Fibroblast Growth Factor Superfamily
FGF Ligands
The Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) superfamily consists of 22 proteins in mice and humans. Of these, 18 are secreted proteins and 4 are intracellular FGFs, known as FGF homologous factors. The secreted FGFs are divided into six subfamilies based on sequence homology and phylogeny. These include the FGF-1, FGF-4, FGF-7, FGF-8, FGF-9, and FGF-19 subfamilies. FGF-1 and FGF-2 belong to the FGF-1 subfamily, FGF-4, FGF-5, and FGF-6 belong to the FGF-4 subfamily, FGF-3, FGF-7, FGF-10, and FGF-22 belong to the FGF-7 subfamily, FGF-8, FGF-17, and FGF-18 belong to the FGF-8 subfamily, FGF-9, FGF-16, and FGF-20 belong to the FGF-9 subfamily, and FGF-19, FGF-21, and FGF-23 belong to the FGF-19 subfamily. With the exception of the FGF-19 subfamily, secreted FGFs have moderate to high affinity for heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) that are tethered to the cell membrane or associated with the extracellular matrix and as a result, they mediate paracrine signaling. In contrast, members of the FGF-19 subfamily bind to HSPGs with significantly lower affinity, allowing them to pass through the extracellular matrix, enter the circulation, and mediate endocrine signaling. The intracellular FGFs include FGF-11, FGF-12, FGF-13, and FGF-14. In contrast to the secreted FGFs, the intracellular FGFs are non-signaling proteins that are associated with the cytosolic C-terminal tail of voltage-gated sodium channels and regulate myocardial and neuronal excitability.
FGF Receptors
There are four FGF signaling receptors, FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4, and one decoy receptor, FGFR5, which can bind to FGFs but lacks an intracellular signaling domain. FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 are single-pass transmembrane proteins with 3 extracellular Ig-like domains, an 8-residue acidic box between the first and second Ig-like domain, and a split intracellular tyrosine kinase domain. The second and third Ig-like domains in the FGF receptor mediate FGF binding. Alternative splicing of FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 can generate two different isoforms of these receptors (b and c isoforms) that differ in their third extracellular Ig-like domain and as a result, have different ligand binding profiles. In addition to FGF receptors, FGF signaling also requires the presence of a co-receptor. HSPGs act as a co-receptor for the paracrine signaling FGFs, while Klotho family proteins function as co-receptors for the endocrine signaling FGFs. In the case of the paracrine signaling FGFs, crystal studies have indicated that HSPGs promote the formation of 2:2:2 HSPG-FGF-FGF receptor complexes.
FGF Signaling
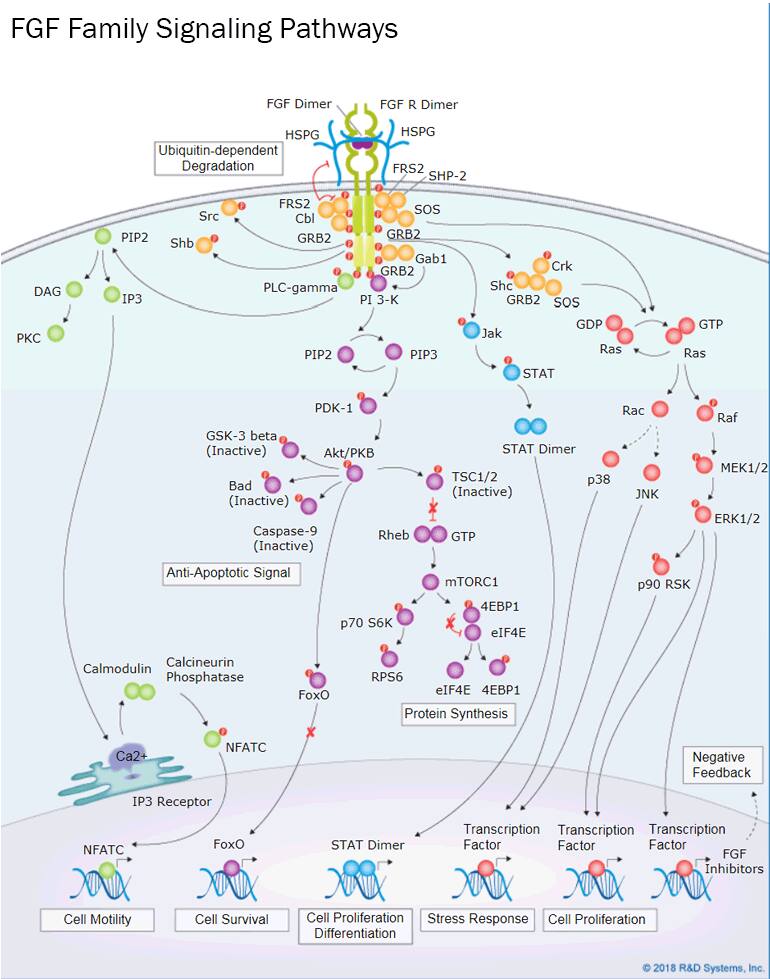
FGF signaling is regulated by the binding specificities of different FGF ligands and their receptors. Ligand binding to the FGF receptor triggers a conformational change in the receptor, resulting in receptor dimerization, activation of its intracellular tyrosine kinase domain, and receptor phosphorylation. Phosphorylated tyrosine residues in the FGF receptor then serve as docking sites for SH2 domain-containing proteins, such as FRS2, GRB2, Shb, Shc, Src, and PLC-gamma, which trigger multiple downstream signaling pathways. These include the Ras-MAPK pathway, the PI 3-K-Akt pathway, the PLC-gamma-PKC pathway, and the Jak-STAT pathway. Activation of these signaling pathways leads to the expression of specific target genes that mediate the biological effects associated with different FGFs. FGF signaling is complicated by the fact that most FGFs can bind to multiple FGF receptors with different affinities. As a result, a single FGF or the presence of multiple FGFs may have synergistic or differential effects depending on the concentration of each and the cellular context.
Biological Effects of FGFs
FGF signaling is essential for both embryonic development and for the maintenance of tissue homeostasis in adult organisms. FGFs promote a broad range of cellular processes including proliferation, survival, differentiation, and migration. During development, secreted FGFs regulate germ layer formation, pattern formation, cellular differentiation, branching morphogenesis, limb formation, and organogenesis, including brain, lung, heart, skeletal system, urinary system, and lymphatic system development. In adult organisms, FGF signaling is involved in tissue repair, regeneration, metabolism, and inflammation. Gain or loss of function mutations in FGFs are associated with a variety of developmental defects and and pathological conditions including genetic skeletal diseases, chronic kidney disease, cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases, metabolic diseases, degenerative diseases, and cancer.
FGF Superfamily Ligands - Products by Molecule
| FGF acidic/FGF-1 | FGF basic/FGF-2 | FGF-3 | FGF-4 | FGF-5 | FGF-6 |
| KGF/FGF-7 | FGF-8 | FGF-9 | FGF-10 | FGF-11 | FGF-12 |
| FGF-13 | FGF-15 | FGF-16 | FGF-17 | FGF-18 | FGF-19 |
| FGF-20 | FGF-21 | FGF-22 | FGF-23 | SUN 11602 (bFGF mimetic) |
FGF Superfamily Receptors - Products by Molecule
| FGFR1 | FGFR1 alpha | FGFR1 beta | FGFR2 | FGFR2 alpha | FGFR2 beta |
| FGFR3 | FGFR4 | FGFR1-4 | FGFR5/FGFRL1 | FGF Receptor Inhibitors | Golgi Glycoprotein 1/GLG1 |
FGF Superfamily Regulators - Products by Molecule
| alpha 2-Macroglobulin | alpha 2-Macroglobulin-like 1/A2ML1 | CNPY2 | FGF-BP | FGFBP2 |
| FGFBP3 | FRS2 | Klotho | Klotho beta | LRIT3 |
| Pentraxin3/TSG-14 | Shisa-4 | SPRY1 | SPRY2 | SPRY3 |
FGF Intracellular Signaling - Products by Molecule
R&D Systems Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF-2 (146 aa) Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human FGF-2 (146 aa) Protein

