IL-12 Family Cytokines

IL-12 Family Cytokines, Receptors, and Intracellular Signaling Pathways
IL-12, IL-23, IL-27, IL-35, and IL-39 are heterodimeric cytokines belonging to the IL-12 family. Each cytokine in this family consists of an alpha subunit (p19, p28, or p35) that is linked through a disulfide bond to one of two beta subunits (p40 or EBI3). The alpha subunits are structurally related to IL-6 and have a four alpha-helix bundle structure oriented in an up-up-down-down topology, while the beta subunits are structurally similar to the soluble class I cytokine receptors (i.e. sIL-6 R alpha). As a result, IL-12 family cytokines have a structure that is equivalent to a cytokine subunit linked to a soluble receptor. Significantly, the alpha and beta subunits that make up these heterodimeric cytokines are shared among different members of the IL-12 family, and chain pairing promiscuity partially contributes to the broad range of effects that IL-12 family cytokines have on host immunity. While IL-12 consists of the p35 alpha subunit paired with the p40 beta subunit, IL-23 consists of the p19 alpha subunit, which is homologous to IL-12 p35, paired with the p40 beta subunit. Similarly, IL-27, IL-35, and IL-39 consist of the p28, p35, or p19 alpha subunits, respectively, paired with the Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3 (EBI3) beta subunit. The p28 alpha subunit of IL-27 is a polypeptide related to the IL-12/IL-35 p35 alpha subunit, while EBI3 is an IL-12/IL-23 p40-related protein. IL-12, IL-23, and IL-27 are primarily produced by activated antigen-presenting cells, including B cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. In contrast, IL-35 is primarily produced by regulatory T cells and activated B cells and IL-39 is produced by activated B cells and keratinocytes.
IL-12 Family Receptors
IL-12 family cytokines signal through heterodimeric receptors belonging to the class I cytokine receptor family. Each receptor subunit is a type I transmembrane protein with an extracellular domain that contains a cytokine receptor homology domain consisting of two fibronectin type III domains. The more N-terminal fibronectin type III domain contains four positionally conserved cysteine residues that form interstrand disulfide bonds, while the second fibronectin type III domain has a conserved Trp-Ser-X-Trp-Ser (WSXWS) sequence motif and is important for the tertiary structure. With the exception of IL-23 R, the cytokine receptor homology domain in the IL-12 family receptor subunits is followed by three additional fibronectin type III domains, and most of these receptor chains also contain an N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain, with the exception of IL-27 R alpha/WSX-1. Similar to the chain promiscuity displayed by the IL-12 family cytokines, the heterodimeric receptors for these cytokines are also composed of shared subunits. IL-12 binds to a receptor complex composed of IL-12 R beta 1 and IL-12 R beta 2, while IL-23 binds to a receptor complex composed of IL-23 R and IL-12 R beta 1. Similarly, IL-27, IL-35 and IL-39 all bind to receptor complexes that contain the gp130 receptor subunit, which is common to the IL-6 cytokine family receptors. The gp130 subunit is paired with either IL-27 R alpha/WSX-1 to form the IL-27 receptor complex, IL-12 R beta 2 to form the IL-35 receptor complex on T cells, or IL-23 R to form the IL-39 receptor complex. In contrast to the other IL-12 family cytokines, IL-35 is unique in that it can bind to more than one receptor complex. Besides the IL-12 R beta 2-gp130 complex, IL-35 has also been shown to bind to gp130 or IL-12 R beta 2 homodimeric receptor complexes, as well as a receptor complex consisting of IL-27 R alpha/WSX-1 and IL-12 R beta 2.
IL-12 Family Signaling
IL-12 family receptors associate with members of the Jak family of kinases (Jak1, Jak2, and Tyk2), which upon activation, promote the recruitment and phosphorylation of STAT proteins. Phosphorylated STATs form homodimers or heterodimers that translocate to the nucleus where they regulate gene expression. Although IL-12 family cytokines promote similar signaling pathways overall, they can activate multiple STAT proteins and their distinct biological effects have been attributed to the primary activation of one or two different STAT proteins. For example, while IL-12 primarily activates STAT4 and to a lesser extent STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5, IL-23 primarily activates STAT3 and to a lesser extent STAT4, STAT1, and STAT5.
Many of the distinct effects of the IL-12 family cytokines involve their abilities to differentially regulate the activities of specific T cell subsets. Although IL-12, IL-23 and IL-27 all promote pro-inflammatory immune responses, IL-12 primarily affects Th1 cells, IL-23 primarily affects Th17 cells, and IL-27 affects both Th1 and Th17 cells. IL-12 and IL-27 signaling promotes the differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells into Th1 cells, while IL-23 signaling promotes the stabilization and maintenance of Th17 cells. Unlike IL-12 and IL-23, IL-27 can also suppress inflammation by inhibiting Th17 differentiation and inducing the conversion of effector T cells into IL-10-producing T regulatory type I-like (Tr1-like) cells. In contrast to the pro-inflammatory effects induced by IL-12, IL-23, and IL-27, IL-35 has anti-inflammatory effects. IL-35 enhances the activity of regulatory T cells, inhibits conventional T cell proliferation, and promotes the conversion of B cells into IL-10-, IL-35-secreting regulatory B cells. Although little is currently known about the effects of IL-39 on different immune cell types, it is also presumed to have pro-inflammatory effects as it was shown to promote neutrophil development and differentiation, which has been suggested to contribute to the pathogenesis of disease in a lupus mouse model. In addition, other recent studies have shown that IL-39 is secreted by keratinocytes and is increased in the serum of patients with acute coronary syndrome, but the significance of these observations is not currently well understood.
IL-12 Family Cytokines - Products by Molecule
| EBI3 | IL-12 | IL-12/IL-23 p35 | IL-12/IL-23 p40 | IL-12 p70 | IL-23 |
| IL-23/IL-39 p19 | IL-27 | IL-27 p28/IL-30 | IL-35 | IL-39 (IL-23p19/EBI3) | IL-Y (IL-12 p40/IL-27 p28) |
IL-12 Family Receptors - Products by Molecule
IL-12 Family Intracellular Signaling - Products by Molecule
Cell Proliferation Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-12 and Neutralization by a Goat Anti-Human IL-12 Polyclonal Antibody

