Spike S1 Subunit: Proteins and Enzymes
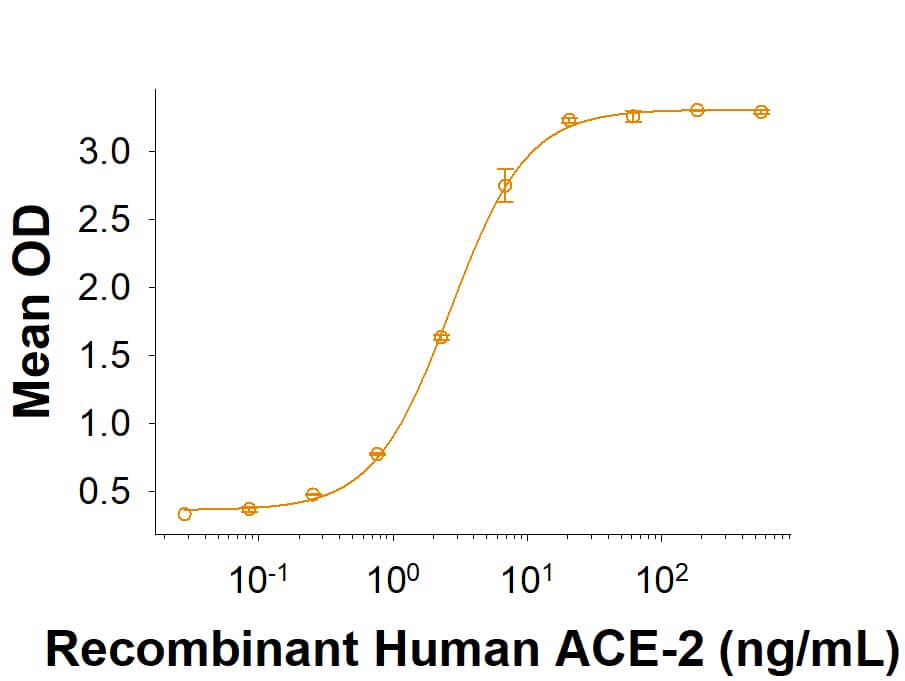
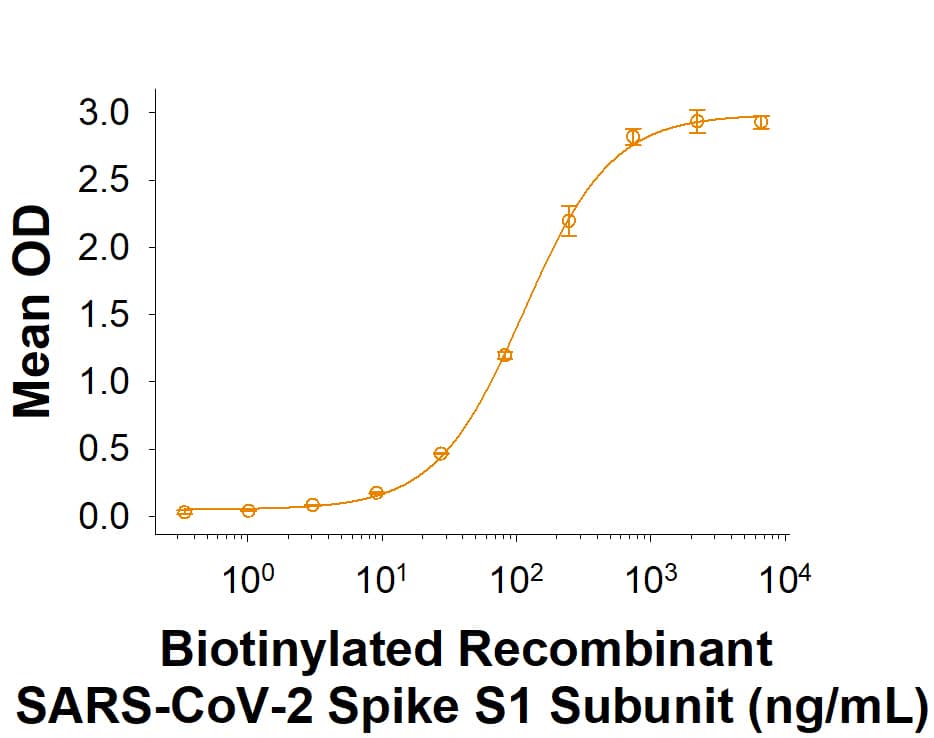
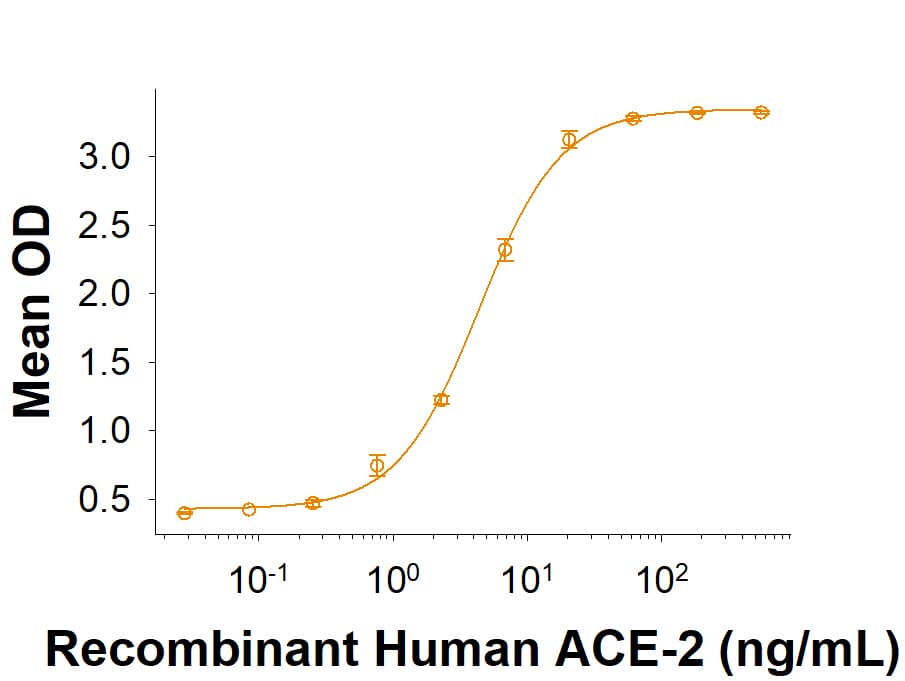
