诱导性多能干细胞 (iPSC)
关于多能干细胞和细胞疗法
Listen as Tenielle Ludwig, Director of the WiCell Stem Cell Bank, defines correct use of the terms stemness and pluripotency. These terms are often used interchangeably by researchers and within scientific publications. Dr. Ludwig discusses how consistent use of this nomenclature can positively impact the field of pluripotent stem cell research.
终末分化的体细胞可以轻松地从各种组织(例如,皮肤成纤维细胞或外周 T 细胞)中回收,并用于生成 iPSC。
- ExCellerate™ iPSC 扩增培养基
- Cultrex™ 基底膜提取物和细胞外基质,R&D Systems
Somatic Cell Reprogramming to iPSC
iPSC Reprogramming
There are four general groups to categorize an iPSC reprogramming strategy:
- Integrative Reprogramming techniques require the reprogramming factors to be inserted permanently into the host cell genome. This strategy can be further divided into viral and non-viral methods. The pioneering iPSC experiments by Takahashi & Yamanaka (2006) were conducted by integrating four transgenes using Retroviral Vectors.
- Viral reprogramming cells to iPSCs, using lentiviral or retroviral-based transduction methods are the most efficient but have distinct drawbacks for clinical and translational applications
- Non-viral transposons technology such as TcBuster™ is a next-generation solution that avoids some of the pitfalls of virus transductions.
- Non-integrative Reprogramming techniques are the preferred methodology for clinical and translational iPSC generation. They require no genomic integration, and therefore have significantly reduced chance of introducing harmful mutations. Small molecules are widely used in non-integrative reprogramming.

After reprogramming cells to iPSC, confirm their phenotype by the detection of appropriate stemness markers. See Cell Characterization below on this page. Cell Banking Reagents Including Cryopreservation Media, CEPT Cocktail Kit (Catalog # 7991), and ROCK Inhibitors.

采用多色流式细胞术验证干性标志物表达。使用人/小鼠多能干细胞多色流式细胞术试剂盒中的试剂对人类细胞进行染色,同时分析 SSEA-1、SSEA-4、Oct-3/4 和 SOX2。SSEA-4 和 Oct-3/4 大量表达,但 SSEA-1 未表达,这表明这些细胞处于未分化状态。
iPSC Expansion and Culture
精心选择的高品质培养基成分可实现稳健的 iPSC 扩增,具有很高的存活率,并能长期维持未分化状态。


在 ExCellerate™ iPSC 扩增培养基中培养的人 iPSC,在长期培养中维持了干性标志物的表达。这些细胞表达未分化干细胞标志物 Oct-3/4(红色)和 TRA-1-60(红色)以及纤维状肌动蛋白(F-Actin,绿色)和 DAPI(蓝色)(A)。经人/小鼠多能干细胞多色流式细胞术试剂盒评估,iPSC 系表达高水平的 Oct-3/4、SSEA-4、SOX2,不表达 SSEA-1 (B-C)。传代超过 45 代后,4 个细胞系中未分化干细胞标志物表达 >97%。图中显示了平均值 ± 标准差。
Gene Engineering for iPSC
对细胞进行改造设计,以使其不受到宿主的免疫排斥、改善组织归巢和植入,以及引入新的功能,如嵌合抗原受体 (CAR)。

使用 DNAscope™ 分析直接可视化 TcBuster 转位 iPSC。检测基于用 DNAscope 探针靶向 TcBuster 载体骨架。野生型 iPSC (A),TcBuster 转导 iPSC 的混合细胞群 (B),从混合细胞群中分离的选定克隆 (C)。
Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation
使用严格符合批次间一致性要求的试剂,简化扩展细胞分化过程中的批次桥接。
神经元分化

免疫细胞化学分析展现了从使用 StemXVivo 神经祖细胞分化试剂盒得到的 iPSC 分化而来的神经元细胞。用神经元特异性 β-III 微管蛋白 (TUJ1) 表达来指示神经元 (A)、用 Pax6 来指示神经祖细胞 (B),以及用 Oct-3/4 来指示未分化 iPSC。在第 10 天和第 32 天,对在 Vitronectin 和 ExCellerate iPSC 扩增培养基中生长的神经元分化的图像进行量化。
肝细胞分化

