RNAscope™ ISH Troubleshooting
RNAscope™ ISH Overview
RNAscope technology is an in situ hybridization (ISH) assay that detects target RNA within intact cells. The assay is based on a patented signal amplification and background suppression technology, representing a major advance over traditional RNA ISH. RNAscope assays do not require an RNase-free environment.
The manual assay procedure can be completed in 7–8 hours or conveniently divided over two days. Most RNAscope assay reagents are available in convenient Ready-To-Use (RTU) dropper bottles and provide a simple, nearly pipette-free workflow. The assay is also available for automation on the Roche DISCOVERY ULTRA or the Leica Biosystems’ BOND RX platforms.
- Key RNAscope Assay Guidelines
- RNAscope Recommended Workflow
- Scoring Guidelines
- Sample Preparation
- Optimize the Assay
- Troubleshooting Staining Patterns
- Troubleshooting High Background
- Troubleshooting Other Issues
Key RNAscope Assay Guidelines
Before you get started refer to our Getting Started Page.
- Follow the protocol exactly as described in the user manual. For manual assays, user manuals are divided into two parts: sample preparation (Part 1), and detection (Part 2). Refer to the User Manual Selection Guide, found in the documents section of each product page.
- Before beginning the assay, review sample pretreatment recommendations. These are critical steps for accessing the RNA in your tissue sample.
- Always run positive and negative control probes (e.g. PPIB/UBC and dapB respectively) on your sample to assess sample RNA quality and optimal permeabilization.
- Please make sure you have all the required materials, especially each of the following:
- ImmEdge pen (Vector Laboratories)
- Superfrost Plus slides (Fisher Scientific)
- Fresh reagents (ethanol and xylene)
- Fresh 10% neutral-buffered formalin (NBF)/4% paraformaldehyde (PFA)
- Tissue-Tek® slide rack, staining dishes, and the HybEZ™ II Hybridization System
- Steamer, hotplate, drying oven, water bath, thermometer, microscope, etc.
- HybEZ™ Hybridization System, required for RNAscope hybridization to maintain optimum humidity and temperature
Workflow guidelines:
- Perform all amplification steps in the right order; omitting any step will result in no signal.
- Flick or tap the slides to remove residual reagent, but do not let the slides dry out at any time.
- Make sure the hydrophobic barrier remains intact so that the tissues do not dry out.
- Always use fresh reagents, including ethanol and xylene.
- Do not alter the protocol in any way.
- Warm probes and wash buffer at 40°C. Precipitation occurs during storage and may affect the assay results.
- Always use the ACD EZ-Batch Wash Tray and Slide Holder for wash steps with RNAscope 1X Wash Buffer.
- Maintain adequate humidity by keeping the humidifying paper wet in the Humidity Control Tray.
For the Roche DISCOVERY ULTRA System
Troubleshoot the Instrument
Check Instrument Maintenance
- Refer to the user manual for instrument maintenance.
- Call your Roche Diagnostics representative to perform the decontamination protocol every three months to prevent microbial growth in the lines.
- Call your Roche Diagnostics representative to consider replacing any bulk solutions recommended for troubleshooting . Rinse the containers thoroughly and make sure the internal reservoir has been purged several times with the appropriate buffer.
- If you use water to clean the instrument, make sure residual water is replaced with the appropriate buffers by purging several times.
Optimize software settings
- Uncheck the Slide Cleaning option.
- Ensure that your system is running with the most up to date mRNA universal procedure. Contact your ACD FAS for additional information.
Do not make any adjustments to the recommended temperatures unless otherwise instructed by ACD support.
Troubleshoot reagents
- Before beginning the assay, refer to the user manual for tissue pretreatment times and recommended guidelines.
- For over- or under-fixed tissues, adjust RNAscope VS Universal Target Retrieval v2 ('Cell Conditioning' in the protocol) and/or VS Protease treatment times. Refer to the user manual.
