Growth factors are secreted proteins that regulate a variety of biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, survival, and migration. They are essential for both embryonic tissue development and for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis in adult organisms. Growth factors can be produced by a variety of different cell types and they bind to specific transmembrane receptors on target cells to initiate intracellular signaling. Growth factor receptors are frequently receptor tyrosine kinases, which upon ligand binding, undergo dimerization, activation of their intracellular tyrosine kinase domains, and autophosphorylation. This leads to the recruitment of adaptor proteins and activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways that result in the expression of specific target genes.
There are many different types of growth factors, which are grouped into families based on structural similarities and evolutionary relationships. Different families of growth factors include the Angiopoietin, Epidermal growth factor (EGF), Ephrin, Fibroblast growth factor (FGF), Hedgehog, Insulin-like growth factor (IGF), Neurotrophin, Notch, Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), TGF-beta, and Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) families. Members of the different growth factor families typically share sequence or structural similarities, signal through common or related receptors, and/or act on specific cell types or tissues.
Growth factors can mediate autocrine, paracrine, juxtacrine, and endocrine signaling. Growth factors affect their local environment by acting directly on the cells that they are secreted by or on neighboring cells through autocrine and paracrine signaling, respectively. Some growth factors, such as Ephrins and the Notch family ligands, can also mediate juxtacrine signaling, which involves contact-dependent signaling between adjacent cells, while others can mediate endocrine signaling by entering the circulation and acting on distant cells.
Growth factors promote a broad range of cellular processes and can have both unique and overlapping functions. During development, growth factors regulate germ layer formation, body axis pattern formation, cellular differentiation, branching morphogenesis, limb formation, and organogenesis. In adult organisms, growth factors are involved in maintaining tissue homeostasis, wound healing, tissue remodeling, inflammation, regeneration, and metabolism. Due to the critical roles that growth factors play in development and growth, deficiencies in these factors are commonly associated with developmental defects, growth problems, and metabolic disorders. Conversely, increased levels of specific growth factors are associated with a variety of pathological conditions, including malignant transformation and tumor progression.
Growth Factor Products by Family

Angiopoietins
Angiopoietins
• Members of the Angiopoietin family of growth factors include Ang-1, Ang-2, Ang-3 (mouse)/Ang-4 (human)
• Angiopoietins signal through the Tie-1 receptor tyrosine kinase, which is primarily expressed on endothelial cells and early hematopoietic cells
• Angiopoietin-Tie signaling plays an important role in angiogenesis by regulating processes such as endothelial cell differentiation, vessel stabilization and remodeling, and pericyte recruitment

EGF Family
EGF Family
• Members of the EGF family include EGF, Amphiregulin, Betacellulin, Epigen, Epiregulin, HB-EGF, Neuregulins, and TGF-alpha
• The EGF R (ErbB) family consists of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGF R (ErbB1), ErbB2 (Her2), ErbB3 (Her3), and ErbB4 (Her4)
• EGF family ligands stimulate cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation and play an important role in many developmental processes

Ephrins
Ephrins
• Ephrins and their receptor tyrosine kinase receptors, Ephs, are divided into two classes, the Ephrin-A and Ephrin-B ligand families
• Ephrin-A ligands (EphrinA1-5) preferentially bind to EphA receptors (EphA1-8), while Ephrin-B ligands (EphrinB1-3) preferentially bind to EphB receptors (EphB1-6)
• Eph-Ephrin interactions are involved in regulating cell migration, tissue morphogenesis, axon guidance, and angiogenesis

FGF Superfamily
FGF Superfamily
• There are 22 FGF proteins in human and mice, 18 are secreted proteins and 4 are intracellular FGFs
• Secreted FGFs bind to one of four receptor tyrosine kinases (FGFR1-4) to promote intracellular signaling
• FGFs promote a broad range of cellular processes, including proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration, and are essential for both embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis

Hedgehog Family
Hedgehog Family
• In vertebrates, the Hedgehog family consists of at least three proteins: Sonic hedgehog (Shh), Desert hedgehog (Dhh), and Indian hedgehog (Ihh)
• Secreted hedgehog proteins bind to the Patched receptor, which transmits a signal to Smoothened resulting in Gli-mediated transcriptional activation
• Shh signaling is required for hematopoiesis, bone formation, neurogenesis, and gonad development

IGF Family
IGF Family
• Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-I and IGF-II belong to the family of insulin-like growth factors
• IGF-I and IGF-II primarily exert their effects through IGF-I R, which is a disulfide-linked, heterotetrameric tyrosine kinase receptor
• IGF signaling plays an important role in mediating cell proliferation, differentiation, motility, development, and metabolism

Neurotrophin Family
Neurotrophin Family
• Members of the Neurotrophin family include NGF, BDNF, Neurotrophin-3, and Neurotrophin-4
• Neurotrophins mediate their effects by binding to different receptors: the p75 neurotrophin receptor (NGF R), Trk receptor tyrosine kinases (TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC), and Sortilin
• Neurotrophins are growth factors that regulate the development, survival, and maintenance of neurons in the both the central and peripheral nervous systems