免疫细胞化学分析展现了从使用 StemXVivo 肝细胞分化试剂盒分化的 iPSC 的情况。将细胞维持在 ExCellerate iPSC 扩增培养基中并分化为肝细胞,用白蛋白和 HHNF-4α 表达来加以指示。
无血清和无动物源细胞培养
在进行再生医学和细胞疗法项目的转化研究时,提高细胞培养的一致性。采用这些培养基将
- 减少培养基成分差异
- 简化监管指南合规
- 简化原材料变更的比较测试
Cell Characterization
在 iPSC 项目中,细胞产品鉴定从头到尾都很重要。密切关注细胞表型、分泌谱、培养异质性和污染颗粒的存在。
多能干细胞表征试剂盒和抗体
- 人多能干细胞功能鉴定试剂盒
- GloLive™ 人多能干细胞活细胞成像试剂盒
- 人/小鼠 PSC 多色流式分析试剂盒
- Proteome Profiler™ 人多能干细胞芯片试剂盒
- 人三胚层 3 色免疫细胞化学分析试剂盒
- 验证活干细胞多能性的 GloLive 抗体
- 人多能干细胞标志物抗体组合
分析仪器平台和免疫分析
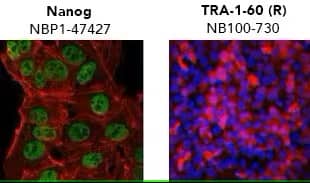
Verification of pluripotency by mmunocytochemistry/ immunofluorescence. (Left) Confocal immunofluorescence analysis of Mouse Anti-Human Nanog Antibody (1E6C4) (Catalog # NBP1-47427) (green). Actin filaments have been labeled with DY-554 phalloidin (red). Nanog staining was confined to the nucleus. (Right) ADLF1 induced pluripotent stem cell line stained with Mouse Anti-Human TRA-1-60 (TRA-1-60) (Catalog # NB100-730) and Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (red) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). TRA-1-60 staining was confined to the cell surface.

iPSC 神经元分化的 Single-Cell Western 分析。每个点代表单个细胞。用 GMP SB 431542 和 GMP 重组人 Noggin 处理 iPSC,然后用 GMP 重组人 FGF、GMP N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂 (100X) 和抗坏血酸进行终末分化。对细胞中的 Pax6 和神经元特异性 β-III 微管蛋白 (Tuj) 进行了分析。在 iPSC 中,检测不到 Pax6,且 46% 细胞表达了 Tuj,而 85% 的神经元为 Tuj+ Pax6+。请参阅我们的应用说明了解更多详情。
- Simple Plex 自动化 ELISA,符合 CFR 第 21 章第 11 款的要求
- RNAscope ISH 专业分析服务,符合 GCLP,ACD
- Micro-Flow Imaging™ 颗粒分析,符合 CFR 第 21 章第 11 款的要求
- 用于病毒载体分析的 iCE™ Maurice,符合 CFR 第 21 章第 11 款的要求
iPSC Applications
Disease research often relies on the use of animal models or two-dimensional (2D) in vitro culture systems. Though extremely useful, animal models are limited in their ability to recapitulate complex diseases and accurately model human cellular responses to new drugs and therapies. Traditional in vitro culture systems rely on examining cellular responses in a contrived 2D environment, with cells grown either in a monolayer plastic dish or in suspension surrounded by culture media. Advancements in cell culture techniques to include organoid and 3D cultures that more closely recapitulate in vivo tissue microenvironment, exponentially expand the applications for iPSCs.