- Always run positive and negative controls (POLR2A/PPIB/UBC and dapB, respectively) to qualify your sample and check assay performance.
For Leica Biosystems’ BOND RX System
- The recommended standard tissue pretreatment is 15 minutes Epitope Retrieval 2 (ER2) at 95°C and 15 minutes Enzyme (LS Protease III) at 40°C.
- For a milder pretreatment, the recommended conditions are 15 min ER2 at 88°C and 15 min Protease at 40°C.
- For extended pretreatment times, increase the ER2 time in increments of 5 minutes and increase the Protease time in increments of 10 minutes, while keeping the temperatures constant (e.g. 20 min ER2 at 95°C and 25 min Protease at 40°C; 25 min ER2 at 95°C and 35 min Protease at 40°C). You may also apply this process to over-fixed tissues. Contact ACD Support for additional information.
- The “Mock probe” and “BOND wash” (LS Multiplex)Open containers are user-filled with 1x BOND Wash Solution.
- The RNAscope™ LS Brown assays utilize Leica Biosystems’ BOND Polymer Refine Detection, BOND Polymer Refine Red Detection, or Research Detection kits. Do not use any other chromogen kits.
- Do not alter the staining protocol in any way. The parameters in the staining protocol have been optimized to run RNAscope on the instrument. You may change the hematoxylin incubation time according to your needs.
Preparing Probes
Channel C1 target probes are Ready-To-Use (RTU), while channel C2, C3, and C4 probes are shipped as 50X concentrated stocks. To independently detect target RNAs in a 2-plex, 3-plex, or 4-plex assay, the target probes must be in different channels and there must be a C1 or S1 probe in the mixture. RNAscope Probe Diluent (Catalog # 300041) can be used if no C1 probe is included in the assay. All HiPlex target probes are shipped as 50X concentrated stocks so probe mixture must be prepared using hiPlex probe diluent (Catalog # 324301).
| Components | Mixing Ratio |
|---|---|
