Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Protein Best Seller
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 5439-DK

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Thr32-His266
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
The ED50 for this effect is 10.0-250 ng/mL.
Reviewed Applications
Read 5 reviews rated 5 using 5439-DK in the following applications:
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Protein
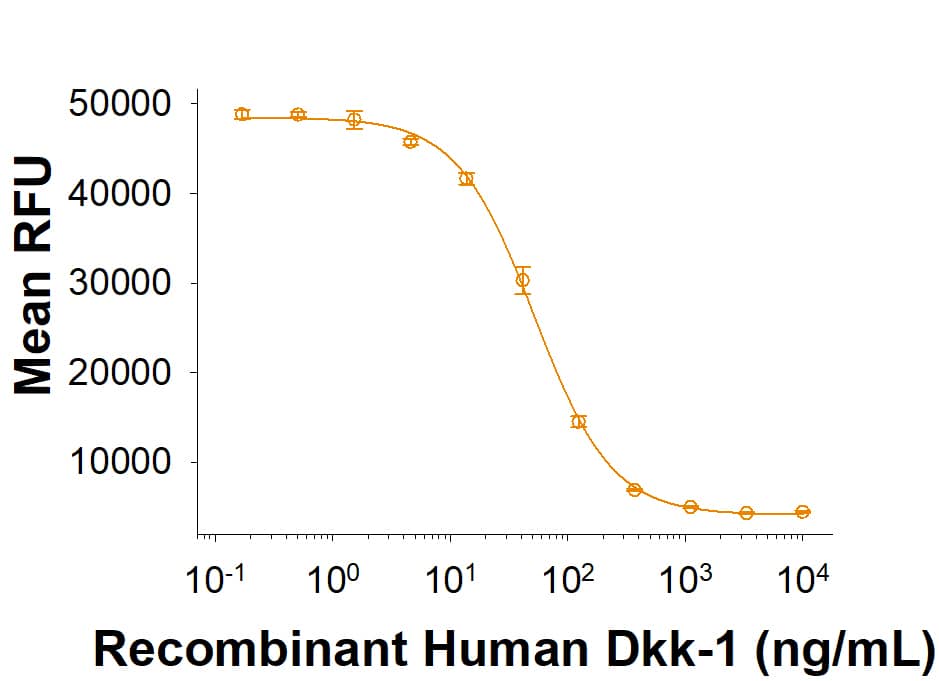
Recombinant Human Dkk‑1 Protein Bioactivity.
Recombinant Human Dkk‑1 (Catalog # 5439-DK) inhibits Wnt induced TCF reporter activity in HEK293 human embryonic kidney cells. The ED50 for this effect is 10.0-250 ng/mL.iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes Differentiated on Cultrex Stem Cell Qualified RGF BME Express Stage-specific Markers.
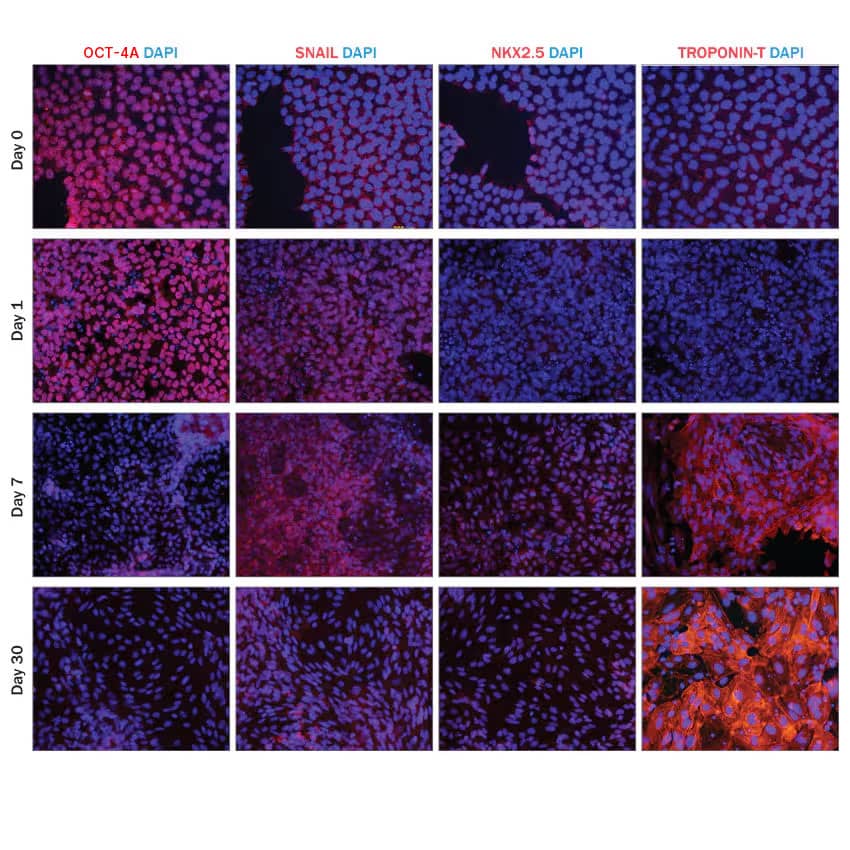
JOY6 human iPSCs were cultured in media containing Cultrex™ Stem Cell Qualified RGF BME (3434-010-02) and N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) along with Recombinant Human Activin A on day 0, Recombinant Human FGF-basic (4114-TC), Recombinant Human BMP-4, and CHIR99021 (4423) on days 1-5, and Recombinant Human Dkk-1 (Catalog # 5439-DK) on days 5-7 to induce cardiomyocyte differentiation. Cells were then cultured in media supplemented with N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) on days 7-12 and media supplemented with N21-MAX Media Supplement (AR008) from day 12 and beyond. Cells were fixed and stained for stage-specific markers at select time points during the procedure. The pluripotency marker Oct-4 was detected using a Mouse Anti-Human Oct-4A Monoclonal Antibody (MAB17591). The mesoderm marker, Snail is expressed intermediately during differentiation (Day 1). It was detected using a Goat Anti-Human Snail Polyclonal Antibody (AF3639). The cardiomyocyte markers NKX2.5 and Troponin T are not present in cells during early (Day 0) and intermediate (Day1) differentiation and become more highly expressed during