Diverse applications of iPSCs. Somatic cells are harvested from patient and reprogrammed into iPSCs. The resulting patient specific iPSCs can then be used in disease modeling and drug screening to generate disease and patient-specific therapies. Additionally, patient-specific iPSCs can be modified to repair genetic mutations. These repaired iPSCs can then be transplanted into the patient to restore tissue functionality.
Drug toxicity screening: new therapies and drugs often fail in human trials due to unforeseen toxicity. To limit this, iPSCs can efficiently be differentiated into organoids to screen target drugs for toxicity. Hepatocytes, neurons, and cardiomyocytes are the three most common tissue for drug toxicity screening.
| Tissue | Selected Markers of Differentiation |
|---|---|
| Hepatocytes | Albumin Transferrin Asialoglycoprotein Receptor (ASGPR1) α-Fetoprotein (AFP) Glutathione-S-transferase P1 (GSTP1) |
|
Neurons |
βIII Tubulin Vimentin GFAP MAP2 Tyrosine Hydroxylase |
|
Cardiomyocytes |
Nkx2.5 Tbx5 Tbx20 Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI ) Cardiac Troponin T (cTnT) Alpha actinin |
Disease modeling: iPSCs allow for direct studying of disease state from the patient’s own cells. Additionally, researchers can directly alter patient cells via gene editing and determine the impact for the individual patient.
- Pancreatic Islet cells for Type 1 Diabetes
- Motor neurons for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Intestinal epithelial cells for Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Lung organoids for Cystic Fibrosis
Regenerative Medicine: With the ability to generate disease-free tissues using off-the-shelf or patient-derived cells, iPSCs have a bright future in regenerative medicine.
- Dopaminergic neurons for Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
- Functional cardiac muscle to treat Cardiovascular Disease
- Neurons and glial cells for spinal cord injuries
- Retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) for Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
During somatic cell reprogramming to iPSCs, there are many genetic and epigenetic changes that occur. With current reprogramming technologies, the epigenetic landscape of the somatic cells is often incompletely or aberrantly modified. This phenomenon, known as epigenetic memory, often biases the iPSCs to differentiate toward their cell of origin.
Resources
Custom Solutions
Custom Solutions
We’re committed to providing optimized solutions to optimize your iPSC workflow. Our custom services team will work with you to deliver reagents and immunoassays that fit your process. Importantly, we have experience developing certified animal-free (AF) reagents as custom projects in cases where AF grade is not otherwise available. We’re experts in the requirements for regulatory compliance as well as custom formulation, vialing, and packaging.
Translational Programs for Cell Therapy
Translational Programs for Cell Therapy
When it’s time to advance your cell therapy product to clinical manufacturing, partner with us for reliable, quality, and/or custom services. We will work with you to provide reproducible production of reagents and assays at clinical scale, with complete documentation. We offer GMP reagents as well as 21 CFR Part 11-compliant analytical instruments for automation and high throughput. We can help you streamline the manufacture of your cell therapies.
Website Resources
- Webinars
- Cell Culture Reagents
- Stem Cells
- Organoid and 3D Cell Culture Products
- Stem Cells Markers Interactive Tool at R&D Systems
- Stem Cell Protocols at R&D Systems
- Streamlining Transition to GMP
- Protocols for Stem Cells at Tocris
- Flow Cytometry Panel Builder