| Probes C2: C1/ S1 | 1: 50 |
| Probes C3: C2:C1/ S1 | 1: 1: 50 |
| Probes C4: C3: C2: C1 | 1: 1: 1: 50 |
| Probes T1- T12 : HiPlex probe diluent | 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 1: 50 |
Mounting Medium
Use assay specific recommendations as listed in the table below.
| Assay | Recommended Mounting Medium |
|---|---|
| RNAscope Brown | Cytoseal or other xylene-based mounting medium |
RNAscope Red/RNAscope Duplex BaseScope v2/BaseScope Duplex miRNAscope Red DNAscope Duplex | VectaMount PT Permanent Mounting Medium (Catalog # 321584) |
RNAscope Multiplex Fluorescent RNAscope Multiomic RNAscope Plus smRNA-RNA RNAscope HiPlex | ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant (Thermo Fisher Scientific) |
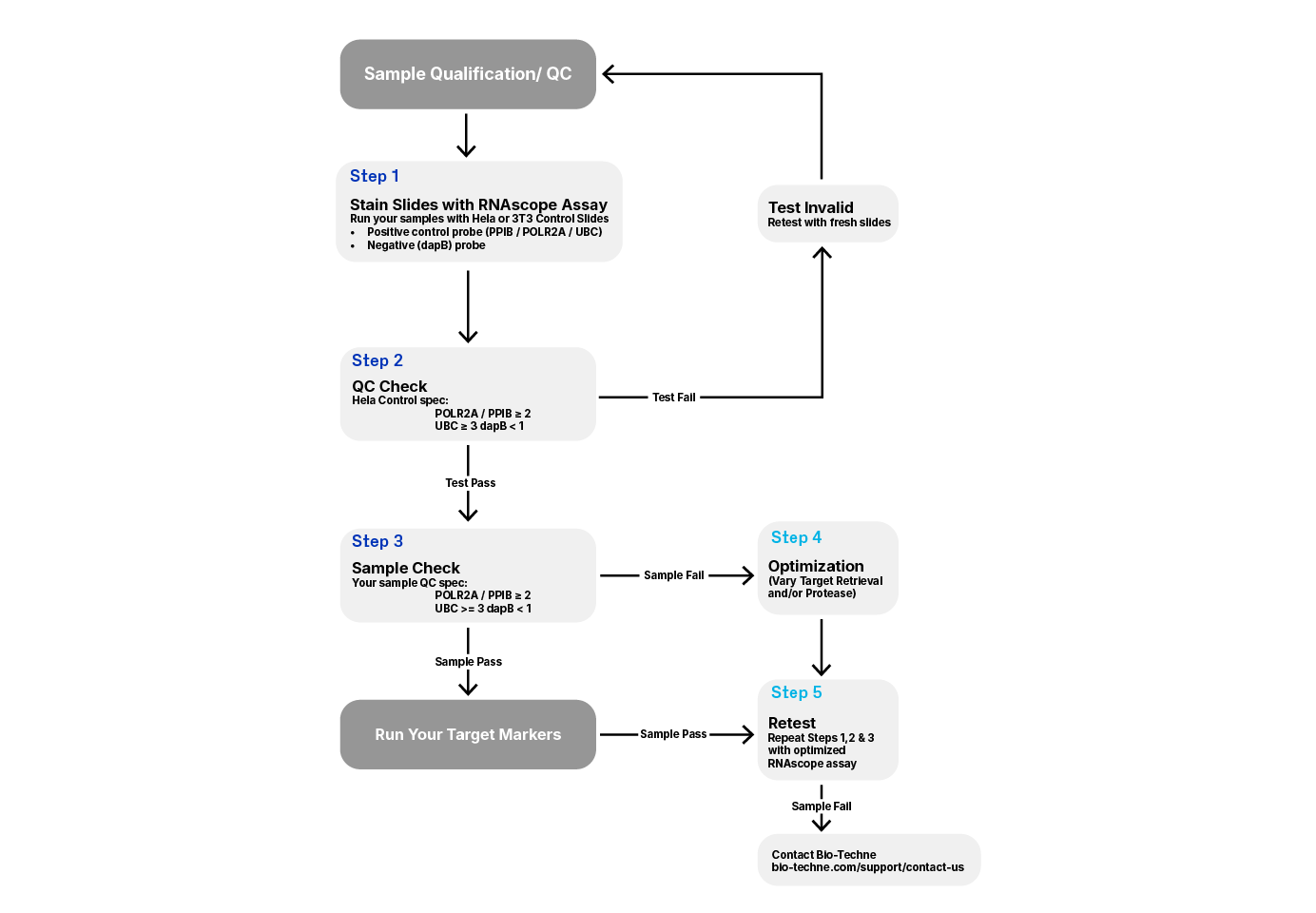
RNAscope Recommended Workflow
If sample preparation conditions do not match recommended guidelines or are unknown, we strongly recommend checking RNA quality and optimizing pretreatment conditions using ACD positive and negative control probes. See Figure 1 for the recommended workflow
1. Run samples along with the control slides provided by ACD (Catalog # 310045 for Human HeLa Cell Pellet and Catalog # 310023 for Mouse 3T3 Cell Pellet).
- The ACD Positive Control Probes include different housekeeping genes to test tissue RNA integrity. You may use the low-copy (10–30 copies per cell) housekeeping genes Cyclophilin B (PPIB) or the low copy (5–15 copies) Polymerase (RNA) II (DNA directed) polypeptide A (POLR2A), or high copy Ubiquitin C (UBC).
- The ACD Negative Control Probe uses bacterial dapB and should not generate signal in properly fixed tissue.
2. Use the RNAscope™ scoring guidelines to evaluate staining results (see Figure 2).
- For RNAscope, successful PPIB staining should generate a score ≥2 and UBC score ≥3 with relatively uniform PPIB/POLR2A/UBC signal throughout the sample. See user manuals for BaseScope or miRNAscope scoring guidelines.