the later stages of differentiation (Day 7, Day 30). NKX2.5 was detected using a Goat Anti-Human NKX2.5 Polyclonal Antibody (AF2444) and Troponin T was detected using a Mouse Anti-Human Cardiac Troponin T Monoclonal Antibody (MAB1874). Snail and NKX2.5 primary antibodies were visualized with a NorthernLights™ 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Goat IgG Secondary Antibody (NL001). Oct-4 and Troponin T were visualized with a NorthernLights 557-conjugated Donkey Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (NL007).iPSC-derived Cardiomyocytes Express Atrial and Ventricular Markers.
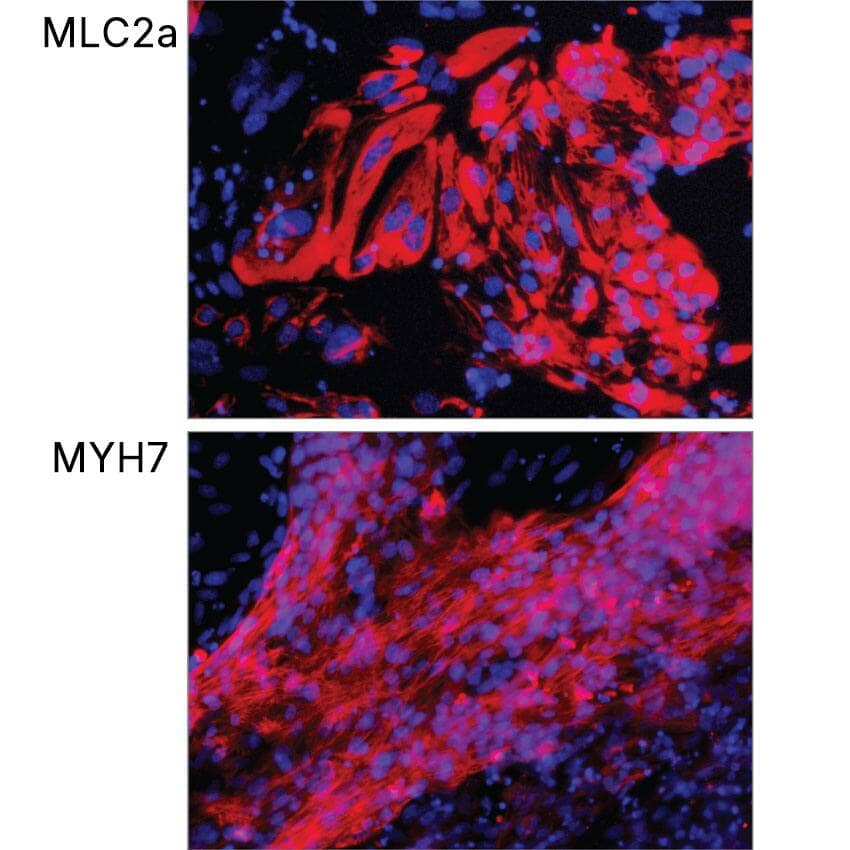
JOY6 human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) were differentiated into cardiomyocytes in media containing Cultrex™ Stem Cell Qualified Reduced Growth Factor Basement Membrane Extract (3434-010-02) and N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) along with Recombinant Human Activin A on day 0, Recombinant Human FGF-basic (4114-TC), Recombinant Human BMP-4, and CHIR99021 (4423) on days 1-5, and Recombinant Human Dkk-1 (Catalog # 5439-DK) on days 5-7. Following culture in media supplemented with N21-MAX Insulin Free Media Supplement (AR010) on days 7-12 and media supplemented with N21-MAX Media Supplement (AR008) from day 12 and beyond, cells were fixed and stained for the atrial-specific marker, MLC2a, and the ventricle-specific marker, MYH7 using a Rabbit Anti-Human MYH7 Monoclonal Antibody (MAB90961).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 5439-DK
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 5439-DK/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 100 μg/mL in PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Dkk-1
