GABA-A R alpha 4 Products
GABA A (γ-aminobutyric acid-type A) receptors are members of the cysteine-loop family of neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. GABA binding to A-type receptors induces anion-selective ion channel opening. These receptors are the principal fast inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS. GABA A receptors are heteropentamer combinations of seven subunit types; α, β, γ, δ, ε, θ, and π. Three subunits, α, β, and γ, have at least three separate gene products in mammals, and typical GABA A receptors have some combination of α, β, and γ subunits.
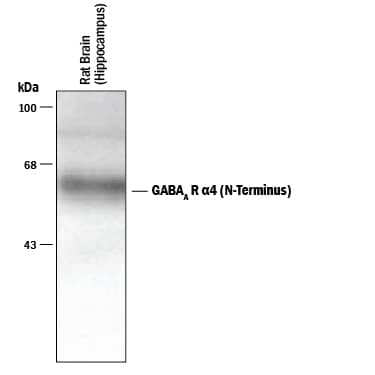
The rat α4 isoform is a 67 kDa, 517 amino acid (aa), 4 transmembrane protein with two terminal extracellular regions. The ligand-binding region is in the N-terminus (aa 14 - 221). The α4 subunit is unusual in that it does not seem to preferentially form channel complexes with the gamma subunit. In hippocampal neurons, α4 subunits apparently form GABA receptors that do not cluster, but exist in diffuse networks in nonsynaptic membrane.
18 results for "GABA-A R alpha 4" in Products
18 results for "GABA-A R alpha 4" in Products
GABA-A R alpha 4 Products
GABA A (γ-aminobutyric acid-type A) receptors are members of the cysteine-loop family of neurotransmitter-gated ion channels. GABA binding to A-type receptors induces anion-selective ion channel opening. These receptors are the principal fast inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS. GABA A receptors are heteropentamer combinations of seven subunit types; α, β, γ, δ, ε, θ, and π. Three subunits, α, β, and γ, have at least three separate gene products in mammals, and typical GABA A receptors have some combination of α, β, and γ subunits.
The rat α4 isoform is a 67 kDa, 517 amino acid (aa), 4 transmembrane protein with two terminal extracellular regions. The ligand-binding region is in the N-terminus (aa 14 - 221). The α4 subunit is unusual in that it does not seem to preferentially form channel complexes with the gamma subunit. In hippocampal neurons, α4 subunits apparently form GABA receptors that do not cluster, but exist in diffuse networks in nonsynaptic membrane.
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine, Canine, +2 More |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | WB |
| Reactivity: | Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Goat IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ELISA |
| Reactivity: | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Details: | Mouse IgG1 Monoclonal Clone #S398A-34 |
| Applications: | IHC, WB, ICC/IF |
| Applications: | WB, ELISA, MA, AP |
| Reactivity: | Human |
| Details: | Rabbit IgG Polyclonal |
| Applications: | IP |
Competitive and selective GABAA antagonist
| Alternate Names: | Gabazine |
| Chemical Name: | 6-Imino-3-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1(6H)-pyridazinebutanoic acid hydrobromide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors
| Alternate Names: | 3a,5a-THPROG |
| Chemical Name: | (3α,5α)-3-Hydroxy-pregnan-20-one |
Potent GABAA agonist; also GABAA-ρ partial agonist
| Chemical Name: | 5-Aminomethyl-3-hydroxyisoxazole |
| Purity: | ≥98% |
Benzodiazepine inverse agonist
| Chemical Name: | N-Methyl-β-carboline-3-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
Benzodiazepine antagonist
| Alternate Names: | Ro 15-1788 |
| Chemical Name: | 8-Fluoro-5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo[1,5-a][1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester |
| Purity: | ≥99% (HPLC) |
GABAA agonist
| Alternate Names: | Gaboxadol |
| Chemical Name: | 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydroisoxazolo[5,4-c]pyridin-3-ol hydrochloride |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Postitive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors
| Chemical Name: | (3α,5β)-3-Hydroxy-pregnan-20-one |
GABAA partial agonist; displays subtype selectivity
| Chemical Name: | 3-(2,5-Difluorophenyl)-7-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-6-[(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methoxy]-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
α5-selective GABAA inverse agonist
| Chemical Name: | 3-(1,1-Dimethylethyl)-7-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)-2-[(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-yl)methoxy]-pyrazolo[1,5-d][1,2,4]triazine |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |
Active metabolite of oxcarbazepine (Cat. No. 3864)
| Alternate Names: | GP 47779 |
| Chemical Name: | 10,11-Dihydro-10-hydroxy-5H-dibenz(Z)[b,f]azepin-5-carboxamide |
| Purity: | ≥98% (HPLC) |



![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody [NB300-193] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody [NB300-193]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-A-R-alpha-4-Antibody-Western-Blot-NB300-193-img0003.jpg)
![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody [NBP1-18844] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody [NBP1-18844]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-A-R-alpha-4-Antibody-Western-Blot-NBP1-18844-img0005.jpg)
![Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody (S398A-34) [NBP2-59326] Western Blot: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody (S398A-34) [NBP2-59326]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-AR-alpha-4-Antibody-S398A-34-Western-Blot-NBP2-59326-img0007.jpg)
![Immunoprecipitation: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody [NBP2-32077] Immunoprecipitation: GABA-AR alpha 4 Antibody [NBP2-32077]](https://resources.bio-techne.com/images/products/GABA-AR-alpha-4-Antibody-Immunoprecipitation-NBP2-32077-img0005.jpg)










