GABA-A R alpha 1 Products
GABA A (γ-aminobutyric acid-type A) receptors are members of the cysteine-loop family of neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. GABA binding to A-type receptors induces anion-selective ion channel opening. These receptors are the principal fast inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS. GABA A receptors are heteropentamer combinations of seven subunit types; α, β, γ, δ, ε, θ, and π. Three subunits, α, β, and γ, have at least three separate gene products in mammals, and typical GABA A receptors have some combination of α, β, and γ subunits.
The rat α1 isoform is a 50 - 52 kDa, 428 amino acid (aa), 4 transmembrane protein with two terminal extracellular regions. The ligand-binding region is in the N-terminus (aa 15 - 222). As with many receptors, phosphorylation of GABA A R is used as a regulatory mechanism. CaM kinase II is known to phosphorylate the a1 GABA A subunit and regulate benzodiazepine binding. The α1 subunits are particularly abundant in the cerebellum and may contribute to GABA receptor distribution. In the hippocampus and amygdala, the α1 GABA A subunit may contribute to amnesia.
25 results for "GABA-A R alpha 1" in Products
25 results for "GABA-A R alpha 1" in Products
GABA-A R alpha 1 Products
GABA A (γ-aminobutyric acid-type A) receptors are members of the cysteine-loop family of neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. GABA binding to A-type receptors induces anion-selective ion channel opening. These receptors are the principal fast inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS. GABA A receptors are heteropentamer combinations of seven subunit types; α, β, γ, δ, ε, θ, and π. Three subunits, α, β, and γ, have at least three separate gene products in mammals, and typical GABA A receptors have some combination of α, β, and γ subunits.
The rat α1 isoform is a 50 - 52 kDa, 428 amino acid (aa), 4 transmembrane protein with two terminal extracellular regions. The ligand-binding region is in the N-terminus (aa 15 - 222). As with many receptors, phosphorylation of GABA A R is used as a regulatory mechanism. CaM kinase II is known to phosphorylate the a1 GABA A subunit and regulate benzodiazepine binding. The α1 subunits are particularly abundant in the cerebellum and may contribute to GABA receptor distribution. In the hippocampus and amygdala, the α1 GABA A subunit may contribute to amnesia.
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Canine, +2 More |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat, Bovine |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, IP, KO |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, IP, KO |
| Reactivity: | Human, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, IP, MA, AP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Kappa Monoclonal Clone #D4 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | WB |
Competitive and selective GABAA antagonist
| Alternate Names: | Gabazine |
| Chemical Name: | 6-Imino-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1(6H)-pyridazinebutanoic acid hydrobromide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Potent GABAA agonist; also GABAA-ρ partial agonist
| Chemical Name: | 5-Aminomethyl-3-hydroxyisoxazole |
| Purity: | ≥98% |
Positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors
| Alternate Names: | 3a,5a-THPROG |
| Chemical Name: | (3α,5α)-3-Hydroxy-pregnan-20-one |
GABAA agonist
| Alternate Names: | Gaboxadol |
| Chemical Name: | 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
CNS stimulant
| Alternate Names: | PTZ |
| Chemical Name: | 6,7,8,9-Tetrahydro-5H-tetrazolo[1,5-a]azepine |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
α5-selective GABAA inverse agonist
| Chemical Name: | 3-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-7-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)-2-[(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methoxy]-pyrazolo[1,5-d][1,2,4]triazine |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
GABAA partial agonist; displays subtype selectivity
| Chemical Name: | 3-(2,5-Difluorophenyl)-7-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-[(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methoxy]-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Postitive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors
| Chemical Name: | (3α,5β)-3-Hydroxy-pregnan-20-one |
Benzodiazepine antagonist
| Alternate Names: | Ro 15-1788 |
| Chemical Name: | 8-Fluoro-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Benzodiazepine partial agonist
| Alternate Names: | Ro 16-6028 |
| Chemical Name: | (13aS)-8-Bromo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9-oxo-9H-imidazo[1,5-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepine-1-carboxylic acid 1,1-dimethylethyl ester |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Active metabolite of oxcarbazepine (Cat. No. 3864)
| Alternate Names: | GP 47779 |
| Chemical Name: | 10,11-Dihydro-10-hydroxy-5H-dibenz(Z)[b,f]azepin-5-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Benzodiazepine inverse agonist
| Chemical Name: | N-Methyl-β-carboline-3-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Benzodiazepine inverse agonist
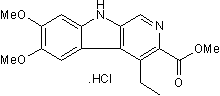
| Chemical Name: | 4-Ethyl-6,7-dimethoxy-9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-3-carboxylic acid methyl ester hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Benzodiazepine partial inverse agonist
| Chemical Name: | 8-Azido-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |

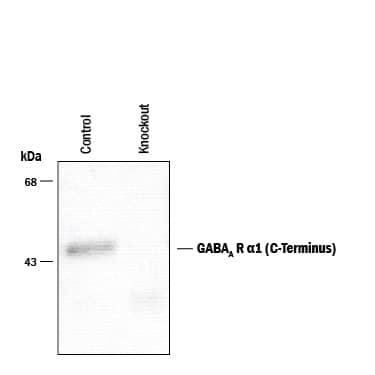
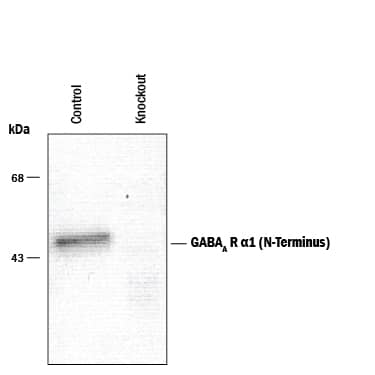

![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NB300-191] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NB300-191]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-A-R-alpha-1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB300-191-img0003.jpg)
![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NB300-207] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NB300-207]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-AR-alpha-1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB300-207-img0001.jpg)
![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NBP2-16565] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NBP2-16565]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-AR-alpha-1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP2-16565-img0005.jpg)
![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NBP2-33762] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Antibody [NBP2-33762]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-AR-alpha-1-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP2-33762-img0002.jpg)

![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-10915] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 1 Overexpression Lysate [NBL1-10915]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-A-Receptor-alpha-1-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBL1-10915-img0002.jpg)