Dickkopf related protein 1 (Dkk-1) is the founding member of the Dickkopf family of proteins that includes Dkk-1, -2, -3, -4, and a related protein, Soggy (1, 2). Dkk proteins are secreted proteins that contain two conserved cysteine-rich domains separated by a linker region. Each domain contains ten cysteine residues (1‑3). Mature human Dkk-1 is a 40 kDa glycosylated protein that shares 86%, 87%, 90% and 91% aa sequence identity with mouse, rat, rabbit and bovine Dkk-1, respectively. It also shares 42% and 36% aa identity with human Dkk-2 and Dkk-4, respectively. Dkk-1 and Dkk-4 are well documented antagonists of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway (1, 2). This pathway is activated by Wnt engagement of a receptor complex composed of the Frizzled proteins and one of two low-density lipoprotein receptor-related proteins, LRP5 or LRP6 (4). Dkk-1 antagonizes Wnt by forming ternary complexes of LRP5/6 with Kremen1 or Kremen2 (4, 5). Dkk-1/LRP6/Krm2 complex internalization has been shown to down-regulate Wnt signaling (4, 5). Dkk-1 is expressed throughout development and antagonizes Wnt-7a during limb development (6, 7). Other sites of expression include developing neurons, hair follicles and the retina of the eye (8, 9). The balance between Wnt signaling and Dkk-1 inhibition is critical for bone formation and homeostasis (10). Insufficient or excess Dkk-1 activity in bone results in increased or decreased bone density, respectively (8, 11). In adults, Dkk-1 is expressed in osteoblasts and osteocytes, and neurons. Cerebral ischemia induces Dkk-1 expression, which contributes to neuronal cell death (12).
References
- Krupnik, V.E. et al. (1999) Gene 238:301.
- Niehrs, C. (2006) Oncogene 25:7469.
- Bullock, C.M. et al. (2004) Mol. Pharmacol. 65:582.
- Mao, B. et al. (2001) Nature 411:321.
- Mao, B. et al. (2002) Nature 417:664.
- Kemp, C. et al. (2005) Dev. Dyn. 233:1064.
- Adamska, M. et al. (2004) Dev. Biol. 272:134.
- Li, J. et al. (2006) Bone 36:754.
- Verani, R. et al. (2006) J. Neurochem. 101:242.
- Pinzone, J.J. et al. (2009) Blood 113:517.
- Morvan, F. et al. (2006) J. Bone Miner. Res. 21:934.
- Cappuccio, I. et al. (2005) J. Neurosci. 25:2647.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Dkk-1 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Dkk-1 Protein
For research use only