- Samples should display a dapB score of <1 indicating low to no background.
3.Use the control slides as a reference to determine if the RNAscope assay was performed correctly.
4. Depending on staining results, you may need to optimize pretreatment conditions for your samples.
Scoring Guidelines
The RNAscope assay uses a semi-quantitative scoring guideline to evaluate the staining results. When interpreting RNAscope staining we recommend scoring the number of dots per cell rather than the signal intensity. The number of dots correlates to the number of RNA copy numbers, whereas dot intensity reflects the number of probe pairs bound to each molecule.
An example of how to develop such a guideline for semi-quantitative assessment of RNAscope staining intensity is presented below for a gene with expression level varying between 1 to > 15 copies per cell (PPIB). If your gene expression level is higher or lower than this range, you may need to scale the criteria accordingly. For BaseScope™ or miRNAscope™ scoring guidelines, please reference respective assay user manuals found on product pages.
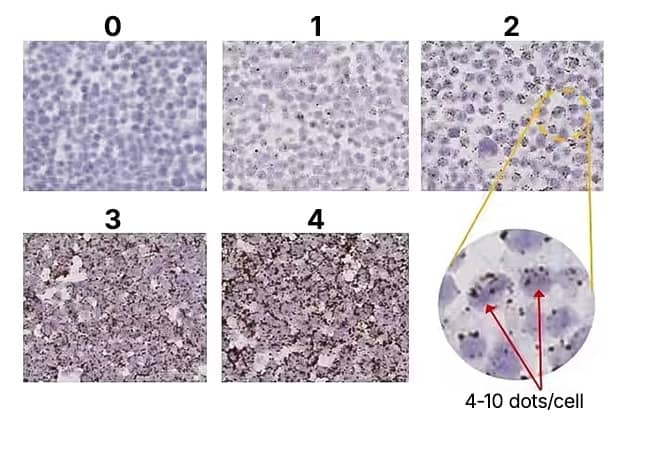
Figure 2: RNAscope Scoring Guidelines on HeLa control slides at 20X magnification.
| Score | Criteria |
|---|---|
| 0 | No staining or <1 dot/ 10 cells |
| 1 | 1-3 dots/cell |
| 2 | 4-9 dots/cell. None or very few dot clusters |
| 3 | 10-15 dots/cell and <10% dots are in clusters |
| 4 | >15 dots/cell and >10% dots are in clusters |
*If <5% of cells score 1 and >95% of cells score 0, a score of 0 will be given. If 5-30% of cells score 1 and >70% of cells score 0, a score of 0.5 will be given. Scoring is performed at 20X magnification.
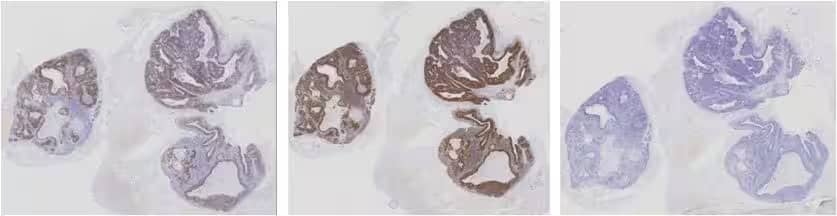
Interpreting RNAscope results
Figure 3. RNAscope assay results comparing a high expressing HR-HPV case study with a positive and a negative control. (Left) HPV-HR18; (Middle) UBC positive control; and (Right) DapB negative control.
Compare the expression of your target gene with both negative (dapB) and positive controls (PPIB, UBC, or POLR2A). Successful staining should have a PPIB/POLR2A score ≥2 or UBC score ≥3 and a dapB score <1. See Figure 3 for an example.
Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is critical for successful staining of tissue with RNAscope ISH methodology. The RNAscope manual assays can be used with FFPE (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded), cultured cells, fresh-frozen, or fixed frozen tissues. Please refer to the appropriate sample preparation guides as shown in the User Manual Selection Guide (found in the documents section of each product page) to ensure your samples are prepared correctly for the detection assay.