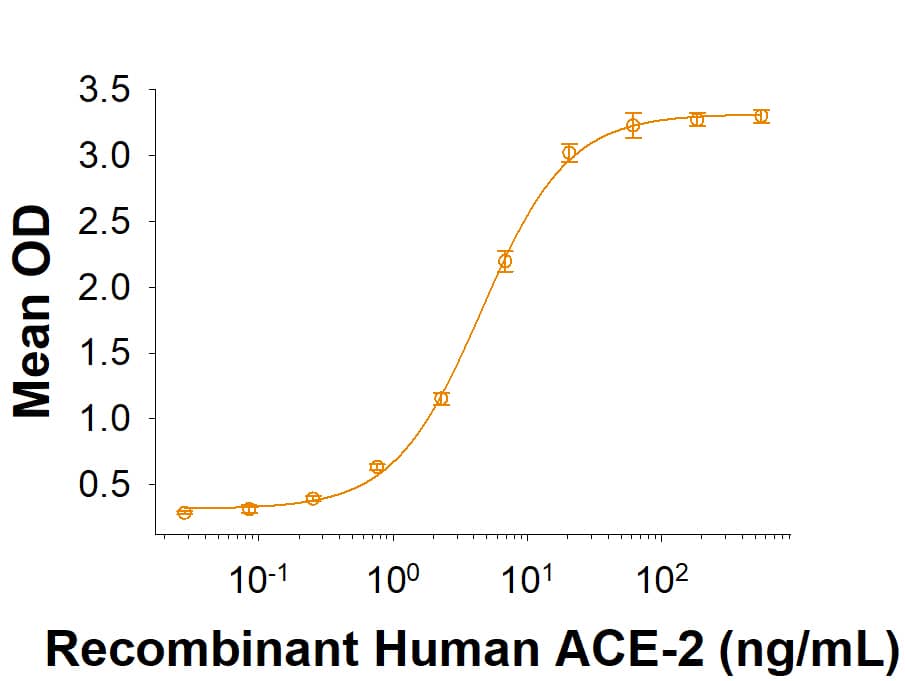
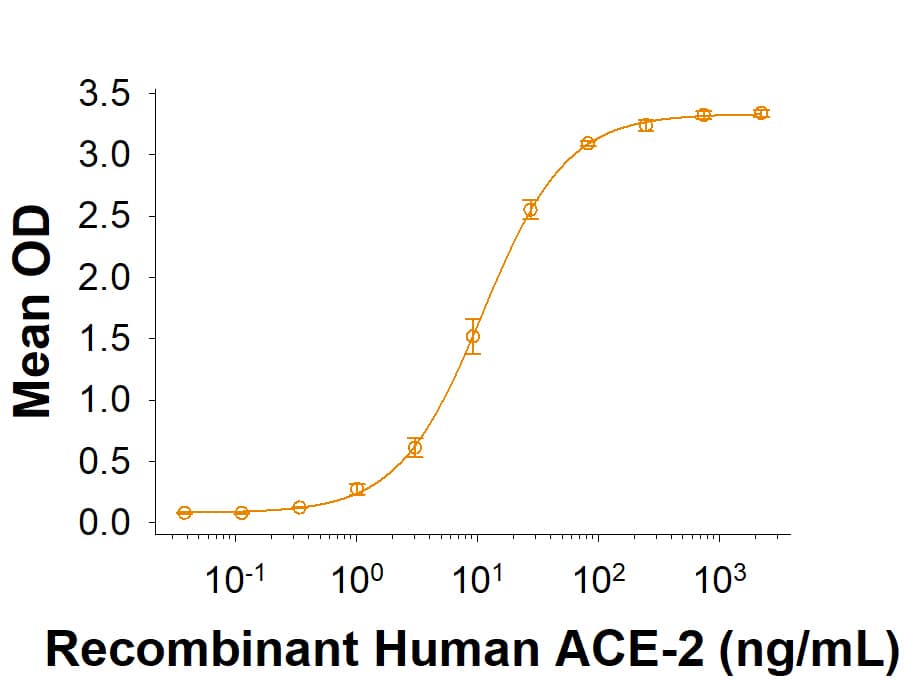
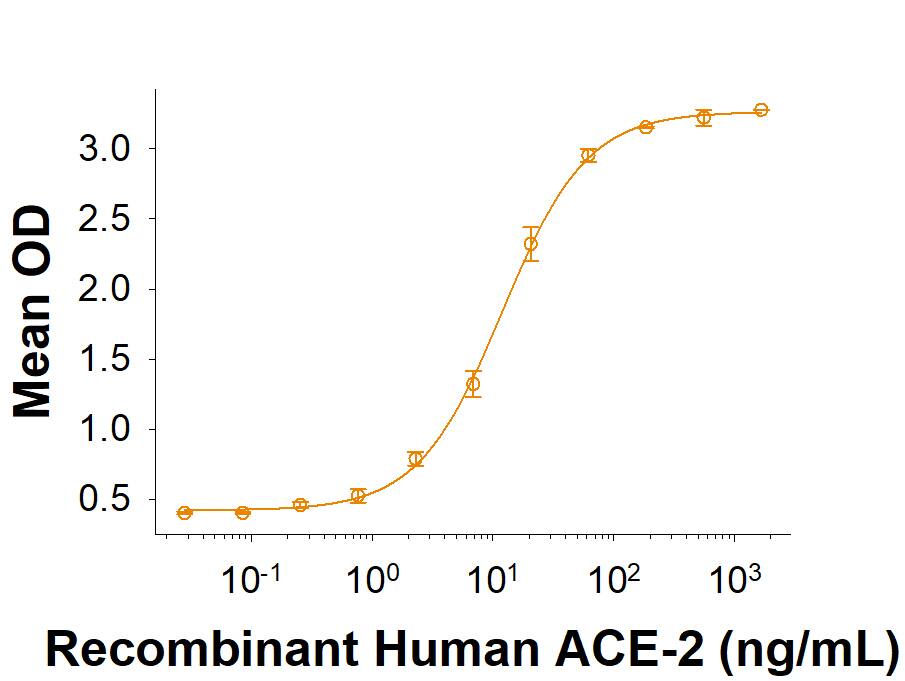