Notch Family
Notch Family
• Mammalian Notch ligands include the transmembrane proteins, DLL-1, DLL-3, DLL-4, Jagged 1, and Jagged 2
• Notch family receptors, Notch-1-4, are type I transmembrane proteins with intracellular domains that are cleaved following ligand-binding and translocate to the nucleus to regulate transcription
• Notch signaling regulates cell fate determination, cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, angiogenesis, and T cell-mediated immune responses
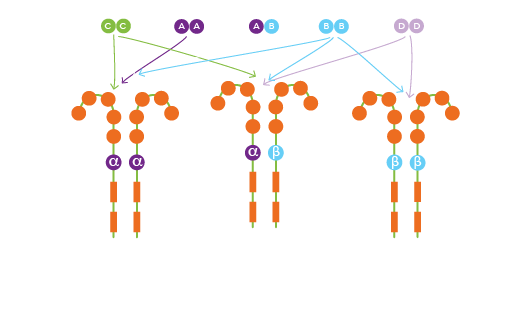
PDGF Family
PDGF Family
• PDGFs are produced from four different genes and are secreted as disulfide-linked homodimers with identical subunits, PDGF-AA, PDGF-BB, PDGF-CC, PDGF-DD, or as PDGF-AB heterodimers
• PDGFs differentially bind homodimer and heterodimer combinations of two receptor tyrosine kinases, PDGF R alpha and PDGF R beta
• PDGFs regulate cell survival, proliferation, and migration during development and wound healing

TGF-beta Superfamily
TGF-beta Superfamily
• Mammalian members of the TGF-beta superfamily include TGF-beta1-3, Activins, Inhibins, BMPs, GDFs, GDNFs, Nodal, Lefty, and MIS
• TGF-beta superfamily ligands form dimers and signal through heteromeric transmembrane receptor complexes consisting of type I and type II receptors with serine/threonine kinase domains
• TGF-beta superfamily proteins regulate cell growth, survival, differentiation, apoptosis, pattern formation, morphogenesis, and adult tissue homeostasis

VEGF Family
VEGF Family
• Members of the VEGF family include VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D, viral VEGF-E, and PlGF
• VEGFs signal through one of three VEGF receptor tyrosine kinases, VEGF R1, VEGF R2, or VEGF R3, and can also bind to HSPGs and Neuropilin-1 and Neuropilin-2 to modulate VEGF signaling
• VEGF signaling promotes cell proliferation, survival, and migration during vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and is important for development and wound healing

Wnt Superfamily
Wnt Superfamily
• In vertebrates, the Wnt family consists of 19 highly conserved, secreted glycoproteins
• Wnts can initiate beta-Catenin-dependent or beta-Catenin-independent signaling pathways through interactions with G protein-coupled Frizzled receptors and the co-receptors, LRP5/6, ROR1/2, Ryk, or PTK7
• Wnt signaling plays a central role in cell proliferation, motility, and differentiation during both embryonic development and adult tissue homeostasis
Growth Factor Products by Application
R&D Systems Growth Factors Are Frequently More Active than Leading Competitors' Proteins

R&D Systems Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 Protein Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1. The bioactivity of R&D Systems Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 (Catalog # 4645-RS; blue line) or recombinant human R-Spondin 1 from another company (purple line) was assessed by measuring the ability of the proteins to stimulate beta-Catenin activation in the HEK293T human kidney cell line using a TOPflash beta-Catenin/TCF reporter assay, in the presence of 5 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse Wnt-3a (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1324-WN). The ED50 for this effect for R&D Systems Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 was approximately 7-fold greater than the leading competitor’s R-Spondin 1 protein.

R&D Systems Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF-2 Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human FGF-2 Protein. The NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of R&D Systems Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF-2 (Catalog # 233-FB; orange line) or recombinant human FGF-2 from another company (blue line) and cell proliferation was assessed. The bioactivity of the R&D Systems FGF-2 protein was approximately 3-fold greater than the leading competitor’s FGF-2 protein.

R&D Systems Recombinant Human GDNF Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human GDNF Protein. The bioactivity of R&D Systems Recombinant Human GDNF (Catalog # 212-GD; orange line) or recombinant human GDNF from another company (blue line) was assessed by measuring the ability of the proteins to stimulate proliferation of SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells, in the presence of Recombinant Human GFR alpha-1 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 714-GR). The activity of the R&D Systems GDNF protein was approximately 9-fold greater than the leading competitor’s GDNF protein.

