EAAT1/GLAST-1 Products
Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 1 (EAAT1), also known as GLAST-1 and SLC1A3, is a member of the SDF symporter family of proteins. Human EAAT1/GLAST-1 is a 542 amino acid (aa), 8-transmembrane variably glycosylated protein with a predicted molecular weight of 60-62 kDa. Its N- and C-terminus are cytoplasmic. EAAT1/GLAST-1 homodimers are reported to exist, but only when the protein is glycosylated. There are at least two potential isoform variants. One shows an Arg substitution for aa 430-475, while a second shows a four aa substitution for aa 62-542.
Over the extracellular loop that encompasses aa 146-237, human EAAT1/GLAST-1 shares 92% aa identity with the mouse ortholog. EAAT1/GLAST-1 is expressed by glia, fibroblasts, and select neuron cell types such as hippocampal neurons. EAAT1/GLAST-1 is known to transport L-glutamate into glia, thus removing glutamate from synaptic areas where it either acts too long or becomes toxic at elevated concentrations. Its action is dependent on its ability to cotransport sodium. Aberrant expression of EAAT1/GLAST-1 is associated with multiple neurological and neurodegenerative disorders including epilepsy and multiple sclerosis.
Products:
77 results for "EAAT1/GLAST-1" in Products
77 results for "EAAT1/GLAST-1" in Products
EAAT1/GLAST-1 Products
Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 1 (EAAT1), also known as GLAST-1 and SLC1A3, is a member of the SDF symporter family of proteins. Human EAAT1/GLAST-1 is a 542 amino acid (aa), 8-transmembrane variably glycosylated protein with a predicted molecular weight of 60-62 kDa. Its N- and C-terminus are cytoplasmic. EAAT1/GLAST-1 homodimers are reported to exist, but only when the protein is glycosylated. There are at least two potential isoform variants. One shows an Arg substitution for aa 430-475, while a second shows a four aa substitution for aa 62-542.
Over the extracellular loop that encompasses aa 146-237, human EAAT1/GLAST-1 shares 92% aa identity with the mouse ortholog. EAAT1/GLAST-1 is expressed by glia, fibroblasts, and select neuron cell types such as hippocampal neurons. EAAT1/GLAST-1 is known to transport L-glutamate into glia, thus removing glutamate from synaptic areas where it either acts too long or becomes toxic at elevated concentrations. Its action is dependent on its ability to cotransport sodium. Aberrant expression of EAAT1/GLAST-1 is associated with multiple neurological and neurodegenerative disorders including epilepsy and multiple sclerosis.
Products:
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Flow, +2 More |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2b Monoclonal Clone #482420 |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | AC |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP, PAGE |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Applications: | WB |
| Applications: | ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Flow |
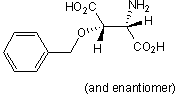
Selective non-transportable inhibitor of EAATs
| Chemical Name: | DL-threo-β-Benzyloxyaspartic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
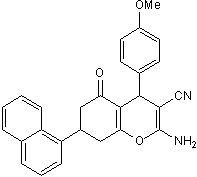
Selective non-substrate EAAT1 inhibitor
| Chemical Name: | 2-Amino-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-(naphthalen-1-yl)-5-oxo-4H-chromene-3-carbonitrile |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
GABA uptake inhibitor; also inhibits glutamate release and blocks NaV channels
| Chemical Name: | 2-Amino-6-trifluoromethoxybenzothiazole hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
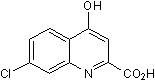
Potent competitive inhibitor of L-glutamate uptake
| Chemical Name: | 7-Chloro-4-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxylic acid |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, Flow |

![Flow (Intracellular): EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-1869] Flow (Intracellular): EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-1869]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/EAAT1-GLAST-1-SLC1A3-Antibody-Flow-Intracellular-NB100-1869-img0011.jpg)

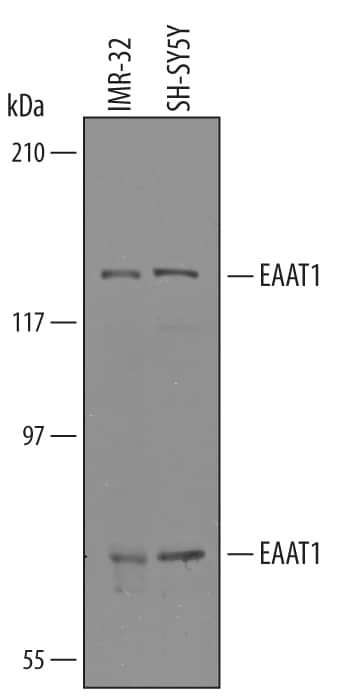
![Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP3-05771] Immunocytochemistry/ Immunofluorescence: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody - BSA Free [NBP3-05771]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/EAAT1-GLAST-1-SLC1A3-Antibody-Immunocytochemistry-Immunofluorescence-NBP3-05771-img0004.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody [NBP1-84940] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody [NBP1-84940]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/EAAT1-GLAST-1-SLC1A3-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-84940-img0017.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody [NBP1-84939] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody [NBP1-84939]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/EAAT1-GLAST-1-SLC1A3-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP1-84939-img0015.jpg)
![ELISA: Human EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP3-31560] - Human EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-31560_human-eaat1-glast-1-slc1a3-elisa-kit-colorimetric-206202415294030.png)

![SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 GST (N-Term) Protein [H00006507-P01] SDS-PAGE: Recombinant Human EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 GST (N-Term) Protein [H00006507-P01]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/qc_test-H00006507-P01-1.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody [NBP2-98747] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Antibody [NBP2-98747]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/EAAT1-GLAST-1-SLC1A3-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NBP2-98747-img0001.jpg)
![Western Blot: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Overexpression Lysate [NBP2-10257] Western Blot: EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 Overexpression Lysate [NBP2-10257]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/SLC1A3-Overexpression-Lysate-Adult-Normal-Western-Blot-NBP2-10257-img0001.jpg)
![ELISA: Human EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 - Ready-To-Use ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) [NBP3-31561] - Human EAAT1/GLAST-1/SLC1A3 - Ready-To-Use ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/nbp3-31561_human-eaat1-glast-1-slc1a3-ready-to-use-elisa-kit-color-206202415311313.png)