R&D Systems Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF-2 Displays Higher Activity than a Leading Competitor’s Recombinant Human FGF-2 Protein. The NR6R-3T3 mouse fibroblast cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of R&D Systems Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF-2 (Catalog # 233-FB; orange line) or recombinant human FGF-2 from another company (blue line) and cell proliferation was assessed. The bioactivity of the R&D Systems FGF-2 protein was approximately 3-fold greater than the leading competitor’s FGF-2 protein.
Protein Characterization Using SEC-MALS Analysis
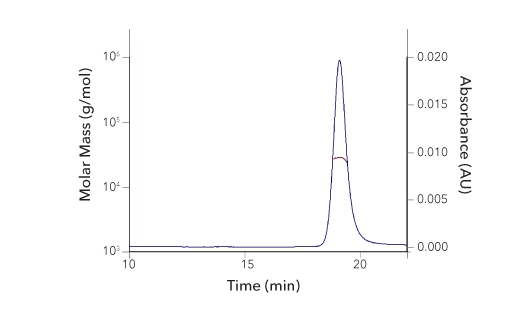
Recombinant Human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF (145 aa), Tissue Culture Grade Protein SEC-MALS. Recombinant human FGF basic/FGF2/bFGF, 145 aa TC Grade (Catalog # 4114-TC) has a molecular weight (MW) of 17.2 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a monomer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).
| SEC-MALS Data | Result |
| Retention Time | 16.0-16.6 min |
| MW-Predicted (Monomer) | 16.0 kDa |
| MW-MALS | 17.2 kDa |
| Polydispersity | 1.001 |
| System Suitability: BSA Monomer 66.4 ± 3.32 kDa | Pass |
Immunostaining of FGF-9 in Human Placenta Using R&D Systems Goat Anti-Human FGF-9 Antigen Affinity-Purified Polyclonal Antibody

