Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF1212

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Applications
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Ala2-Arg207
Accession # O43320
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Endotoxin Level
Scientific Data Images for Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antibody
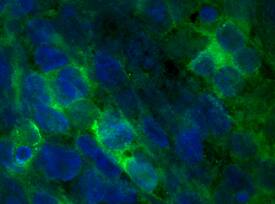
FGF‑16 in Human iPS cells.
FGF-16 was detected in immersion fixed human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells differentiated into cardiomyocytes using Sheep Anti-Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1212) at 8 µg/mL for 3 hours at room temperature. Cells were stained using the NorthernLights™ 493-conjugated Anti-Sheep IgG Secondary Antibody (green; Catalog # NL012) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). Specific staining was localized to cytoplasm. View our protocol for Fluorescent ICC Staining of Stem Cells on Coverslips.FGF‑16 in Human Heart.
FGF-16 was detected in immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human heart using Sheep Anti-Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1212) at 3 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Sheep HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS019) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to cardiomyocytes. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Paraffin-embedded Tissue Sections.FGF‑16 in Mouse Embryo.
FGF-16 was detected in perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (13 d.p.c.) using Sheep Anti-Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antigen Affinity-purified Polyclonal Antibody (Catalog # AF1212) at 15 µg/mL overnight at 4 °C. Tissue was stained using the Anti-Sheep HRP-DAB Cell & Tissue Staining Kit (brown; Catalog # CTS019) and counterstained with hematoxylin (blue). Specific staining was localized to roots of dorsal ganglia and spinal cord. View our protocol for Chromogenic IHC Staining of Frozen Tissue Sections.Applications for Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antibody
Immunocytochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells differentiated into cardiomyocytes
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Immersion fixed paraffin-embedded sections of human heart and perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse embryo (13 d.p.c.)
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Human FGF-16 (Catalog # 1212-FG)
Neutralization
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: FGF-16
Fibroblast growth factor 16 (FGF-16) belongs to the large FGF family which has at least 23 members (1). All FGF family members are heparin-binding growth factors with a core 120 amino acid (aa) FGF domain that allows for a common tertiary structure. FGFs are expressed during embryonic development and in restricted adult tissues. They act on cells of mesodermal and neuroectodermal origin to regulate diverse physiologic functions including angiogenesis, cell growth, pattern formation, embryonic development, metabolic regulation, cell migration, neurotrophic effects and tissue repair (2, 3). Signaling receptors for FGFs are type I transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. Four distinct but related classes of FGF receptors, FGF R1, 2, 3, and 4, exist. Through alternative splicing, multiple isoforms for FGF R1, 2 and 3, with distinct ligand recognition profiles, are also generated (3).
FGF-16 was originally identified in rat heart tissue by homology based polymerase chain reaction. Human FGF-16 cDNA predicts a 207 aa precursor protein with one N-linked glycosylation site. FGF-16 lacks a typical signal peptide, but is efficiently generated by mechanisms other than the classical protein secretion pathway. Among FGF family members, FGF-16 is most similar to FGF-9, sharing 73% aa sequence homology. Human FGF-16 shares 99% and 98.6% aa sequence identity with the mouse and rat FGF-16, respectively. In rat embryos, FGF-16 message is expressed predominantly in brown adipocytes. In adult animals, it is localized primarily in heart tissue. FGF-16 binds to and activates FGF receptor 4 (4). FGF-16 induces proliferation of primary adipocytes and oligodendrocytes in vitro and stimulates liver weight increase in vivo (4, 5). The expression pattern of FGF-16 and its effect on adipocyte proliferation suggest a role for this protein on the proliferation of embryonic brown adipose tissue (4).
References
- Miyake, A. et al. (1998) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 243:148.
- Goldfarb, M. (1996) Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews 7:311.
- Green, P. et al. (1996) BioEssays 18:639.
- Konishi, M. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275:12119.
- Danilenko, D.M. et al. (2000) Archiv. Biochem. Biophys. 361:34.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Entrez Gene IDs
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional FGF-16 Products
Product Documents for Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Human/Mouse FGF-16 Antibody
For research use only