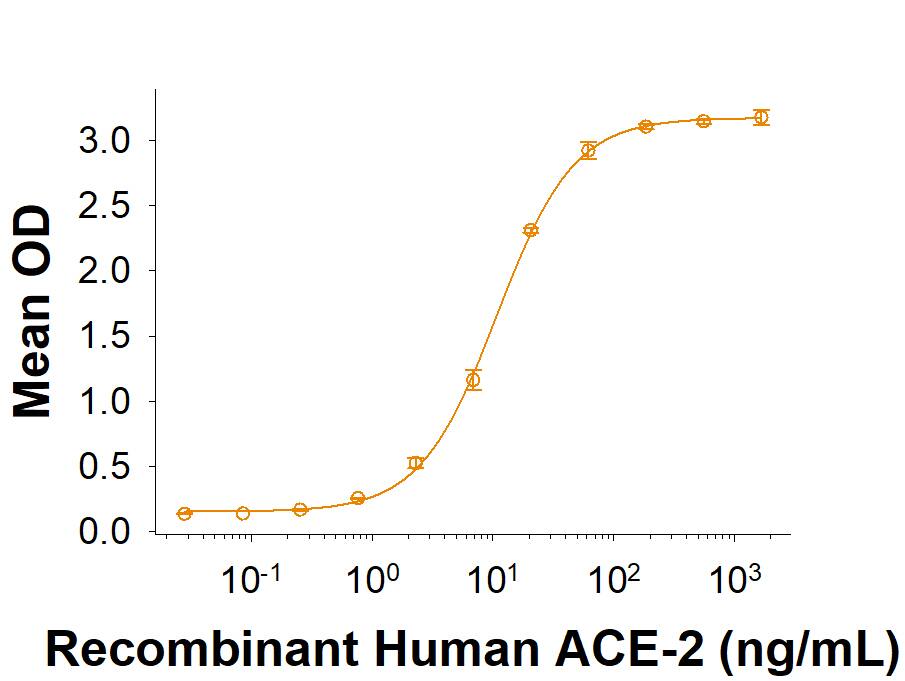
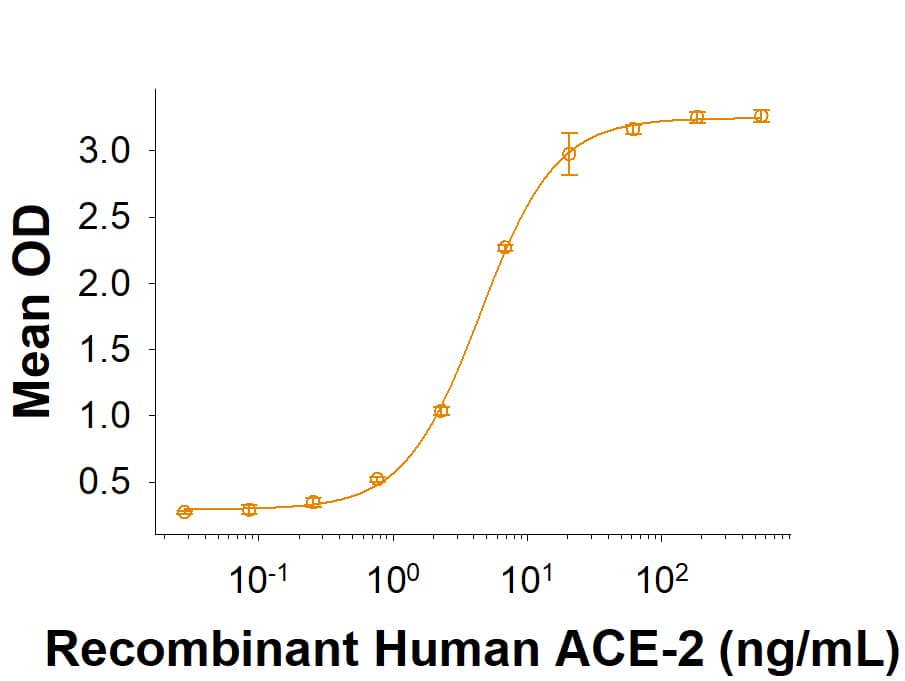
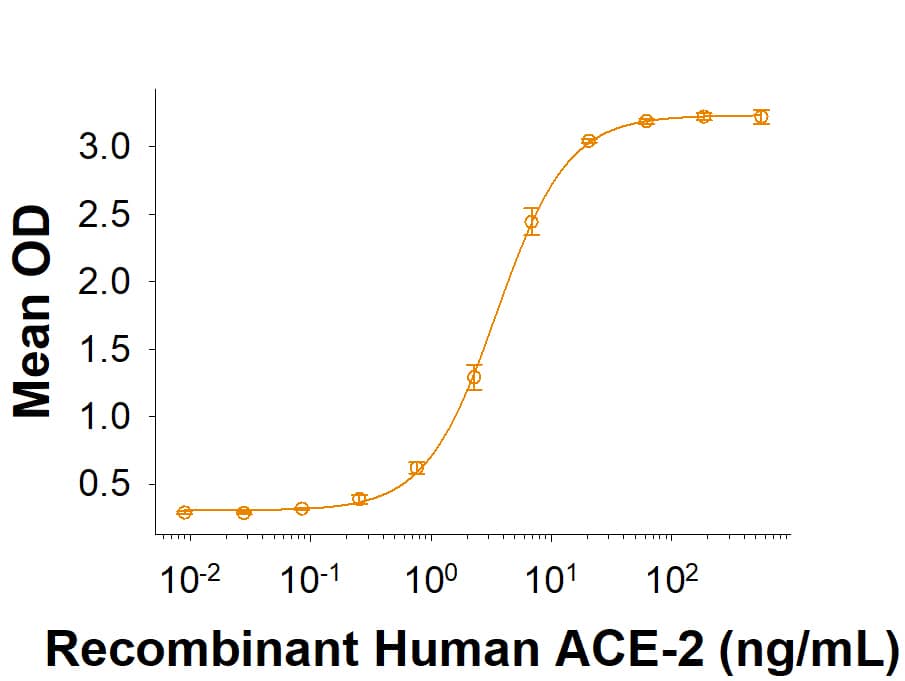
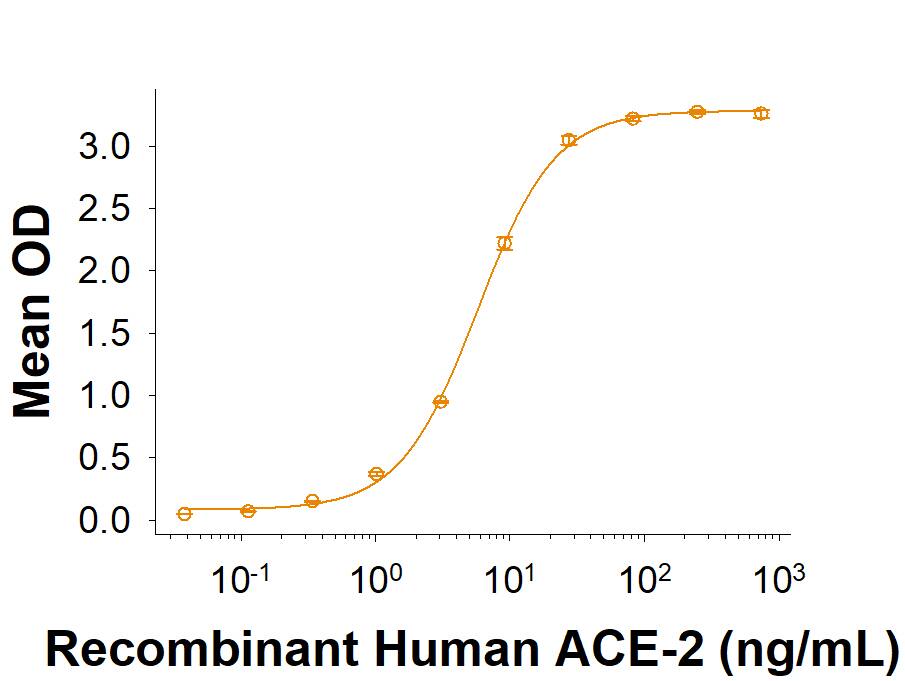
