Notch-3 Products
Notch proteins (so named for 'notches' in fly wings) are type I transmembrane glycoproteins involved in specifying cell fates and defining boundaries between different cell types during developmental processes. Notch extracellular domains are large, having 34-36 EGF-like repeats followed by three notch/Lin-12 repeats. Notch proteins interact with transmembrane ligands Jagged, Delta, and Serrate expressed on the surface of a neighboring cell. Upon ligand binding, a series of cleavage events results in the release of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD), which translocates to the nucleus and initiates transcription of Notch-responsive genes. Thus, Notch acts as both a ligand-binding receptor and a nuclear factor that regulates transcription.
The four mammalian Notch receptors appear to have distinct functions, since they do not compensate for one another in genetic studies. Mutations in Notch receptors also lead to specific developmental disorders. For example, Notch-3 is predominantly expressed in the developing central nervous system of mice. Mutations in Notch-3 in humans cause an autosomal dominant condition called CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy). This disorder is characterized by recurrent ischemic strokes at an early age without any underlying vascular risk and progressive dementia.
146 results for "Notch-3" in Products
146 results for "Notch-3" in Products
Notch-3 Products
Notch proteins (so named for 'notches' in fly wings) are type I transmembrane glycoproteins involved in specifying cell fates and defining boundaries between different cell types during developmental processes. Notch extracellular domains are large, having 34-36 EGF-like repeats followed by three notch/Lin-12 repeats. Notch proteins interact with transmembrane ligands Jagged, Delta, and Serrate expressed on the surface of a neighboring cell. Upon ligand binding, a series of cleavage events results in the release of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD), which translocates to the nucleus and initiates transcription of Notch-responsive genes. Thus, Notch acts as both a ligand-binding receptor and a nuclear factor that regulates transcription.
The four mammalian Notch receptors appear to have distinct functions, since they do not compensate for one another in genetic studies. Mutations in Notch receptors also lead to specific developmental disorders. For example, Notch-3 is predominantly expressed in the developing central nervous system of mice. Mutations in Notch-3 in humans cause an autosomal dominant condition called CADASIL (cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy). This disorder is characterized by recurrent ischemic strokes at an early age without any underlying vascular risk and progressive dementia.
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Genentech patent anti-Notch3 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Genentech patent anti-Notch3 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Genentech patent anti-Notch3 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Genentech patent anti-Notch3 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Human IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #Genentech patent anti-Notch3 |
| Applications: | ELISA, Flow, Func |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Flow, IHC, Block, CyTOF-ready, +1 More |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2a Kappa Monoclonal Clone #1G5 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA, ICC/IF |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, Block |
| Source: | Sf 21 (stably transfected) |
| Accession #: | Q9UM47 |
| Applications: | Bind |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, ELISA, Flow, IP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
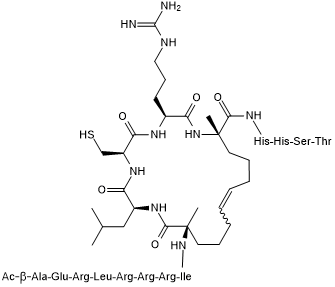
Notch pathway inhibitor; prevents Notch complex assembly
| Purity: | ≥95% (HPLC) |
| Reactivity: | Mouse |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB, IHC |
| Source: | Sf 21 (stably transfected) |
| Accession #: | Q61982 |
| Applications: | Bind |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Sheep IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse |
| Details: | Mouse IgG2B Monoclonal Clone #2E4D11 |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, ICC/IF, CyTOF-ready |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #603532 |
| Applications: | Flow |




![ELISA: Notch-3 Antibody (1G5) [H00004854-M01] ELISA: Notch-3 Antibody (1G5) [H00004854-M01]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-3-Antibody-1G5-ELISA-H00004854-M01-img0003.jpg)
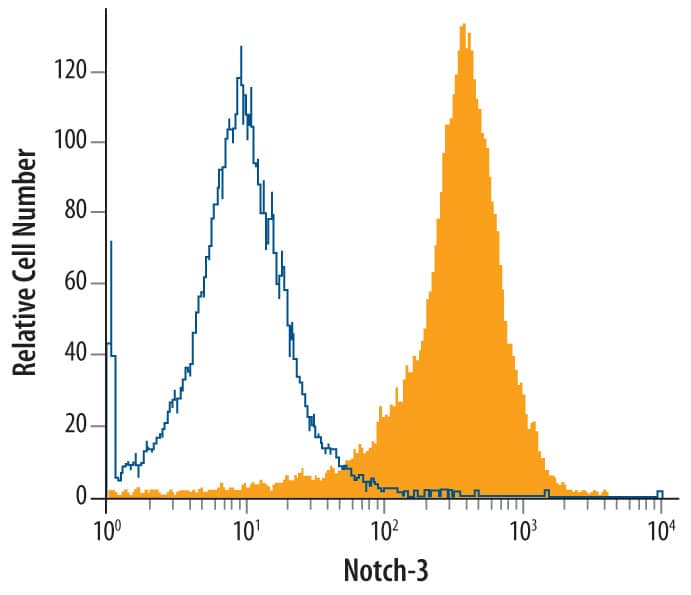

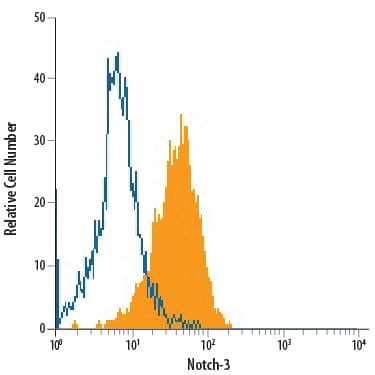
![Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Notch-3 Antibody [NB100-2414] Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin: Notch-3 Antibody [NB100-2414]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-3-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin-NB100-2414-img0003.jpg)

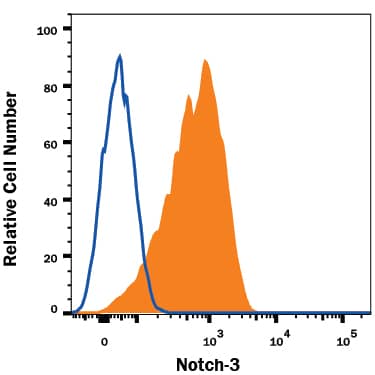
![Western Blot: Notch-3 Antibody (2E4D11)BSA Free [NBP2-52521] Western Blot: Notch-3 Antibody (2E4D11)BSA Free [NBP2-52521]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch-3-Antibody-2E4D11-Western-Blot-NBP2-52521-img0001.jpg)
![Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: Notch-3 Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-93550] Immunohistochemistry-Frozen: Notch-3 Antibody - BSA Free [NB100-93550]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/Notch3-Antibody-Immunohistochemistry-Frozen-NB100-93550-img0002.jpg)