Note: Tissue thickness for fixed frozen tissue should be between 7–15 µm and 10–20 µm for fresh frozen tissue and 4-6 µm for FFPE tissue. Use Fisher Scientific SuperFrost Plus Slides for all tissue types to avoid tissue loss.
Pointers for preparing FFPE tissue
Prepare tissues according to standard methods:
- Tissue specimens should be fixed in fresh 10% NBF for 16–32 hours at room temperature and blocked into a thickness of 3–4 mm.
Note: Under-fixation will result in significant RNA loss during storage and may result in low signal when performing the RNAscope Assay.
- Dehydrate in a graded series of ethanol and xylene, followed by infiltration by melted paraffin held at no more than 60°C
- Trim paraffin blocks as needed and cut embedded tissue into 5 +/- 1 µm sections using a microtome.
- Place paraffin ribbon in water bath, and mount sections on SuperFrost Plus Slides.
- Air dry slides overnight at room temperature.
When tissue preparation method is unknown:
In many situations information on tissue preparation procedures may be unavailable. Tissue optimization steps depend not only on the type of tissue, but also the age of the animal. If you intend to perform in situs on embryonic tissue, each developmental stage may require differential treatment. Simple optimization steps can help obtain quality data. Optimal conditions are dependent on tissue type, age, and fixation.
Optimize the Assay
In IHC, antigen retrieval conditions often require optimization and depend on the tissue type and how the sample was fixed and processed. RNAscope target retrieval conditions may also need optimization, particularly if tissue samples were not fixed for 16–32 hours in fresh 10% neutral-buffered formalin (NBF) at room temperature.
Guidelines to follow:
- Always test representative samples with positive and negative control probes. Positive controls should give a uniform signal, while negative controls should display little to no signal.
- Evaluate the positive and negative staining results of your samples following our evaluation guidelines (see V. Scoring Guidelines). If results are acceptable, no further optimization is needed. Otherwise, adjustment of pretreatment conditions may be required to obtain optimal results.
Troubleshooting Staining Patterns
1. Staining examples for various pretreatment digestion conditions
Note: When optimizing RNAscope, BaseScope, or miRNAscope workflows, please use a combination of Target Retrieval and -Protease or Protease only (fresh frozen tissue).
Figure 4. Possible Morphology Patterns
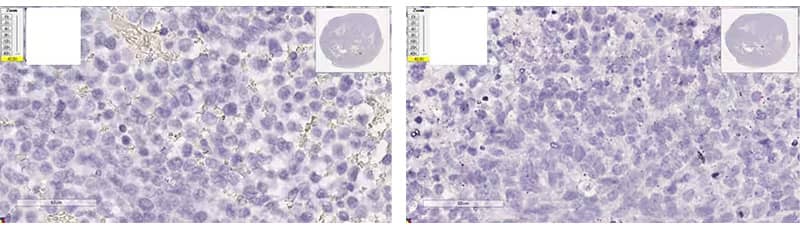
a. Under-digested
Image: Left - Xenograft tissue, negative control dapB (8 min Target Retrieval + 15 min Protease Plus); Right - Xenograft tissue, positive control Hs-PPIB (8 min Target Retrieval + 15 min Protease Plus)
Morphology Description: Excellent morphology, strong hematoxylin staining.
Possible Effects: Weak/no signal due to poor probe accessibility; nuclear background in liver/kidney tissue.
