Mouse Desert Hedgehog/Dhh C-Terminus Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # AF196


Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Cys199-Gly396
Accession # Q61488
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse Desert Hedgehog/Dhh C-Terminus Antibody
Detection of Marsupial Desert Hedgehog/Dhh by Immunohistochemistry
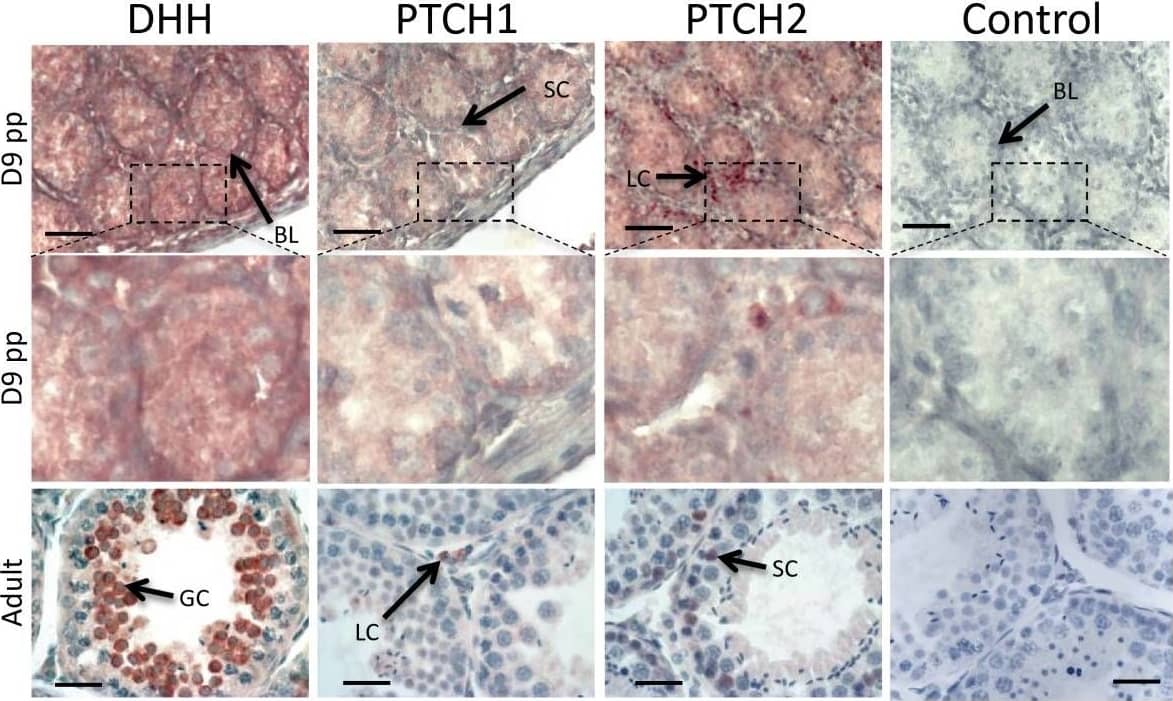
Immunohistochemistry of DHH, PTCH1 and PTCH2 in the tammar wallaby testis at key developmental time points. Red/brown staining indicates protein distribution while the heamatoxalin counterstain appears blue. It is important to note that DHH is a highly secreted molecule and staining does not imply cell of origin. DHH staining was most intense at the basal lamina (BL). In the adult staining is concentrated in the develop spermatocytes (GC). At day D9pp PTCH1 was present within the Sertoli cells (SC) while PTCH2 was predominant in the Leydig cells (LC). This expression profile is reversed in the adult testis with PTCH1 found predominantly in the Leydig cells, while PTCH2 was predominate in the Sertoli cells. Scale bars indicate 40 μm, controls show immunohistochemistry with the primary antibody omitted. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22132805), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Detection of Marsupial Desert Hedgehog/Dhh by Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry of DHH, PTCH1 and PTCH2 in the tammar wallaby testis at key developmental time points. Red/brown staining indicates protein distribution while the heamatoxalin counterstain appears blue. It is important to note that DHH is a highly secreted molecule and staining does not imply cell of origin. DHH staining was most intense at the basal lamina (BL). In the adult staining is concentrated in the develop spermatocytes (GC). At day D9pp PTCH1 was present within the Sertoli cells (SC) while PTCH2 was predominant in the Leydig cells (LC). This expression profile is reversed in the adult testis with PTCH1 found predominantly in the Leydig cells, while PTCH2 was predominate in the Sertoli cells. Scale bars indicate 40 μm, controls show immunohistochemistry with the primary antibody omitted. Image collected and cropped by CiteAb from the following open publication (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22132805), licensed under a CC-BY license. Not internally tested by R&D Systems.Applications for Mouse Desert Hedgehog/Dhh C-Terminus Antibody
Immunohistochemistry
Sample: Perfusion fixed frozen sections of mouse spinal cord
Western Blot
Sample: Recombinant Mouse Desert Hedgehog (C23II), N-Terminus (Catalog # 733-DH)
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: Desert Hedgehog/Dhh
