Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB123

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Met150-Ser321
Accession # P06734
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII Antibody
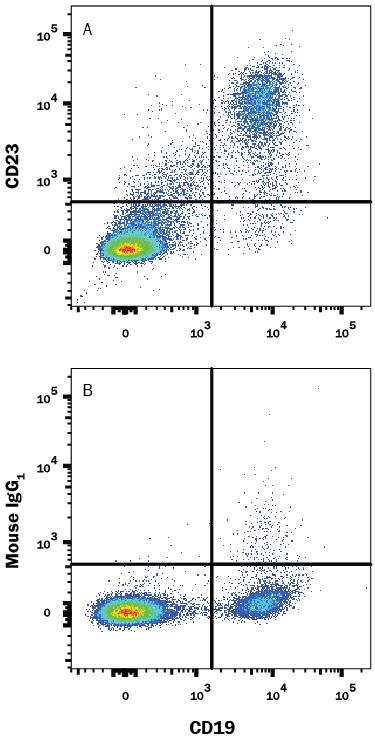
Detection of CD23/Fc epsilon RII in Human Blood Lymphocytes by Flow Cytometry.
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were stained with Mouse Anti-Human CD19 APC-conjugated Monoclonal Antibody (FAB4867A) and either (A) Mouse Anti-Human CD23/Fce RII Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB123) or (B) Mouse IgG1Isotype Control (MAB002) followed by Phycoerythrin-conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG Secondary Antibody (F0102B). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Detection of CD23/Fc epsilon RII in Human Lymph Nodes.
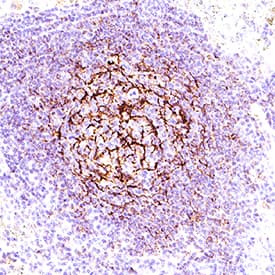
CD23/Fc epsilon RII was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Lymph Nodes using Mouse Anti-Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB123) at 5 µg/mL for 1 hour at room temperature followed by incubation with the Anti-Goat IgG VisUCyte™ HRP Polymer Antibody (Catalog # VC004). Before incubation with the primary antibody, tissue was subjected to heat-induced epitope retrieval using VisUCyte Antigen Retrieval Reagent-Basic (Catalog # VCTS021). Tissue was stained using DAB (brown) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cell membrane in lymphocytes. View our protocol for IHC Staining with VisUCyte HRP Polymer Detection Reagents.Applications for Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII Antibody
Blockade of Receptor-ligand Interaction
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: Human peripheral blood lymphocytes
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of Human Lymph Nodes
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII (Catalog # 123-FE)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
*Small pack size (-SP) is supplied either lyophilized or as a 0.2 µm filtered solution in PBS.
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: CD23/Fc epsilon RII
CD23 (also named B cell differentiation antigen) is a member of subgroup II of the C-type (Ca++-dependent) lectin superfamily (1‑5). Human CD23 is a 47 kDa type II transmembrane glycoprotein that is expressed by a wide variety of cell types (6‑10). The full-length receptor is 321 amino acids (aa) in length and contains a 274 aa extracellular region, a 26 aa transmembrane segment, and a 21 aa cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular region contains a C-type lectin domain and a connecting stalk with coiled-coil topography (3, 11). The lectin domain binds both protein and carbohydrate in an apparently Ca++ independent manner (11). The coiled-coil region contributes to oligomerization (11, 12). The lectin domain in human CD23 (aa 162‑284) is 64%, 62% and 68% aa identical to the lectin domains in mouse, rat and bovine CD23, respectively. In the cytoplasmic region, two FC isoforms exist which arise from alternate start sites (6, 12). The “a” (or long) isoform begins with the sequence MEEGQYS and is constitutively expressed by B cells. It is believed to participate in IgE-mediated endocytosis (13). The “b” (or short) isoform begins with MNPPSQ and is induced on a wide variety of cell types by IL-4 (6). Fcb reportedly contributes to IgE-mediated phagocytosis (13). Fcb expressing cells include eosinophils, monocytes, visceral smooth muscle and intestinal epithelium (6, 14, 15). At least four soluble forms of CD23 are known to exist. They range in molecular weight from 25 kDa to 37 kDa, with the 25 kDa form predominating in sera (16). Soluble CD23 (sFc) is generated by metalloprotease (ADAM8; ADAM15; ADAM28) and cysteine-protease activity (16‑18). Cleavage usually occurs between aa 150‑160 (7, 8). It is unclear if sequential metalloprotease-cysteine protease activity is necessary for the generation of all soluble forms. Both soluble and membrane-bound CD23 show bioactivity. Ligands for CD23 include CD21, IgE, CD11b, and CD11c (19‑21). CD23 binding to CD11b and Cd11c on monocytes results in oxidative product generation and proinflammatory cytokine release (21). On B cells, sCD23 induces IgE secretion by binding CD21. Conversely, secreted IgE will, in turn, bind B cell membrane CD23, rendering it unavailable for cleavage, and thus shutting down IgE production (11).
References
- Kijimoto-Ochiai, S. (2002) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 59:648.
- Heyman, B. (2000) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:709.
- Bajorath, J. and A. Aruffo (1996) Protein Sci. 5:240.
- Drickamer, K. (1993) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 3:393.
- Drickamer, K. (1999) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 9:585.
- Yokota, A. et al. (1988) Cell 55:611.
- Ludin, C. et al. (1987) EMBO J. 6:109.
- Ikuta, K. et al. (1987) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:819.
- Kikutani, H. et al. (1986) Cell 47:657.
- Letellier, M. et al. (1988) J. Immunol. 141:2374.
- Hibbert, R.G. et al. (2005) J. Exp. Med. 202:751.
- Beavuil, A.J. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:753.
- Yokota, A. et al. (1992) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:5030.
- Belleau, J.T. et al. (2005) Clin. Mol. Allergy 3:6.
- Tu, Y. et al. (2005) Gastroenterology 129:928.
- Marolewski, A.E. et al. (1998) Biochem. J. 333:573.
- Fourie, A.M. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:30469.
- Karagiannis, S.N. et al. (2001) Immunology 103:319.
- Aubry, J-P. et al. (1992) Nature 358:505.
- Sarfati, M. and G. Delespeese (1988) J. Immunol. 141:2195.
- Lecoanet-Henchoz, S. et al. (1995) Immunity 3:119.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional CD23/Fc epsilon RII Products
Product Documents for Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human CD23/Fc epsilon RII Antibody
For research use only