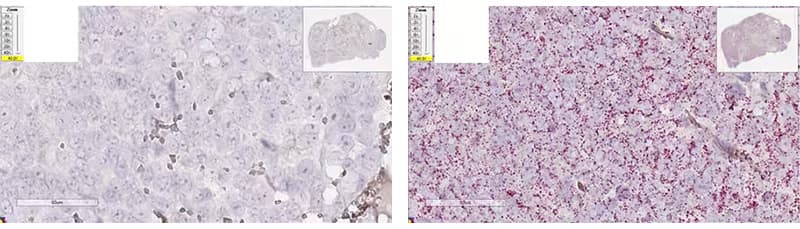
b. Over-digested
Image: Left - Xenograft tissue, dapB (8 min Target Retrieval + 15 min Protease Plus); Right - Xenograft tissue, Hs-PPIB (8 min Target Retrieval + 15 min Protease Plus)
Morphology Description: Destroyed tissue morphology, Doughnut/ghost nuclei, weak hematoxylin staining.
Possible Effects: High background, non-uniform strong/weak signal.
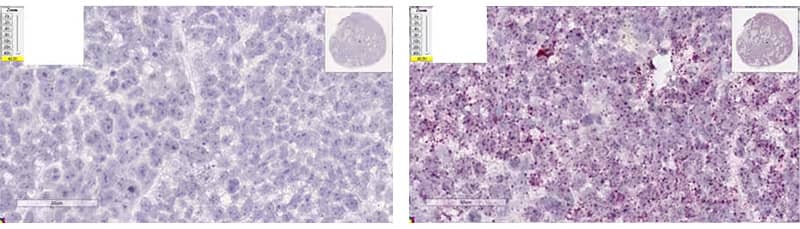
c. Optimal Digestion
Image: Left - Xenograft tissue, dapB (8 min Target Retrieval + 15 min Protease Plus); Right - Xenograft tissue, Hs-PPIB (8 min Target Retrieval + 15 min Protease Plus)
Morphology Description: Intact Tissue morphology and nuclei. Homogenous hematoxylin staining.
Possible Effects: High signal to noise ratio. Strong staining for positive controls with no/negligible background.
2. Staining Patterns
| Issue | Probable Cause | Suggested Action |
|---|---|---|
| No staining |
Suboptimal tissue preparation (overfixation**/under-fixation*) |
Prepare tissue samples according to ACD recommended procedures. The best pretreatment conditions are listed in user manuals and tech notes for specific sample types and are available at: User Manual Selection Guide (found in the documents section of each product page) To optimize pretreatment conditions (boiling and protease digestion times):
|
| Hybridization temperature not optimal |
|
|
| Reagents are used in the wrong sequence | Apply reagents in the correct order | |
| Gene of interest not expressed | Check positive control to confirm the technical accuracy of the assay |
**Over-fixed/under-digested tissue: Tissue morphology looks excellent with weak/no signal and low signal/background ratio due to poor probe accessibility.
*Under-fixed/over-digested tissue: Poor tissue morphology (tissue appear faded with loss of cell borders), loss of RNA due to protease over-digestion.
Troubleshooting High Background
| Issue | Probable Cause | Suggested Action |
|---|---|---|
| Nuclear background | Pretreatment conditions not optimal
| Optimize pretreatment conditions
|
| Nuclear hazy background (Leica BOND RX) | Under-pretreatment | The presence of nuclear background staining (entire nuclei stained brown) can sometimes be removed by increasing pretreatment times. Increase the ER2 time in increments of 5 min and increase the protease time in increments of 10 min while keeping the temperature constant. You may also apply this process to over-fixed tissues. |
| Extracellular Background | Incomplete paraffin removal | Use fresh/unused EtOH and Xylene and agitate slides during incubation steps. |
| Suboptimal tissue preparation | Prepare tissue samples according to our recommended procedures. | |
| Cytoplasmic background | Tissue dries out during assay |
|
**Over-fixed/under-digested tissue: Tissue morphology looks excellent with weak/no signal and low signal/background ratio due to poor probe accessibility.
*Under-fixed/over-digested tissue: Poor tissue morphology (tissue appear faded with loss of cell borders), loss of RNA due to protease over-digestion.
