Human LRIG1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # FAB8140G

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala35-Ser779
Accession # Q96JA1
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Human LRIG1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody
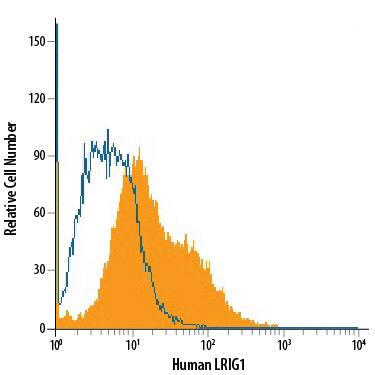
Detection of LRIG1 in LNCaP Hman Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
LNCaP human prostate cancer cell line was stained with Sheep Anti-Human LRIG1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # FAB8140G, filled histogram) or isotype control antibody (Catalog # IC016G, open histogram). View our protocol for Staining Membrane-associated Proteins.Applications for Human LRIG1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody
Flow Cytometry
Sample: LNCaP human prostate cancer cell line
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, 2 to 8 °C as supplied.
Background: LRIG1
LRIG1 (leucine-rich repeats and Ig-like domains-1; also LIG-1) is an approximately 134-145 kDa glycoprotein that belongs to the LRIG gene family. It is widely expressed, and appears on the surface of prostatic epithelium, endothelial cells, vascular and visceral smooth muscle, mammary epithelium, cardiac muscle, keratinocytes and neurons. LRIG1 is believed to negatively regulate the ErbB family of receptors. In particular, and in a ligand-independent manner, LRIG1 complexes with all four ErbBs, promoting their ubiquitination and decreasing their number. Alternatively, LRIG1 is suggested to bind to the ErbBs, preventing their dimerization and signal transduction. Mature human LRIG1 is a 1059 amino acid (aa) type I transmembrane protein. It contains a large 760 amino acid (aa) extracellular domain (ECD) (aa 35-794) plus a 278 aa cytoplasmic region. The ECD contains 17 LRRs (aa 35‑491) and three C2-type Ig-like domains (aa 495-780). These two domain types are each sufficient for EGFR binding. There are two potential alternative splice forms. One contains a 27 aa insertion after Gly874, while another shows a 24 aa insertion after Lys387 coupled to a Gln substitution for aa 644-691. The LRIG1 ECD undergoes proteolysis, generating 100-110 and 55-60 kDa soluble fragments. Over aa 35‑779, human LRIG1 shares 90% aa sequence identity with mouse LRIG1.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional LRIG1 Products
Product Specific Notices for Human LRIG1 Alexa Fluor® 488-conjugated Antibody
This product is provided under an agreement between Life Technologies Corporation and R&D Systems, Inc, and the manufacture, use, sale or import of this product is subject to one or more US patents and corresponding non-US equivalents, owned by Life Technologies Corporation and its affiliates. The purchase of this product conveys to the buyer the non-transferable right to use the purchased amount of the product and components of the product only in research conducted by the buyer (whether the buyer is an academic or for-profit entity). The sale of this product is expressly conditioned on the buyer not using the product or its components (1) in manufacturing; (2) to provide a service, information, or data to an unaffiliated third party for payment; (3) for therapeutic, diagnostic or prophylactic purposes; (4) to resell, sell, or otherwise transfer this product or its components to any third party, or for any other commercial purpose. Life Technologies Corporation will not assert a claim against the buyer of the infringement of the above patents based on the manufacture, use or sale of a commercial product developed in research by the buyer in which this product or its components was employed, provided that neither this product nor any of its components was used in the manufacture of such product. For information on purchasing a license to this product for purposes other than research, contact Life Technologies Corporation, Cell Analysis Business Unit, Business Development, 29851 Willow Creek Road, Eugene, OR 97402, Tel: (541) 465-8300. Fax: (541) 335-0354.
For research use only