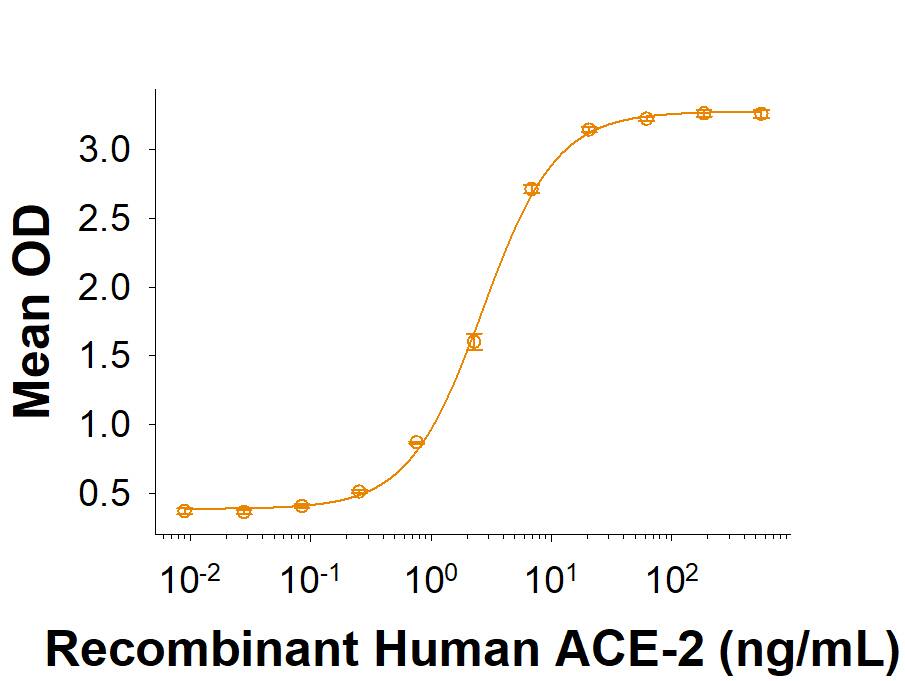
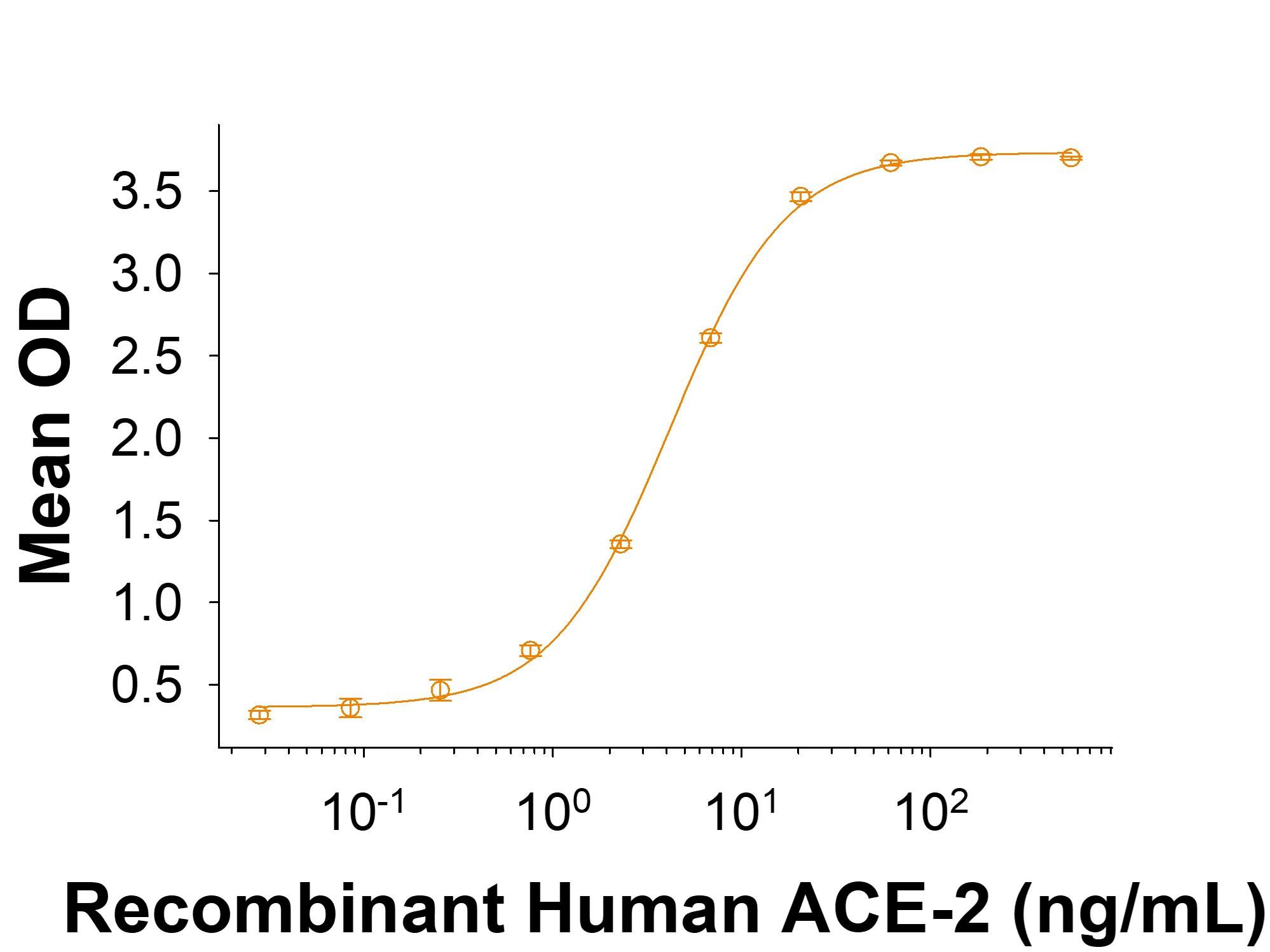
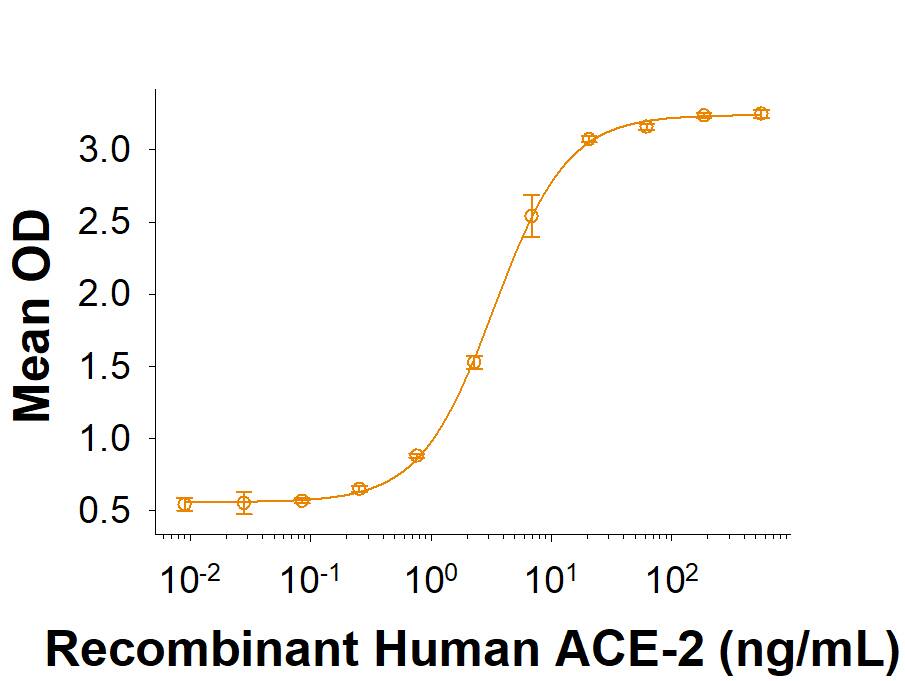
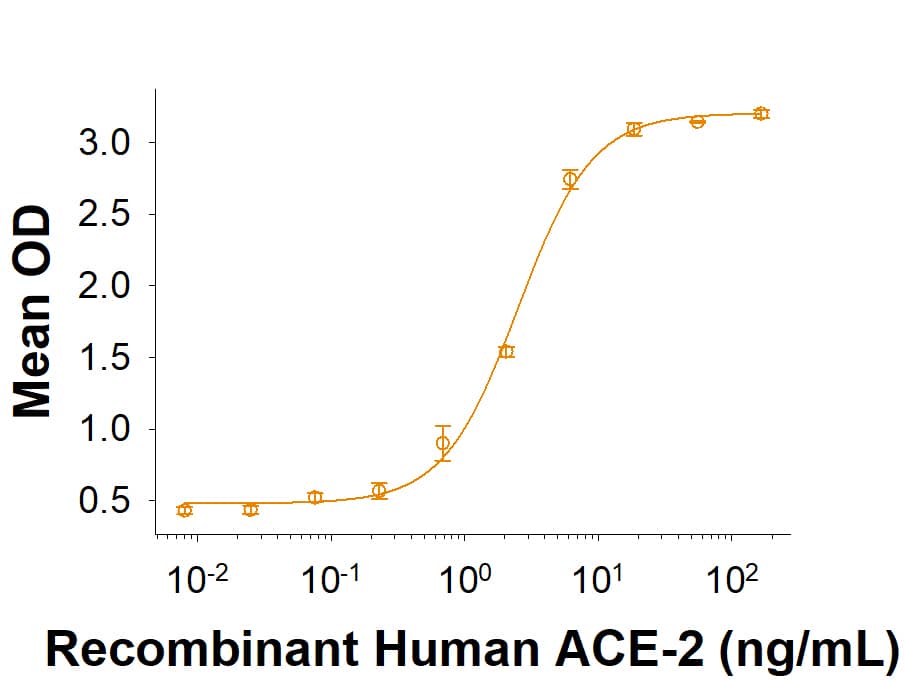
Spike S1 subunit refers to the N-terminal part of the coronavirus Spike protein. The S1 subunit contains an N-terminal domain in addition to the much-studied receptor binding domain (RBD). Spatially, the S1 subunit represents the most membrane-distal portion of the spike protein. For SARS-CoV-2, this subunit, specifically the RBD domain, is responsible for binding to ACE-2 on the surface of human cells and initiating viral entry.