Figure 5: Background Troubleshooting Examples
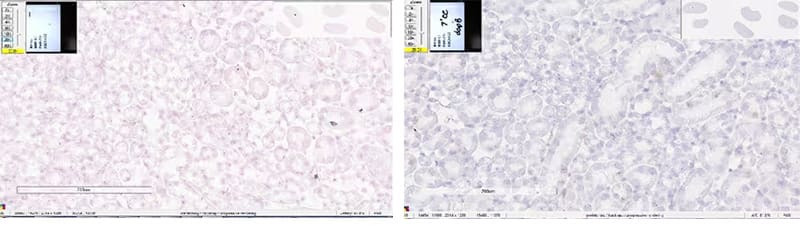
a. Nuclear Background
Left - Standard pretreatment on mouse kidney – dapB, nuclear background observed; Right - 7 min Target Retrieval on mouse kidney - dapB, clean background
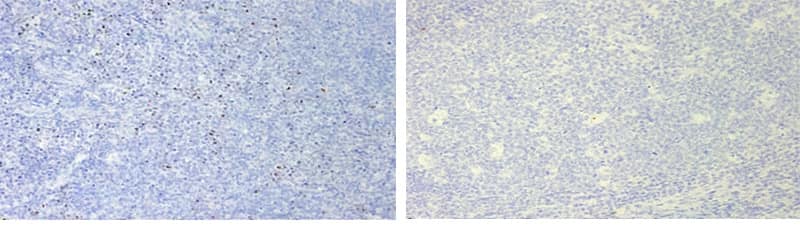
b. Nuclear Hazy Background
Left - Human Tonsil: 15 min ER2 + 15 min Protease (image represents RNAscope LS BOND RX staining); Right - Human Tonsil: 20 min ER2, 20 min Protease (image represents RNAscope LS BOND RX staining), clean background.
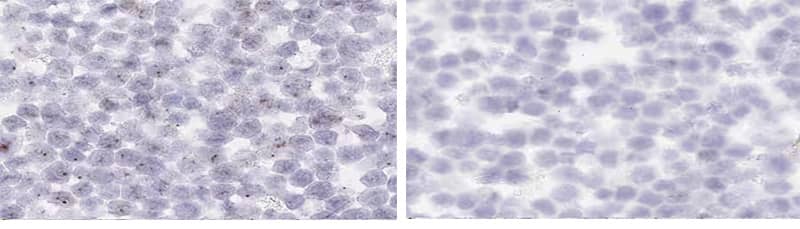
c. Cytoplasmic Background
Left - HeLa cell pellet, dapB; Dried out tissue, cytoplasmic background; Right - HeLa cell pellet, dapB; No drying between Amp steps, clean background.
Troubleshooting Other Issues
| Issue | Probable Cause | Suggested Action |
|---|---|---|
| Tissue detaches from slides | Wrong slides used | Use only SuperFrost® Plus slides to avoid tissue sliding off (Fischer Scientific, Catalog # 12-550-15) |
| Suboptimal tissue preparation |
Troubleshooting workflow illustrations by sample type: | |
| Unknown tissue preparation method | Sample provider/clinical site/vendor did not provide detailed instructions | Refer to the appropriate sample preparation guidelines to determine whether samples are appropriately fixed and processed
For optimal pretreatment conditions for each assay and tissue type, please refer to the user manual, found on individual product pages, or see our protocols. |
Example:
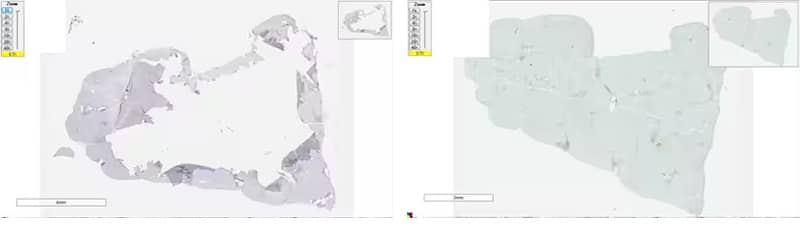
Issue: Detached Tissue
Left - Tissue detaches from slides; Right - Slides baked for 1 hour at 60 °C.