| MW-MALS | 27.5 kDa |
| Polydispersity | 1.002 |
| System Suitability: BSA Monomer 66.4 ± 3.32 kDa | Pass |
TGF-beta Family Ligands - Products by Molecule
| LAP (TGF-beta 1) | TGF-beta | TGF-beta 1 | TGF-beta 1.2 | TGF-beta 1/1.2 | TGF-beta 2 |
| TGF-beta 2/1.2 | TGF-beta 3 | TGF-beta 1, 2, 3 | TGF-beta 5 |
TGF-beta Family Receptors - Products by Molecule
| ALK-1 | ALK-7 | CD109 | Cripto | Endoglin/CD105 | MIS RII |
| TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 | TGF-beta RII | TGF-beta RIII | TGF-beta Receptor Inhibitors |
TGF-beta Family Signaling Modulators - Products by Molecule
Inhibition of IL-4-Induced Mouse T Cell Proliferation by R&D Systems Recombinant Human TGF-beta 1

Recombinant Human TGF-beta 1 Inhibits IL-4-induced T Cell Proliferation. The HT-2 mouse T cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human TGF-beta 1 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 7754-BH) and cell proliferation was assessed. The ED50 for this effect is 0.04-0.2 ng/mL.
Immunostaining of TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 in LPS/Monensin-Stimulated Human PBMCs Using R&D Systems Goat Anti-Human TGF-beta RI Antigen Affinity-Purified Polyclonal Antibody

Detection of TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 in LPS/Monensin-Stimulated Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 was detected in immersion-fixed human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) following stimulation with LPS and monensin using a Goat Anti-Human TGF-beta RI/ALK-5 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF3025) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # NL001; yellow) and counterstained with DAPI (Tocris, Catalog # 5748; blue).
Detection of Lefty-2 in Day 3 Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Treated with Recombinant Human Activin A

Detection of Lefty-2 in Day 3 Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells treated with Recombinant Human/Mouse Activin A. Lefty-2 was detected in immersion-fixed day 3 mouse embryonic stem cells that were either (A) untreated or (B) treated with Recombinant Human/Mouse Activin A (R&D Systems, Catalog # 338-AC) using a Sheep Anti-Mouse Lefty-2 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF7648) for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # NL010; red) and counterstained with DAPI (Tocris, Catalog # 5748; blue). Specific staining was localized to the cytoplasm of Activin A-stimulated cells.
TGF-beta Superfamily Intracellular Signaling - Products by Molecule
Featured Products for TGF-beta Superfamily Research

Preclinical Animal-Free™ and GMP-grade Recombinant Proteins
Preclinical Animal-Free™ and GMP-grade Recombinant Proteins
To simplify the transition from basic research to preclinical applications and ex vivo cell manufacturing, we offer research-grade, preclinical Animal-Free, and Animal-Free GMP-grade cytokines and growth factors. Our GMP-grade proteins frequently originate from the same clone, sequence, and expression system as our traditional research-grade proteins to make the switch to GMP as seamless as possible.

Products for Stem Cell Culture
Products for Stem Cell Culture
Optimize your stem cell culture conditions with reagents from Bio-Techne. Our catalog includes stem cell media, supplements, and proteins to promote robust cell growth while maintaining reproducible culture conditions. Additionally, we offer stem cell differentiation and functional identification kits to simplify your workflow.
Organoid and 3-D Cell Culture Products
Organoid and 3-D Cell Culture Products
Promote robust organoid growth and minimize variability in your culture conditions by using our organoid culture reagents. From basement membrane extracts to R&D Systems™ growth factors, small molecules, media, and media supplements, we provide a complete collection of reagents designed to optimize your organoid culture conditions.
Featured Resources for TGF-beta Superfamily Research

TGF-beta Signaling and Cancer Poster
TGF-beta Signaling and Cancer Poster
TGF-beta is a multifunctional cytokine that can have tumor-suppressing or tumor-promoting effects in a cell- and context-dependent manner. Learn about the genes that are regulated by TGF-beta signaling and the mechanisms by which these genes inhibit or promote tumor formation and progression in this miniposter.

Growth Factor Signaling Pathways
Growth Factor Signaling Pathways
Growth factors promote a broad range of cellular processes including proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration and they are essential for both embryonic development and for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis in adult organisms. Explore the signaling pathways that are activated by different growth factor families and the biological effects that they mediate using our interactive signaling pathways.

Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors Poster
Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors Poster
Learn about the different families of growth factors that regulate human development with our Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors wall poster. The poster includes information on the structures, native molecular weights, and receptors for each protein and will serve as a great reference tool to keep in your lab or office space.