Human ECM1 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB3937

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala20-Glu540
Accession # Q16610
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human ECM1 Antibody
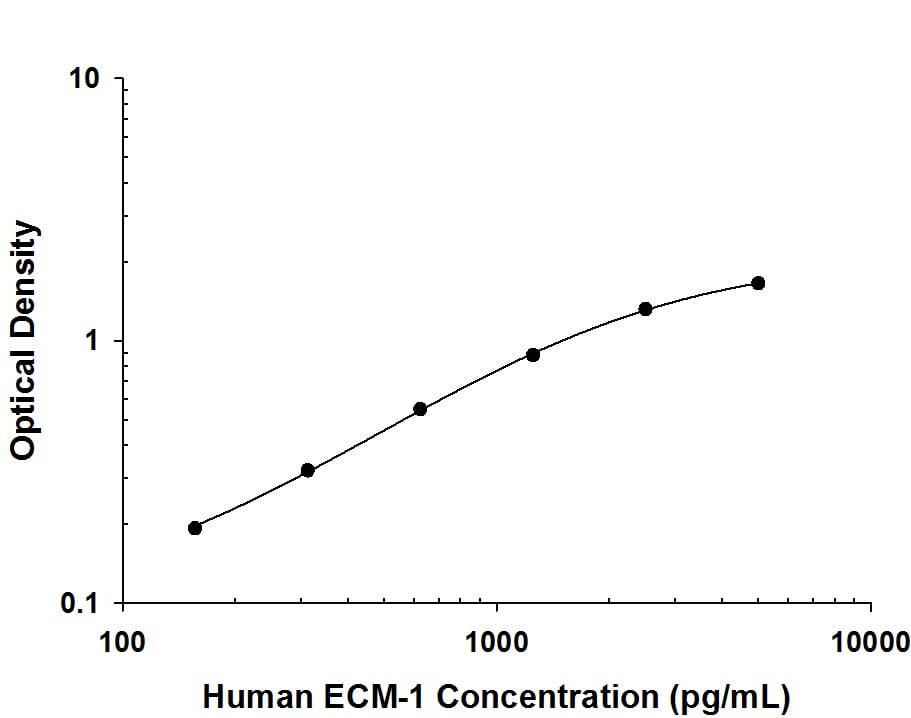
Human ECM‑1 ELISA Standard Curve.
Recombinant human ECM-1 protein was serially diluted 2-fold and captured by Mouse Anti-Human ECM-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB39371) coated on a Clear Polystyrene Microplate (Catalog # DY990). Mouse Anti-Human ECM-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB3937) was biotinylated and incubated with the protein captured on the plate. Detection of the standard curve was achieved by incubating Streptavidin-HRP (Catalog # DY998) followed by Substrate Solution (Catalog # DY999) and stopping the enzymatic reaction with Stop Solution (Catalog # DY994).Applications for Human ECM1 Antibody
ELISA
This antibody functions as an ELISA detection antibody when paired with Mouse Anti-Human ECM‑1 Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB39371).
This product is intended for assay development on various assay platforms requiring antibody pairs.
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: ECM1
Extracellular matrix protein-1 (ECM-1) is an 85 kDa, secreted glycoprotein important in connective tissue organization (1‑3). Of three identified splice variants the 540 amino acid (aa) form, ECM-1a, is the most widely expressed, with the highest expression in the placenta and heart (2). ECM-1b (415 aa) is found only in tonsil and associated with suprabasal keratinocytes (2, 4). Since ECM-1b expression is differentiation-dependent, a role in terminal keratinocyte differentiation has been suggested (4). ECM-1c (559 aa) accounts for approximately 15% of skin ECM-1 (5). Human ECM-1a contains a 19 aa signal peptide and a 521 aa secreted portion that includes an N-terminal proline-rich, cysteine-free region, two tandem repeat domains, and a C-terminal domain. There are six repeats of a CC(X7 ‑10)C motif (x = any aa) within the tandem repeat and C‑terminal domains. These motifs are involved in ligand binding to members of the albumin family, and are expected to form two (in ECM-1b) or three (in ECM-1a) “double loop” structures (2). Mature human ECM-1a shows 69%, 71%, 72%, and 76% aa identity with corresponding isoforms of mouse, rat, canine, and bovine ECM-1, respectively. ECM-1 is over-expressed in many malignant epithelial tumors and has demonstrated angiogenic activity (6, 7). A variety of ECM-1 mutations, mainly within the first tandem repeat, are considered causative of lipoid proteinosis, a condition showing thickened and irregular extracellular matrix within connective tissue (8). In the autoimmune condition lichen sclerosis, auto-antibodies mainly recognize the second tandem repeat or the C-terminus of ECM-1 (9). These domains also bind the extracellular matrix molecules fibulin-1 and perlecan (5, 10). The phenotypes of lipoid proteinosis and lichen sclerosis support a role for ECM-1 as a “biological glue” in the dermis (1).
References
- Chan, I. (2004) Exp. Dermatol. 29:52.
- Smits, P. et al. (1997) Genomics 45:487.
- Bhalerao, J. et al. (1995) J. Biol. Chem 270:16385.
- Smits, P. et al. (2000) J. Invest. Dermatol. 114:718.
- Mongiat, M. et al. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278:17491.
- Han, Z. et al. (2001) FASEB J. 15:988.
- Wang, L. et al. (2003) Cancer Lett. 200:57.
- Hamada, T. et al. (2003) J. Invest. Dermatol. 120:345.
- Oyama, N. et al. (2004) J. Clin. Invest. 113:1550.
- Fujimoto, N. et al. (2005) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 333:1327.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional ECM1 Products
Product Documents for Human ECM1 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human ECM1 Antibody
For research use only