Recombinant Human Dkk-4 Protein
R&D Systems, part of Bio-Techne | Catalog # 1269-DK

Key Product Details
Product Specifications
Source
Leu19-Leu224, with a C-terminal 10-His tag
Purity
Endotoxin Level
N-terminal Sequence Analysis
Predicted Molecular Mass
SDS-PAGE
Activity
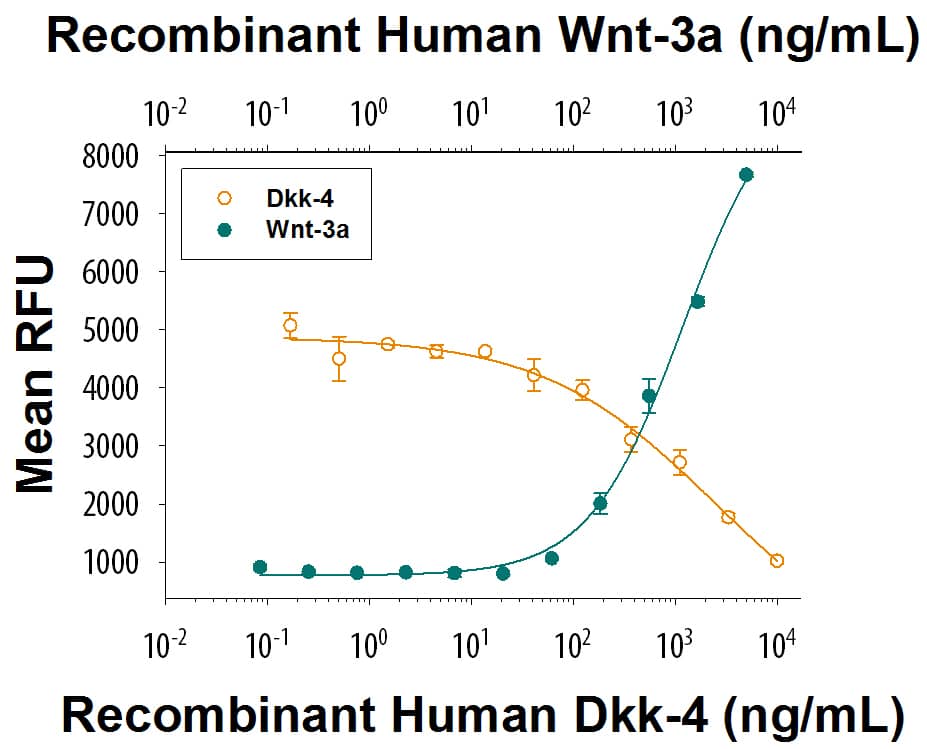
Recombinant Human Dkk-4 (Catalog # 1269-DK) inhibits a constant dose of 500 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (Catalog # 5036-WN). The ED50 for this effect is 150-900 ng/mL.
Scientific Data Images for Recombinant Human Dkk-4 Protein
Recombinant Human Dkk-4 Protein Bioactivity
Recombinant Human Wnt-3a (Catalog # 5036-WN) induces a dose responsive increase in Wnt reporter activity in HEK293 cells (green circles). Recombinant Human Dkk-4 (Catalog # 1269-DK) inhibits a constant dose of 500 ng/mL of Recombinant Human Wnt-3a. The ED50 for this effect is 150-900 ng/mL (orange circles).Formulation, Preparation and Storage
Carrier Free
What does CF mean?CF stands for Carrier Free (CF). We typically add Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) as a carrier protein to our recombinant proteins. Adding a carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at a more dilute concentration. The carrier free version does not contain BSA.
What formulation is right for me?In general, we advise purchasing the recombinant protein with BSA for use in cell or tissue culture, or as an ELISA standard. In contrast, the carrier free protein is recommended for applications, in which the presence of BSA could interfere.
Carrier: 1269-DK
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris-Citrate and NaCl with BSA as a carrier protein. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 200 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Carrier Free: 1269-DK/CF
| Formulation | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in Tris-Citrate and NaCl. |
| Reconstitution | Reconstitute at 200 μg/mL in sterile PBS. |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature recommended below. |
| Stability & Storage | Use a manual defrost freezer and avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
Background: Dkk-4
Dickkopf related protein 4 (Dkk-4) is a member of the Dkk protein family that includes Dkk-1, -2, -3, and -4 (1). All four members are secreted proteins that are synthesized as precursor proteins with an N‑terminal signal peptide and 2 conserved cysteine‑rich domains, which are separated by a linker region. Dkk proteins have potential furin type proteolytic cleavage sites, and short forms of Dkk-2 and Dkk-4 containing only the second cysteine‑rich domain can be generated by proteolytic processing (1). Dkk proteins have distinct patterns of expression in adult and embryonic tissues, suggesting that they may play diverse roles in these tissues.
The Dkk proteins have distinct effects on Wnt signaling. Dkk-1 and Dkk-4 are Wnt antagonists. Dkk-3 has not been demonstrated to affect Wnt signaling, and Dkk-2 acts as an agonist or antagonist, depending on the cellular context. Wnt signaling regulates many important developmental processes including neural crest differentiation, brain development, kidney morphogenesis, and sex determination. In addition, Wnt signaling has also been implicated in tumor formation. Canonical Wnt signaling via the beta-catenin pathway is transduced by a receptor complex composed of the Frizzled proteins (Fz) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-related proteins (LRP5/6) (2, 3). Unlike many soluble Wnt antagonists that function by binding extracellular Wnt ligands to prevent interaction of Wnt with the Fz-LRP5/6 receptor complex, Dkk-1 and Dkk-4 antagonize Wnt/ beta-catenin signaling by direct high-affinity binding to the Wnt coreceptor LRP5/6 and inhibiting interaction of LRP5/6 with the Wnt-Frizzled complex (4). Dkk-1 and Dkk-4 also bind the transmembrane proteins Kremen1 (Krm1) and Krm2 with high-affinity (5). Krm2 has been shown to form a ternary complex with Dkk-1 or -4 and LRP5/6 to trigger internalization of the complex and removal of LRP6 from the cell surface. Thus, Dkk-1/4 and Kremens function synergistically to antagonize LRP5/6-mediated Wnt activity. Dkk-2 also binds to LRP5/6 and the Kremens, but Dkk-2 acts as an antagonist of the Wnt signaling pathway only in the presence of Krm2 (5, 6). Dkk-2 binding to LRP5/6 in the absence of Krm2 activates rather than inhibits Wnt signalling (6).
References
- Krupnik, V.E. et al. (1999) Gene 238:301.
- Zorn, A.M. (2001) Current Biology R592.
- Mao, J. et al. (2001) Mol. Cell 7:801.
- Nusse, R. et al. (2001) Nature 411:255.
- Mao, J. et al. (2002) Nature 417:664.
- Mao, B. and C. Niehrs (2003) Gene 302:179.
Long Name
Alternate Names
Gene Symbol
UniProt
Additional Dkk-4 Products
Product Documents for Recombinant Human Dkk-4 Protein
Product Specific Notices for Recombinant Human Dkk-4 Protein
For research use only