R&D Systems Recombinant Human Wnt-3a Protein Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Wnt-3a. The bioactivity of R&D Systems Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (Catalog # 5036-WN; orange line) or recombinant human Wnt-3a from another company (green line) was assessed by measuring the ability of the proteins to induce alkaline phosphatase production in the MC3T3-E1 mouse preosteoblast cell line. The ED50 of R&D Systems Recombinant Human Wnt-3a was 1.7-fold better than the leading competitor’s Wnt-3a protein, with more than twice the maximum response.
Protein Characterization Using SEC-MALS Analysis
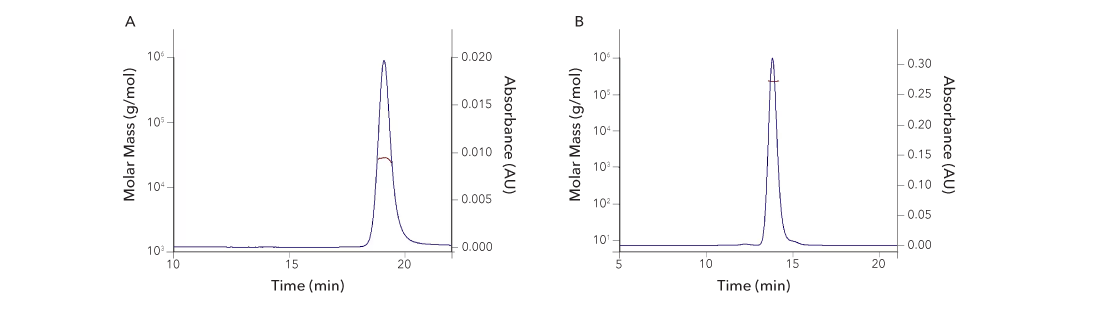
A. Recombinant Human GDNF Protein SEC-MALS. Recombinant human GDNF (Catalog # 212-GD) has a molecular weight (MW) of 27.5 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a homodimer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).
| SEC-MALS Data | Result |
| Retention Time | 18.8-19.4 min |
| MW-Predicted (Monomer) | 11.6 kDa |
| MW-MALS | 27.5 kDa |
| Polydispersity | 1.002 |
| System Suitability: BSA Monomer 66.4 ± 3.32 kDa | Pass |
B. Recombinant Human EGFR Fc Chimera Protein SEC-MALS Recombinant Human EGFR Fc Chimera (Catalog # 344-ER) has a molecular weight (MW) of 229 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a homodimer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).
| SEC-MALS Data | Result |
| Retention Time | 13.4-14.1 min |
| MW-Predicted (Monomer) | 95.1 kDa |
| MW-MALS | 229 kDa |
| Polydispersity | 1 |
| System Suitability: BSA Monomer 66.4 ± 3.32 kDa | Pass |
R&D Systems Proteins Are Rigorously Tested for Lot-to-Lot Consistency

R&D Systems Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 Displays Minimal Lot-to-Lot Variability. Three independent lots of Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 4645-RS) were tested for their ability to stimulate beta-Catenin activation in the HEK293T human kidney cell line using a TOPflash beta-Catenin/TCF reporter assay, in the presence of 5 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse Wnt-3a (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1324-WN). Each trace on the graph represents data obtained from Recombinant Human R-Spondin 1 from a different manufacturing run, demonstrating the lot-to-lot consistency of the protein.

R&D Systems Recombinant Human Wnt-3a Displays Minimal Lot-to-Lot Variability. Three independent lots of Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (R&D Systems, Catalog # 5036-WN) were tested for their ability to induce alkaline phosphatase production in the MC3T3-E1 mouse preosteoblast cell line. Each trace on the graph represents data obtained from Recombinant Human Wnt-3a from a different manufacturing run, demonstrating the lot-to-lot consistency of the protein.
Customer Success Stories
Featured Growth Factor Products

Animal-Free Recombinant Proteins
Animal-Free Recombinant Proteins
Ensure a seamless transition from preclinical research into clinical manufacturing by starting your preclinical experiments with our Animal-Free RUO proteins. R&D Systems Animal-Free RUO proteins are produced in dedicated animal-free laboratories and are manufactured using the same systems as our Animal-Free GMP-Grade proteins.

Growth Factor Blocking/Neutralizing Antibodies
Growth Factor Blocking/Neutralizing Antibodies
Blocking and neutralizing antibodies bind to their targets and either directly interfere with their functions or negatively regulate their downstream cellular effects. Bio-Techne offers a large selection of R&D Systems™ blocking/neutralizing antibodies against specific growth factors or their receptors that have been validated in relevant biological assays.

Immunoassays for Growth Factor Detection
Immunoassays for Growth Factor Detection
From our complete, ready-to-use Quantikine™ ELISA Kits to our multiplex Luminex® Assays and fully automated Simple Plex™ Assays, you can count on our immunoassays to deliver accurate, reproducible, high-quality data for every experimental sample that you test.
Featured Growth Factor Resources

Growth Factor Signaling Pathways
Growth Factor Signaling Pathways
Growth factors activate intracellular signaling pathways that regulate a diverse range of biological processes, including development, cell proliferation, differentiation, motility, angiogenesis, and adult tissue homeostasis. Explore the signaling pathways that are activated by different growth factor families and the biological effects that they mediate using our interactive signaling pathways.

Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors Wall Poster
Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors Wall Poster
Learn about the different families of growth factors and morphogens that regulate human development with our Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors wall poster. The poster includes information on the structures, native molecular weights, and receptors of each protein and will serve as a great reference tool to keep in your lab or office space.

Cell Culture Reagents
Cell Culture Reagents
Browse our complete collection of products for cell culture. We offer a comprehensive range of reagents to promote robust cell growth, including media and supplements, basement membrane extracts, and custom cell culture services.





