Detection of FGF-9 in Human Placenta. FGF-9 was detected in immersion-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections of human placenta using a Goat Anti-Human FGF-9 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF-273-NA). Tissue was stained with an Anti-Goat HRP-AEC Cell & Tissue Staining Kit and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue).
Cell Proliferation Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human KGF/FGF-7 and Neutralization by a Goat Anti-Human KGF/FGF-7 Antigen Affinity-Purified Polyclonal Antibody

KGF/FGF-7-induced Cell Proliferation is Neutralized Using a Goat Anti-Human KGF/FGF-7 Polyclonal Antibody. The 4MBr-5 rhesus monkey epithelial cell line was treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human KGF/FGF-7 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 251-KG) and cell proliferation was assessed (orange line). The ED50 for this effect is 6-60 ng/mL. Proliferation stimulated by 125 ng/mL Recombinant Human KGF/FGF-7 was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Goat Anti-Human KGF/FGF-7 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF-251-NA; blue line). The ND50 for this effect is typically 6-12 ug/mL.
Immunostaining of FGF-15 in Day E15 Mouse Embryo Using R&D Systems Sheep Anti-Mouse FGF-15 Antigen Affinity-Purified Polyclonal Antibody

Detection of FGF-15 in Mouse Embryo. FGF-15 was detected in immersion-fixed, frozen sections of day E15 mouse embryo using a Sheep Anti-Mouse FGF-15 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF6755). Tissue was stained using the Anti-Sheep HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # CTS019; brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to the processes of dorsal root ganglia neurons.
Cell Proliferation Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human FGF-21 and Neutralization by a Goat Anti-Human FGF-21 Monoclonal Antibody

FGF-21-induced Cell Proliferation is Neutralized Using a Goat Anti-Human FGF-21 Monoclonal Antibody. In the presence of Recombinant Mouse Klotho beta (R&D Systems, Catalog # 2619-KB), the BaF3 mouse pro-B cell line transfected with human FGF-RIIIc was treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human FGF-21 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 2539-FG) and cell proliferation was assessed (orange line). The ED50 for this effect is 0.06-0.4 ug/mL. Under these conditions, proliferation stimulated by 500 ng/mL Recombinant Human FGF-21 was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Goat Anti-Human FGF-21 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB25373; blue line). The ND50 for this effect is typically 0.5-3 ug/mL.
Featured Products for FGF Superfamily Research

Immunoassays for Detecting FGFs
Immunoassays for Detecting FGFs
From our complete ready-to-use Quantikine™ ELISA Kits to our more flexible DuoSet™ ELISA Development Systems, we offer a large selection of immunoassays for measuring different FGFs. Whatever target you’re interested in, you can count on our immunoassays to deliver accurate, reproducible data for every experimental sample that you test.

Proteome Profiler™ Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array
Proteome Profiler™ Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array
The Proteome Profiler Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array offers a simple and inexpensive method to simultaneously detect the phosphorylation of 37 different kinases in a single sample using chemiluminescence and standard Western blotting equipment. Utilize this multiplex membrane-based assay to explore the signaling pathways activated by different FGFs.
Featured FGF Superfamily-Related Resources

Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors Wall Poster
Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors Wall Poster
Learn about the different families of growth factors and morphogens that regulate human development with our Periodic Table of Human Developmental Factors wall poster. The poster includes information on the structures, native molecular weights, and receptors for each protein and will serve as a great reference tool to keep in your lab or office space.

Growth Factor Signaling Pathways
Growth Factor Signaling Pathways
Growth factors activate intracellular signaling pathways that regulate a diverse range of biological processes, including development, cell proliferation, differentiation, motility, angiogenesis, and adult tissue homeostasis. Explore the signaling pathways that are activated by different growth factor families and the biological effects that they mediate using our interactive signaling pathways.

Products for Stem Cell Research
Products for Stem Cell Research
Minimize variability in your stem cell experiments and ensure high performance by using our stem cell culture reagents. From isolation and culture to verification, reprogramming, differentiation, and characterization, we have the products that you need for your stem cell work.