IL-12-induced Cell Proliferation is Neutralized Using a Goat Anti-Human IL-12 Polyclonal Antibody. PHA-activated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human IL-12 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 219-IL) and cell proliferation was assessed (orange line). The ED50 for this effect is 0.01-0.05 ng/mL. Proliferation stimulated by 1 ng/mL Recombinant Human IL-12 was neutralized by treating the cells with increasing concentrations of a Goat Anti-Human IL-12 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF-219-NA; blue line). The ND50 for this effect is typically 5–50 ng/mL.
Protein Characterization Using SEC-MALS Analysis
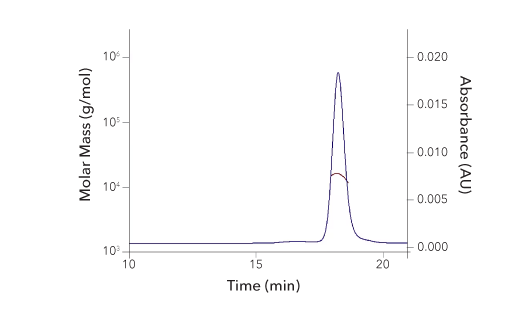
Recombinant Human IL‑12 Protein SEC-MALS. Recombinant human IL-12 (Catalog # 219-IL) has a molecular weight (MW) of 61.3 kDa as analyzed by SEC-MALS, suggesting that this protein is a heterodimer. MW may differ from predicted MW due to post-translational modifications (PTMs) present (i.e. Glycosylation).
| SEC-MALS Data | Result |
| Retention Time | 17.2-17.9 min |
| MW-Predicted (Monomer) | 34.7 kDa (p40) & 22.5 kDa (p35) |
| MW-MALS | 61.3 kDa |
| Polydispersity | 1.003 |
| System Suitability: BSA Monomer 66.4 ± 3.32 kDa | Pass |
Analysis of the Binding of R&D Systems Avi-tag Biotinylated Recombinant Human IL-12 R beta 1 and Recombinant Human IL-12 Proteins

IL-12 R beta 1 Binds to IL-12. Recombinant Human IL-12 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 219-IL) was immobilized at 1 ug/mL and the indicated concentrations of Avi-tag Biotinylated Recombinant Human IL-12 R beta 1 Fc Chimera (R&D Systems, Catalog # AVI10382) were added. The concentration of Avi-tag Biotinylated Recombinant Human IL-12 R beta 1 that produces 50% the optimal binding response is 15-90 ng/mL.
Detection of IL-23 R in Th17-differentiated Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry

Detection of IL-23 R in Mouse Splenocytes by Flow Cytometry. Mouse splenocytes were treated with 10 ug/mL Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3 epsilon Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # MAB484), 5 ug/mL Goat Anti-Mouse CD28 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # AF483), 10 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse TGF-beta 1 (R&D Systems, Catalog 100-B), 20 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse IL-23 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1887-ML), 40 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse IL-6 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 406-ML), and 10 ng/mL Recombinant Mouse IL-1 beta (R&D Systems, Catalog # 401-ML) for 5 days to induce Th17 differentiation. The cells were then stained with a PE-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB554P) and either (A) an APC-conjugated Rat Anti-Mouse IL-23 R Monoclonal Antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog # FAB16861A) or (B) an APC-conjugated Rat IgG1 Isotype Control (R&D Systems, Catalog # IC005A).
R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-35 Displays Higher Binding Activity with IL-12 R beta 2 than two Leading Competitors’ Recombinant Human IL-35 Proteins

R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-35 Displays Higher Binding Activity with IL-12 R beta 2 than two Leading Competitors’ Recombinant Human IL-35 Proteins. Recombinant Human IL-12 R beta 2 Fc Chimera (R&D Systems, Catalog # 1959-B2B) was immobilized at 5 ug/mL (100 uL/well), and increasing concentrations of R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-35 Fc Chimera (Catalog # 8608-IL; orange line) or recombinant human IL-35 from two other companies (blue and red lines) were added. R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-35 bound to Recombinant Human IL-12 R beta Fc Chimera with an ED50 of 20-120 ng/mL, while the two competitors’ proteins displayed much weaker binding activity.
IFN-gamma Secretion Induced by R&D Systems Recombinant Human IL-39

IL-39 Induces IFN-gamma Secretion by Mouse Splenocytes. Mouse splenocytes were treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human IL-39 Fc Chimera (R&D Systems, Catalog # 9990-IL) and the levels of IFN-gamma in the cell culture supernatants were measured using the Mouse IFN-gamma Quantikine™ ELISA Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # MIF00). The ED50 for this effect is 50–250 ng/mL.
Featured Products for IL-12 Family Research

Immunoassays for Detecting IL-12 Family Cytokines
Immunoassays for Detecting IL-12 Family Cytokines
From our complete, ready-to-use Quantikine™ ELISA Kits to our more flexible DuoSet™ ELISA Development Systems, we offer a wide selection of immunoassays for measuring IL-12 family cytokines. Whatever your needs you can count on our immunoassays to deliver accurate, reproducible, high-quality data for every experimental sample that you test.

CellXVivo™ Immune Cell Differentiation and Expansion Kits
CellXVivo™ Immune Cell Differentiation and Expansion Kits
Ensure consistent and reliable immune cell differentiation and expansion with our CellXVivo Kits. CellXVivo Kits contain optimized combinations of R&D Systems™ proteins and antibodies, along with simple, reproducible protocols that will increase the consistency of your experiments and save you time. Kits are available for differentiating or expanding dendritic cells, macrophages, natural killer cells, B cells, T helper cells, and regulatory T cells.

Custom Protein Libraries
Custom Protein Libraries
Are you spending valuable research time aliquoting proteins into plates? Let us help. We offer Custom Protein Libraries, which come with the proteins that you select already aliquoted into the wells of a 96-well plate. This custom product allows you to select the proteins that you need from a portfolio of over 5,000 R&D Systems bioactive proteins and will significantly reduce the amount of time needed to set-up your experiments.
Featured IL-12 Family-Related Resources

Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cytokine Signaling Pathways
Cytokines activate a diverse array of intracellular signaling pathways that can induce processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, and inflammation. Explore the signaling pathways that are activated by different cytokine families, the primary target cells that they affect, and the biological effects that they mediate using our interactive signaling pathways.
CD4+ T Cell Subsets Product Guide
CD4+ T Cell Subsets Product Guide
Explore this guide to learn about the characteristics of different CD4+ T cells subsets and view a listing of our products for basic T cell research. We offer kits for T cell isolation, proteins and antibodies for T cell activation and differentiation, along with antibodies and single and multianalyte immunoassays for the identification and characterization of different T cell subsets.

T Cell Subsets Poster
T Cell Subsets Poster
Immune cells are frequently identified based on the expression of cell surface and intracellular markers. Learn about the different types of T cells and the markers that are most commonly used to distinguish them with our T Cell Subsets poster. This poster will serve as a great reference tool and will make a colorful addition to your lab space.