Because this interaction is so important for viral entry into host cells, the RBD domain has been the focus of therapeutic and vaccine development for COVID-19. The N-terminal domain of the S1 subunit may also be involved in receptor binding independent of ACE-2. Current research is underway to better understand this domain as it may unlock new therapeutic strategies to fight SARS-CoV-2.
Products:
41 results for "Spike S1 Subunit Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
41 results for "Spike S1 Subunit Proteins and Enzymes" in Products
Spike S1 Subunit: Proteins and Enzymes
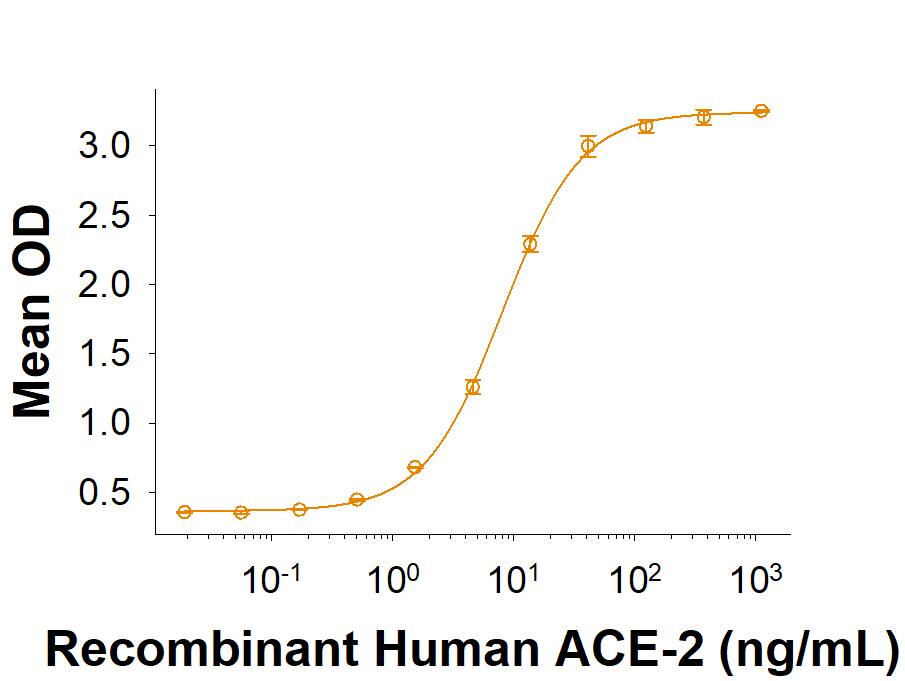
Spike S1 subunit refers to the N-terminal part of the coronavirus Spike protein. The S1 subunit contains an N-terminal domain in addition to the much-studied receptor binding domain (RBD). Spatially, the S1 subunit represents the most membrane-distal portion of the spike protein. For SARS-CoV-2, this subunit, specifically the RBD domain, is responsible for binding to ACE-2 on the surface of human cells and initiating viral entry.
Because this interaction is so important for viral entry into host cells, the RBD domain has been the focus of therapeutic and vaccine development for COVID-19. The N-terminal domain of the S1 subunit may also be involved in receptor binding independent of ACE-2. Current research is underway to better understand this domain as it may unlock new therapeutic strategies to fight SARS-CoV-2.
Products:
HEK293 Expressed
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
HEK293 Expressed
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
CHO Expressed
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Sf21 Insect Cell Expressed
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
His-tag. Biotinylated via Amines
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | K9N5Q8.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Sf21 Insect Cell Expressed
| Source: | Sf 21 (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | NP_828851.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
CHO Expressed
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | QHR63300.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
Tn5 Insect Cell Expressed
| Source: | T. ni (baculovirus) |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
CHO Expressed
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009825051.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009825051.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
CHO Expressed
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
CHO Expressed
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009825051.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | AAP41037.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Biotinylated
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_007188579.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | QHR63300.2 |
| Applications: | BA |
S477N, D614G
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
Alpha Variant (UK)
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
| Source: | CHO |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
D614G, Q677H
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | GelChrom |
D614G, Q677P, 20C-US Regional Variant
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |
A222V, D614G
| Source: | HEK293 |
| Accession #: | YP_009724390.1 |
| Applications: | BA |