- Cell Expansion and Characterization Instruments
- Cell and Gene Therapy Response Profiling Instruments
- Gene Transfer Assessment Instruments
Literature
- GMP Cytokines and Growth Factors for Therapeutic Manufacturing Brochure
- Accelerating Cell Therapy Discovery & Development With Non-Viral Gene Engineering Article
- Unraveling the Signaling Web in Stem Cells for Regenerative Medicine with Simple Western App Note
- Key Considerations for Cytokine Supplier Selection for Cell Therapies Article
- Stem Cell Research Product Guide
- Basement Membrane Basics Technical Guide at R&D Systems
- Evolution of Cell Culture Models eBook at R&D Systems
- Assessing the Pluripotent Status of Stem Cells Technical Note at R&D Systems
- Differentiation Potential of iPSC Article at R&D Systems
- Next-Generation Analytical Solutions For Cell & Gene Therapy eBook
Background Information
间充质干细胞 (MSC)
StemXVivo™ 间充质干细胞扩增培养基在使用前是否需要添加血清?
StemXVivo 间充质干细胞扩增培养基不需要添加血清。产品中含有胎牛血清,是完整的培养基,为即用型产品。培养基中可以添加细胞因子或生长因子,以用于所需的细胞培养应用。
间充质干细胞 (MSC) 可在 StemXVivo 间充质干细胞扩增培养基中培养多长时间?
MSC 可生长至 80-90% 的融合度,随后按照产品说明书中提供的方案进行传代培养。研究人员应确定其项目可接受的传代次数。MSC 对传代敏感,如果传代培养次数过多,可能会开始失去其 MSC 特性。我们的 MSC 功能鉴定试剂盒可用于验证 MSC 的多潜能性。
StemXVivo 间充质干细胞扩增培养基是否含有酚红?
是,StemXVivo 间充质干细胞扩增培养基含有酚红。
StemXVivo 无异种人 MSC 扩增培养基中出现晶体是否正常?
是的。晶体为含钙沉淀物,可能在该培养基中形成,但程度有限。含量有限的晶体不会影响 MSC 扩增。避免对培养基进行多次冻融有助于减少晶体量。
人间充质干细胞功能鉴定试剂盒是否包含成脂、成骨和成软骨试剂盒补充剂?
是的,StemXVivo 人成脂补充剂、StemXVivo 人成骨补充剂和 StemXVi 人成软骨补充剂分别与人间充质干细胞功能鉴定试剂盒中部件号 390415、390416 和 390417 对应的产品相同。
必须要使用不含核糖核苷和脱氧核糖核苷的培养基来培养间充质干细胞吗?
关于使用含不含有核糖核苷和脱氧核糖苷的培养基来培养间充质干细胞,我们尚未在并列比较实验中对两者加以比较。有文献支持使用不含核糖核苷和脱氧核糖核苷的培养基对培养间充质干细胞有益。
人间充质干细胞功能鉴定试剂盒能否用于非人灵长类动物间充质干细胞?
试剂盒中包含的抗体很可能与其他灵长类动物成分发生交叉反应。试剂盒中包含的补充剂并非为特定物种所准备的。然而,该试剂盒尚未用灵长类间充质干细胞进行测试。
对于人间充质干细胞功能鉴定试剂盒,如何监测诱导分化?
对于成脂分化,5-7 天后细胞中出现空泡是分化的标志,可以通过对细胞的显微镜检查来监测。对于成骨分化,大约 14 天后,细胞开始脱离是分化的标志。在这种情况下,应监测细胞脱离。对于成软骨分化,除了在分化第 14 - 21 天固定和染色冷冻颗粒外,没有确切的标志物可用。确切的时间可能需要通过一些经验来决定。
人或小鼠间充质干细胞多色流式分析试剂盒是否适用于鉴定大鼠 MSC?
人间充质干细胞多色流式分析试剂盒或小鼠间充质干细胞多色流式分析试剂盒不适用于鉴定大鼠间充质干细胞。
对间充质干细胞成功进行成软骨分化,是否有任何实验技巧/提示?
以下技巧/提示有助于完成成软骨分化:a) 间充质干细胞 (MSC) 不应来自晚期传代(第 8 代或以下),b) 如果使用人间充质干细胞功能鉴定试剂盒或 StemXVivo 成软骨补充剂,应使用方案中指明的起始 MSC 细胞数,c) 成软骨分化早期应有颗粒形成。随着分化的进行,颗粒会生长并呈现出球状外观。d) 颗粒不应附着在试管上,因此注意在更换培养基时不要将其取出。
StemXVivo 心肌细胞分化试剂盒能否用于人间充质干细胞 (MSC)?
这种试剂盒不太可能适用于人 MSC,因为这些细胞处于不同的发育阶段,可能需要不同的信号。
N-2 Plus 培养基补充剂含有牛胰岛素,而 N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂含有重组人胰岛素。N-2 Plus 和 N-2 MAX 中的所有其他培养基成分和浓度均相同。这两种产品在并列比较测试中表现相当。由于牛胰岛素供应有限,产品的定价有所不同。
N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂是否含有任何钙盐成分?
否。
N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂是否含有使用杆状病毒产生的任何蛋白质?
否。
N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂是否含有除人转铁蛋白以外的任何动物源性成分?
否。N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂不含除人转铁蛋白以外的任何动物源性成分。GMP N-2 MAX 培养基补充剂是一种无动物源补充剂。
NPC 是否应维持在涂有 Cultrex™ RGF BME 的平板上?
是。在 NPC 维持期间,细胞应在涂有 Cultrex RGF BME 的平板上培养。另一种选择是使用 Cultrex Poly-L-Lysine (10 µg/mL) 涂布平板,然后使用 Cultrex Laminin (20 µg/mL) 进行涂布。
人类/小鼠/大鼠神经系功能鉴定试剂盒是否适用于胚胎和成年神经祖细胞?
人/小鼠/大鼠神经系功能鉴定试剂盒已经用胚胎神经祖细胞进行了测试。该试剂盒应该也适用于成年神经祖细胞,因为成年细胞具有类似的生长条件。
人/小鼠多巴胺能神经元分化试剂盒能否用于起始神经祖细胞群(而非小鼠多能干细胞)?
该试剂盒可能适用于起始神经祖细胞群,但我们尚未对此进行测试。如果从神经祖细胞开始分化,我们建议从多巴胺能神经元分化试剂盒实验方案的第 5 阶段开始。起始细胞密度也必须进行优化。
在分化第 7 天获得的神经祖细胞 (NPC) 在用于实验/应用之前可以经历多少次传代?
分化后,NPC 可传代大约五次。但是,最好在 7-8 天分化后冷冻保存 NPC,以备将来实验适用。
在使用神经祖细胞 (NPC) 分化成星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞时有哪些建议?
第一个建议是将 NPC 维持在约 50,000-100,000 细胞/cm2 的细胞密度下。第二个建议是让 NPC 在分化成星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞之前经历 2-4 次传代,因为胞龄更大的 NPC 能更好地分化为这些神经元。
心肌细胞
使用 StemXVivo 心肌细胞分化试剂盒生成心肌细胞需要多少天?
早在分化的第 10-13 天就可以看到搏动细胞。接下来的一周,博动会更加普遍。
我应该何时从心肌细胞分化试剂盒转换为心肌细胞维持培养基补充剂?
在开始搏动或试剂盒中提供的试剂用完后,可以随时从心肌细胞分化试剂盒转换到心肌细胞维持培养基补充剂。
肝细胞
肝细胞分化开始后,细胞在哪个时间点达到定型内胚层阶段?
细胞在分化开始后的第 4 天左右达到定型内胚层阶段。可以在本科学海报上查看分化进程示意图。
Luminex 是 Luminex Corporation 的注册商标。