Desert Hedgehog (Dhh) belongs to the highly conserved Hedgehog family of proteins which are involved in multiple developmental processes. Hedgehogs are synthesized as 45 kDa precursors that are cleaved autocatalytically. The 19 kDa N-terminal fragment remains membrane associated due to its cholesterol and palmitate modifications. Binding of this fragment to Patched receptors results in the loss of Patched repression of Smoothened signaling (1‑4). Dhh binds both Patched and Patched 2 as well as Hedgehog interacting protein (Hip) (5). Within the N-terminal peptide, mouse Dhh shares 97% and 100% amino acid (aa) sequence identity with human and rat Dhh, respectively. It shares 74% aa seqeuence identity with mouse Indian (Ihh) and Sonic hedgehog (Shh) (6, 7). Dhh is produced by Sertoli cells and is required for testis development and spermatogenesis (8, 9). It induces steroidogenic factor 1 which is instrumental in promoting Leydig cell differentiation (10, 11). It also promotes the deposition of basal lamina surrounding seminiferous tubules (8). In humans, mutations of Dhh are associated with pure gonadal dysgenesis (12). Dhh is expressed in the female by ovarian granulosa cells and the corpus luteum (13). Its up‑regulation in human ovarian cancer correlates positively with proliferative index and negatively with prognosis (14). Dhh is also expressed by Schwann cells and is up‑regulated following nerve injury (15, 16). It induces the expression of Patched and Hip in nerve fibroblasts and promotes the formation of the connective tissue sheath surrounding peripheral nerves (15).
References
- van den Brink, G.R. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87:1343.
- Riobo, N.A. and D.R. Manning (2007) Biochem. J. 403:369.
- Porter, J.A. et al. (1995) Nature 374:363.
- Carpenter, D. et al. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 95:13630.
- Pathi, S. et al. (2001) Mech. Dev. 106:107.
- Echelard, Y. et al. (1993) Cell 75:1417.
- Chang, D.T. et al. (1994) Development 120:3339.
- Pierucci-Alves, F. et al. (2001) Biol. Reprod. 65:1392.
- Bitgood, M.J. et al. (1996) Curr. Biol. 6:298.
- Yao, H.H.-C. et al. (2002) Genes Dev. 16:1433.
- Park, S.Y. et al. (2007) Endocrinology 148:3704.
- Canto, P. et al. (2004) J. Clin. Endocrinol. 89:4480.
- Russell, M.C. et al. (2007) Biol. Reprod. 77:226.
- Chen, X. et al. (2007) Cancer Sci. 98:68.
- Parmantier, E. et al. (1999) Neuron 23:713.
- Bajestan, S.N. et al. (2006) J. Neurobiol. 66:243.
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Desert Hedgehog/Dhh Products
Product Documents for Mouse Desert Hedgehog/Dhh C-Terminus Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse Desert Hedgehog/Dhh C-Terminus Antibody
For research use only