Human BAFFR/TNFRSF13C Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF1162


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Arg2-Ala71
Accession # Q96RJ3
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human BAFFR/TNFRSF13C Antibody
BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Inhibition of BAFF/BLys/ TNFSF13B-dependent Cell Proliferation and Neutralization by Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Antibody.
Recombinant Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Fc Chimera (Catalog # 1162-BR) inhibits Recombinant Human BAFF/BLyS/TNFSF13B (Catalog # 2149-BF) induced proliferation in mouse B cells in a dose-dependent manner (orange line). Inhibition of Recombinant Human BAFF/BLyS/TNFSF13B (5 ng/mL) activity elicited by Recombinant Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Fc Chimera (0.3 µg/mL) is neutralized (green line) by increasing concentrations of Goat Anti-Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1162). The ND50 is typically 0.1-1 µg/mL.BAFF R/TNFRSF13C in Human Spleen.
BAFF R/TNFRSF13C was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human spleen using Goat Anti-Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1162) at 3 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # CTS013). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to plasma membrane and cytoplasm. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Detection of BAFF R/TNFRSF13C in PBMCs by Flow Cytometry.
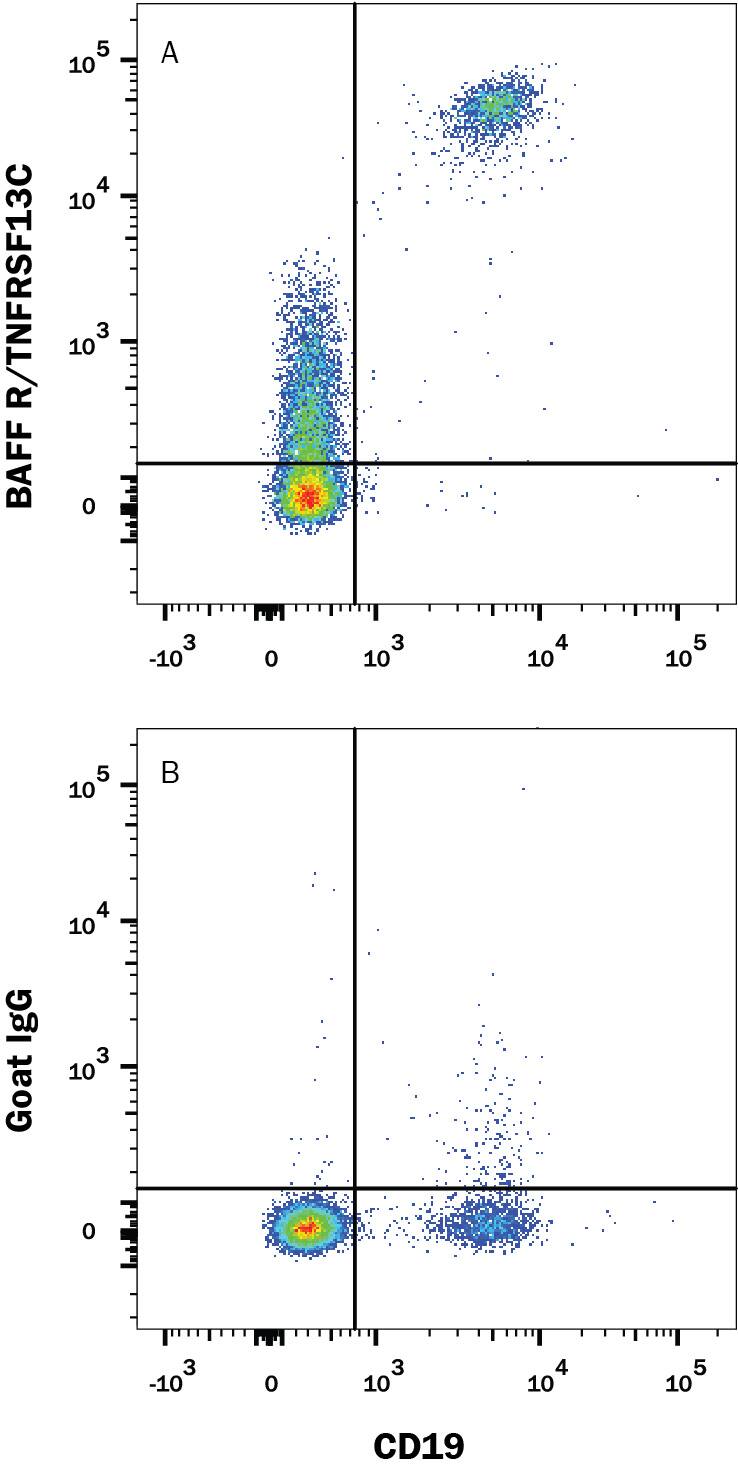
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were stained with Mouse Anti-Human CD19 Fluorescein-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB4867F) and either (A) Goat Anti-Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1162) or (B) Normal Goat IgG Control (Catalog # AB-108-C) followed by APC-conjugated anti-goat secondary antibody (Catalog # F0108). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human BAFFR/TNFRSF13C Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human spleen
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human BAFF R/TNFRSF13C Fc Chimera (Catalog # 1162-BR)
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: BAFFR/TNFRSF13C
B cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as BlyS, TALL-1, TNAK, and zTNF4, is a TNF ligand superfamily member and has been designated TNFSF13B. Produced by macrophages, dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes, BAFF promotes the survival of B cells and is essential for B cell maturation (1-4). BAFF binds to three TNF receptor superfamily members: B cell maturation antigen (BCMA/TNFRSF17), transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI/TNFRSF13B) and BAFF receptor (BAFF R/BR3/TNFRSF13C). These receptors are type III transmembrane proteins that lack a signal peptide. Whereas TACI and BCMA bind BAFF and another TNF superfamily ligand, APRIL (a proliferation-inducing ligand), BAFF R selectively binds BAFF. The BAFF R extracellular domain lacks the TNF receptor canonical cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and contains only a partial CRD with four cysteine residues. Human and mouse BAFF R share 56% aa sequence identity. BAFF R is highly expressed in spleen, lymph node and resting B cells. It is also expressed at lower levels in activated B cell, in resting CD4+ T cells, in thymus and peripheral blood leukocytes. BAFF knockout mice lack mature B cells. Similarly, A/WySnJ mice that are defective in BAFF-R intracellular signaling also lack mature B cells, suggesting that BAFF R is the critical receptor for BAFF during B lymphopoiesis. In contrast, BCMA- or TACI-deficient mice have no major defect in B cell development. While the function of BCMA is not defined, TACI has been shown to control B cell homeostasis and T cell-independent immune responses.
References
- Rolink, A.G. and F. Melcher (2002) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 14:266.
- Mackay F. and J.L. Browning (2002) Nature Reviews Immunology 2:464.
- Laabi, Y. et al. (2001) Current Biol. 11:R1013.
- Thompson, J.S. et al. (2001) Science 14:2108.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional BAFFR/TNFRSF13C Products
Product Documents for Human BAFFR/TNFRSF13C Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human BAFFR/TNFRSF13C Antibody
For research use only