Mouse MARCO Antibody
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # MAB29561

Key Product Details
Species Reactivity
Validated:
Cited:
Applications
Validated:
Cited:
Label
Antibody Source
Product Specifications
Immunogen
Gln70-Ser518
Accession # Q60754
Specificity
Clonality
Host
Isotype
Scientific Data Images for Mouse MARCO Antibody
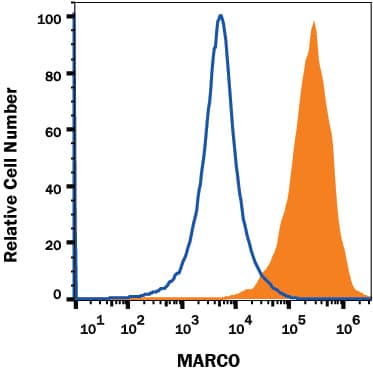
Detection of MARCO in J774 Mouse Cell Line by Flow Cytometry.
J774 mouse monocyte-macrophage cell line, resting (open histogram), or treated with 500 ng/ml LPS for 3 days (filled histogram) were stained with Rabbit Anti-Mouse MARCO Monoclonal Antibody (Catalog # MAB29561) followed by anti-Rabbit IgG APC-conjugated secondary antibody (F0111). Staining was performed using our Staining Membrane-associated Proteins protocol.Applications for Mouse MARCO Antibody
CyTOF-ready
Flow Cytometry
Sample: J774 mouse monocyte-macrophage cell line treated with LPS
Formulation, Preparation, and Storage
Purification
Reconstitution
Formulation
Shipping
Stability & Storage
- 12 months from date of receipt, -20 to -70 °C as supplied.
- 1 month, 2 to 8 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
- 6 months, -20 to -70 °C under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
Background: MARCO
MARCO (macrophage receptor with collagenous structure), also known as SCARA2, is an 80 kDa type II transmembrane glycoprotein that belongs to the class A scavenger receptor family (1). Mouse MARCO consists of a 48 amino acid (aa) cytoplasmic domain, a 21 aa transmembrane segment, and a 449 aa extracellular domain (ECD) that includes a stalk region, a collagen-like region, and one SRCR domain (2). Within the ECD, mouse MARCO shares 69% and 86% aa sequence identity with human and rat MARCO, respectively. It shares 18%-28% aa sequence identity with other mouse class A scavenger receptors CL-P1, SCARA3, SCARA5, and SR-A1/MSR. MARCO is constitutively expressed on the surface of splenic and lymph node macrophages (2, 3). Its expression is induced on Kupffer cells and alveolar macrophages by microbial infection, chemical irritants, and Th1 polarizing factors (3-5). MARCO binds LPS, lipoteichoic acid, and other determinants on Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria (2, 6-8). It also binds modified LDL, CpG oligonucleotides, UGRP1, silica, and TiO2 (2, 9-11). MARCO is required for the organization of the splenic marginal zone and the interaction of local macrophages and B cells (12, 13). The SRCR domain mediates binding of MARCO to its various ligands (3, 12), while the collagen-like region mediates assembly into a disulfide-linked trimeric molecule (2, 7). MARCO ligation induces, but is not required for the production of IL-12, NO, or TNF-alpha by macrophages (5, 6, 9). MARCO knockout mice show a reduced clearance of bacterial infections, reduced mast cell mediated silicosis, increased pulmonary inflammation, and increased sensitivity to ozone induced lung damage (4, 9, 14-16).
References
- Murphy, J.E. et al. (2005) Atherosclerosis 182:1.
- Elomaa, O. et al. (1995) Cell 80:603.
- Van der Laan, L.J.W. et al. (1999) J. Immunol. 162:939.
- Dahl, M. et al. (2007) J. Clin. Invest. 117:757.
- Jozefowski, S. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:8032.
- Mukhopadhyay, S. et al. (2006) Eur. J. Immunol. 36:940.
- Sankala, M. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277:33378.
- Chen, Y. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:12767.
- Jozefowski, S. et al. (2006) J. Leukoc. Biol. 80:870.
- Bin, L.-H. et al. (2003) J. Immunol. 171:924.
- Hamilton, Jr. R.F. et al. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281:34218.
- Karlsson, M.C.I. et al. (2003) J. Exp. Med. 198:333.
- Chen, Y. et al. (2005) J. Immunol. 175:8173.
- Arredouani, M. et al. (2004) J. Exp. Med. 200:267.
- Arredouani, M.S. et al. (2007) J. Immunol. 178:5912.
- Brown, J.M. et al. (2007) Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 36:43.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional MARCO Products
Product Documents for Mouse MARCO Antibody
Product Specific Notices for Mouse MARCO Antibody
For research use only